
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Primary quartz watch. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
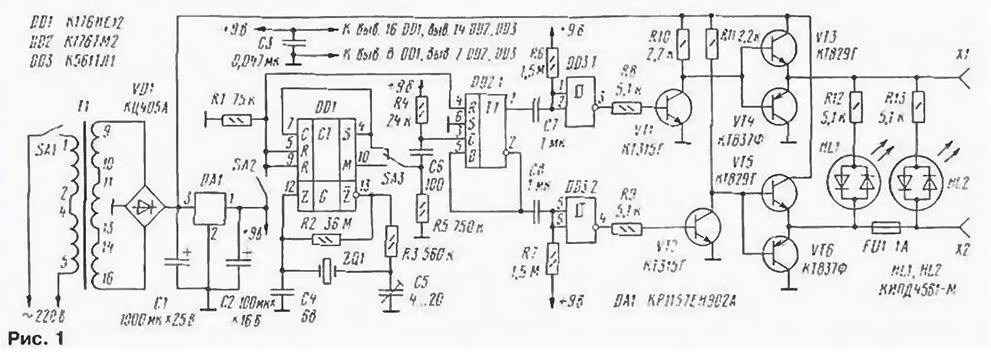
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Clocks, timers, relays, load switches At many enterprises, in institutions, schools, and other public places, an electric clock is installed. They feed on the so-called primary clock, which often fails. In such cases, the author proposes to replace them with simple home-made devices. Primary quartz clocks are highly accurate, provide accurate starts, as well as fast forward movement, which is necessary after power outages, as well as during the transition to daylight saving time and returning to winter time. They are small and. importantly, they are able to work for 40 secondary hours. A schematic diagram of such clocks is shown in fig. 1. It was developed on the basis of an earlier publication by the author of an article in the Radio magazine. No. 10, 1985. Instead of relays, electronic keys are used in the new watch, which made it possible to increase its reliability and increase its service life. The accuracy of the clock is determined by a quartz oscillator with a frequency divider up to one pulse per minute on the DD1 chip. Through the switch SA3 and the differentiating circuit C6R5, the pulses are fed to the input of the counting trigger DD2.1. The voltage at its outputs changes once per minute. The trigger output signals are differentiated by chains C7R6 and C8R7 and converted by Schmitt triggers DD3.1 and DD3.2 into positive polarity pulses with a duration of slightly more than 1 s. At the end of each minute, transistor VT1 or VT2 turns on for such a time. Through push-pull emitter followers on transistors VT3, VT4 and VT5. VT6 pulses from the collectors of transistors VT1 and VT2 through the fuse FU1 are fed to the secondary clock. Thus, pulses with a period of 1 min, an amplitude of about 24 V, a duration of about 1 s, and a polarity changing every minute are formed on the stepper motors of the secondary clock. LEDs HL1 and HL2 indicate the operation of the clock. Fuse FU1 protects them from short circuits in the output circuit. When it burns out, only the HL1 LED turns on. Asymmetry of emitter followers on transistors VT3 - VT6 - apparent. Transistors VT3 and VT5 are switched on through resistors R10 and R11 of rather high resistance, so it was necessary to use composite devices of the KT829 series. Transistors VT4 and VT6 are switched on through the included transistors VT1 and VT2. having a low resistance in a saturated state, in which case conventional transistors of the KT837 series can be used. Switch SA2 is used for accurate start of the clock, switch SA3. through which pulses with a frequency of 1 Hz are fed from the output of the DD1 microcircuit. provides control of the operation of the primary clock and the possibility of accelerated transfer of the secondary clock forward. In this case, the duration of the pulses on the secondary clock is exactly 1I s. To start the primary clock, all secondary clocks are manually set to the nearest full hour. In the primary close the contacts of the switch SA2. switch SA3 is set to the lower position according to the diagram. Then, the SA1 toggle switch turns on the primary clock and checks the readings of all secondary ones. If any of them show the set hour plus 1 min. then they are disconnected from the primary ones, set again for the same whole hour and. reversing the polarity of the connection, reconnect to the primary. 1 s after the sixth time check signal, the contacts of the switch SA2 open. The state of the trigger DD2.1 does not change. After another 39 s, a high logic level appears at the output M (pin 10) of the DD1 chip, but the state of the DD2.1 trigger remains the same. 1 min after the sixth signal, the high level at the output M will change to low, the resulting voltage drop will be differentiated by the C6R4 circuit and, in the form of a short pulse of negative polarity, will go to the input C of the trigger DD2.1. The decline of this pulse will switch trigger DD2.1 In the absence of a differentiating circuit, the trigger would switch not after 1 min, but 39 s after switching SA2, which would make it difficult to start. Adjust the readings of the secondary clock during their operation as follows. In the last minute of the hour, when the minute hands of the secondary clock show 59 min. close the contacts of the switch SA2. at the same time, all hours are switched and start showing 00 minutes. 1 s after the sixth time check signal, the contacts of the SA2 switch are opened. which ensures an accurate start of the clock. The described device uses resistors MLT-0.125 (R1. R3-R9). MLT-0.25 (R10-RJ3) m KIM (R2). capacitors K50-29 (CI). K52-1 (C2). KT4-256 (C5) and KM-6 (others). Quartz resonator - from a wristwatch to a frequency of 32768 Hz. transformer - TN32. Switches SA1. SA2 and switch SA3 - any small-sized. The KTs405A bridge rectifier can be replaced with any four diodes for an operating current of at least 0.5 A; transistors KT315G - for any low-power p-pn structures with an operating voltage of at least 30 V. Transistors VT3 and VT5 must be composite p-pn structures of the KT827 series. KT829, KT834. KT972 with any letter indexes. VT4 and VT6 - p-n-p structures of high or medium power with a current transfer coefficient of at least 50 - KT814 series. KT816. KT818; KT837 - with indices B, E.K.N.S.F. The KRI57EN902A microcircuit is interchangeable with 78L09, as well as with any stabilizer with a voltage of 9 V or with a resistor with a resistance of 2.2 kOhm and a zener diode for a voltage of 8 ... 10 V. When replacing two-color LEDs with conventional ones, in order to avoid breakdown in the opposite direction, a silicon diode should be connected in series with each of them for a voltage of at least 50 V. Almost all parts of the primary clock are installed on a printed circuit board measuring 70 - 90 mm (Fig. 2). the LEDs are soldered on the side of the printed conductors. The board is placed in a metal case measuring 200x100x80 mm, on the top panel of which all other watch parts are placed. The LEDs are brought out through the holes in the top panel.
The course of the clock is adjusted using a digital frequency meter, the input of which is connected to the output S (pin 4) of the DD1 microcircuit. After two to three weeks of operation, the clock setting is refined. Well-adjusted watches provide an accuracy of at least 10 s per month. Author: S. Biryukov, Moscow
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Face mask with microphone and speakers ▪ Nanospaghetti for health and longevity ▪ 3D glasses for TV without remote control ▪ A laser the size of a virus particle
▪ section of the Electrician website. PUE. Article selection ▪ article The tit has made glory, but the sea has not ignited. Popular expression ▪ How long can a camel go without water? Detailed answer ▪ article Mouse peas. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Ultrasonic delay lines. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: