Indicator of beta and gamma radiation. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Dosimeters
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The figure shows a diagram of a simple indicator that detects even weak beta and gamma radiation. The sensor (VL1) is a domestically produced Geiger-Muller counter of the CTC-5 type, which has been produced for more than thirty years. It has the form of a metal cylinder about 113 mm long and 12 mm in diameter. Its operating voltage is 400 V. From foreign sensors, you can use the ZP1400, ZP1310 or ZP1320 from Philips.
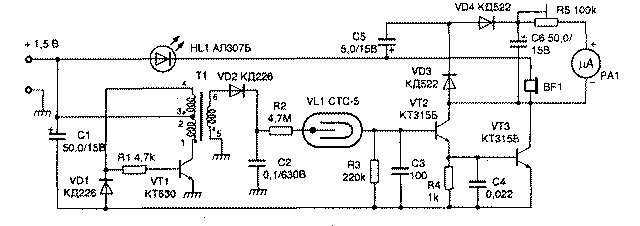
(click to enlarge)
The device is powered by one galvanic cell with a voltage of 1,5 V and consumes a current of not more than 10 mA. The -12V voltage for powering the amplifier and the high voltage for powering the sensor are obtained from the converter on the transistor VT1. The converter transformer T1 is wound on an armored magnetic core with a diameter of about 25 mm. Winding 1-2 has 45 turns of wire with a diameter of 0,25 mm, 3-4 - 15 turns of the same wire, and 5-6 - 550 turns of wire with a diameter of 0,1 mm. The beginning of the windings in the diagram are marked with dots. The converter is a blocking generator. The high voltage pulses arising on the winding 5-6 of the transformer T1 are rectified by the high-frequency diode VD2.
Conventional rectifier diodes are unsuitable here, since the pulses are too short and their repetition rate is too high. While there is no radiation, there is no voltage at the input of the amplifier, made on transistors VT2 and VT3, and the transistors are locked. When beta or gamma particles hit the sensor, the gas with which it is filled is ionized and a pulse is formed at the output, which excites the amplifier, and a click is heard from the loudspeaker (telephone capsule) BF1, while the HL1 LED flashes. Outside the irradiation zone, clicks and flashes of the LED are repeated after 1-2 s. This is the reaction of the sensor to cosmic radiation and the natural background. If you bring the sensor closer to a radiating object (an old watch with a luminous dial or a wartime aircraft instrument scale), the clicks will become more frequent and finally merge into a continuous crackle, and the LED will glow continuously. Thus, it is possible to judge the frequency of particles hitting the sensor, and, consequently, the radiation intensity.
The device also has a pointer indicator. The alternating voltage taken from the telephone capsule is fed through the capacitor C5 to a full-wave rectifier on germanium diodes VD3, VD4 (they can be of any type).
The rectified voltage, after smoothing by capacitor C6, is fed through a variable resistor R5 to a microammeter (RA1). the resistance of the resistor is set so that with strong radiation the needle of the microammeter does not go off scale, and with weak radiation it noticeably deviates. If necessary, the device can be calibrated by comparing its readings with an industrial radiation meter. The device is assembled on a printed circuit board placed in a box measuring 150x90x40 mm. The sensor is located in a separate housing and is connected to the device by a cable with a connector. Transistor VT1 can be replaced with KT630 with any letter index, KT315B - with KT342A. The LED can be AL307, AL341. As VD2, you can use two KD104A diodes by connecting them in series. Diode KD226 can be replaced by KD105V. A telephone capsule should be selected with a voice coil impedance of at least 50 ohms. The pointer measuring head can be selected in any type with a total deflection current of 50 μA.
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Dosimeters.
See other articles Section Dosimeters.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
Exploring space and its mysteries is a task that attracts the attention of astronomers from all over the world. In the fresh air of the high mountains, far from city light pollution, the stars and planets reveal their secrets with greater clarity. A new page is opening in the history of astronomy with the opening of the world's highest astronomical observatory - the Atacama Observatory of the University of Tokyo. The Atacama Observatory, located at an altitude of 5640 meters above sea level, opens up new opportunities for astronomers in the study of space. This site has become the highest location for a ground-based telescope, providing researchers with a unique tool for studying infrared waves in the Universe. Although the high altitude location provides clearer skies and less interference from the atmosphere, building an observatory on a high mountain poses enormous difficulties and challenges. However, despite the difficulties, the new observatory opens up broad research prospects for astronomers. ... >>
Controlling objects using air currents
04.05.2024
The development of robotics continues to open up new prospects for us in the field of automation and control of various objects. Recently, Finnish scientists presented an innovative approach to controlling humanoid robots using air currents. This method promises to revolutionize the way objects are manipulated and open new horizons in the field of robotics. The idea of controlling objects using air currents is not new, but until recently, implementing such concepts remained a challenge. Finnish researchers have developed an innovative method that allows robots to manipulate objects using special air jets as "air fingers". The air flow control algorithm, developed by a team of specialists, is based on a thorough study of the movement of objects in the air flow. The air jet control system, carried out using special motors, allows you to direct objects without resorting to physical ... >>
Purebred dogs get sick no more often than purebred dogs
03.05.2024
Caring for the health of our pets is an important aspect of the life of every dog owner. However, there is a common assumption that purebred dogs are more susceptible to diseases compared to mixed dogs. New research led by researchers at the Texas School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences brings new perspective to this question. A study conducted by the Dog Aging Project (DAP) of more than 27 companion dogs found that purebred and mixed dogs were generally equally likely to experience various diseases. Although some breeds may be more susceptible to certain diseases, the overall diagnosis rate is virtually the same between both groups. The Dog Aging Project's chief veterinarian, Dr. Keith Creevy, notes that there are several well-known diseases that are more common in certain breeds of dogs, which supports the notion that purebred dogs are more susceptible to disease. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive A new state of matter: a crystal of bosons
19.06.2023
A group of physicists from the University of California at Santa Barbara have made a sensational discovery, revealing the secrets of a unique material created from bosons. Until now, the scientific community has focused on the study of fermions - subatomic particles responsible for the stability and interaction of matter. However, the latest breakthrough opens a new chapter in the study of the special properties of bosons and expands our knowledge in the field of elementary particle physics.
By superimposing the lattices of diselenide and tungsten disulfide in a special twisted configuration known as a moiré pattern, the scientists created a highly ordered crystal of bosonic particles called excitons. This led to the emergence of a new state of matter, which was called the "bosonic correlated insulator".
Bosons differ from fermions in their unique behavior. While fermions cannot occupy the same energy level, bosons share it easily, resulting in their special properties.
Professor Chenghao Jin, an expert in condensed matter physics from the University of California at Santa Barbara, explains: "Bosons have the ability to occupy the same energy level, while fermions avoid it. This difference forms the basis of the universe that we observe." .
To observe and identify excitons in the material, the researchers used the "pump probe spectroscopy" method. By superimposing two gratings and intense illumination, the scientists stimulated the formation and interaction of excitons. This method made it possible to study the behavior of excitons and reveal their properties.
It is interesting to note that with an increase in the density of excitons, they became immobile due to strong interaction, which led to the formation of a highly ordered crystalline state and an insulating effect. As a result of the correlation between these bosonic particles, at a certain density, they organized themselves into a symmetrical and charge-neutral insulator. This discovery is the first time that such a material has been created in a real system of matter, and not just under synthetic conditions.
The scientists note: "We have established a correlation that brought bosons into a highly ordered state. We have created a platform for studying bosons in real materials that did not exist before."
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Thimble game with wolves
▪ Fujifilm X-T2 mirrorless camera
▪ Drones against coronavirus
▪ Absolutely smooth surfaces
▪ New Lithographic Process for Growing Semiconductor Crystals
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Spy stuff. Article selection
▪ article The eye sees, but the tooth is numb. Popular expression
▪ article Can birds smell? Detailed answer
▪ article Carrying out silvicultural works on slopes. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Broadband UMZCH with low distortion. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Inhibitors are substances that slow down a chemical reaction. Chemical experience
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: