
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Lighting device. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
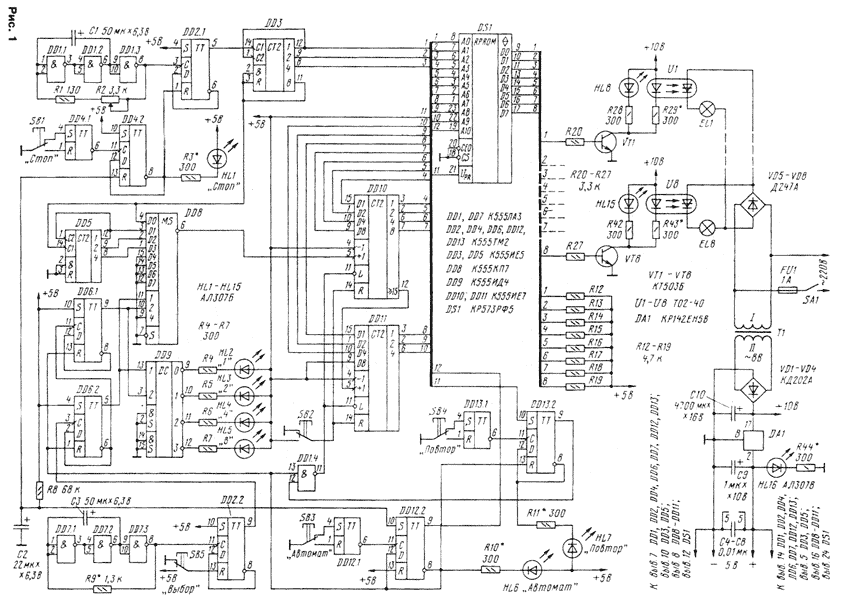
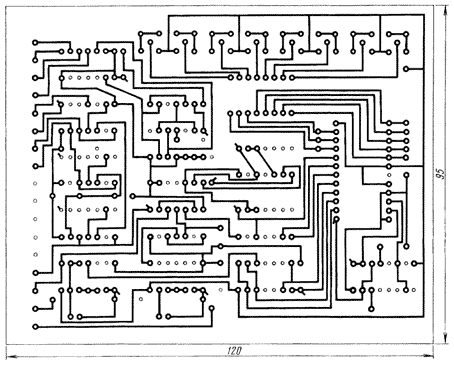
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Lighting Various designs of "running lights" are described in amateur radio magazines, but they usually have few lighting effects, a maximum of eight. The proposed device allows you to get 128 effects that can be selected at will, and the same number of effects in automatic mode, following one after another. The scheme of the device is shown in fig. one. A master oscillator is assembled on the elements DD1.1-DD1.3, the frequency of which, and hence the speed of switching lamps, can be adjusted by resistor R2. From the output of the generator, the signal is fed to the input of the trigger DD2.1, which acts as a divider by two. From its output, a signal of half the frequency is fed to the input of the counter DD3, the outputs of which are connected to the lower bits of the address input of the ROM DS1. Eight states of the DD3 counter provide a sequence of switching on the lamps, forming one effect, for example, "running fire". The number of repetitions of such effects is determined by the state of the counter on triggers DD6.1, DD6.2, it can be 1, 2, 4 or 8. The effects are changed by counters DD10 and DD11 - a total of 128 effects. effect), it will be reset to zero. At the same time, the counter DD3 increases its state by one by the output signal of the multiplexer DD10, and the effect changes. This will happen until all 8 effects have passed, after which everything will repeat, starting from the first. Automatic mode sets trigger DD12. After the supply voltage is applied, the R8C2 circuit sets the DD12.2 trigger to a single state, the HL6 "Automatic" LED turns on. From the direct log output. 1 is applied to the most significant bit of the address input of the ROM, which forms a cycle of switching effects one after another. From the inverse trigger output DD12.2 log. 0 switches triggers DD6 and DD13 to the zero state. In turn, the log. 0 from the trigger outputs DD6 goes to the address inputs of the multiplexer DD8 and decoder DD9, the HL2 LED "1" turns on, signaling that each effect will be repeated once. When the SB3 "Automatic" button is pressed, the DD12.2 trigger switches from single to zero, the HL6 LED goes out, log.O from the direct output of DD12.2 goes to ROM, the effects change. Log.1 from the inverse output DD12.2 enables the operation of triggers of the DD6 and DD13 microcircuits. When the SB4 button is pressed, the DD13.2 trigger switches, including the HL7 "Repeat" LED. Log.1 from its direct output goes to the element DD1.4. Log.O from the output of the element DD1.4 switches the counters DD10, DD11 to the parallel recording mode from their outputs. In this case, the desired effect will be repeated until the button SB4 "Repeat" is pressed again. If you press the SB5 "Select" button, the trigger DD2.2 goes into counting mode. From the multivibrator on the elements DD7.1-DD7.3, the signal goes to the counter, made on the triggers of the DD6 chip. From the counter, the binary code is fed to the address inputs of the DD8 multiplexer and the DD9 decoder, which determine the number of repetitions of one effect. For example, with a binary code of 10, a log appears at the inputs of the DD8 and DD9 microcircuits on the first bit of the DD9 decoder, the HL3 "2" LED turns on, signaling that the effect will be repeated twice. At the same time, code 10 at the address inputs of the DD8 multiplexer turns on the first channel. Counter DD5 is designed to count repetitions of effects. When resetting the counter DD3, the same signal is fed to the input C1 of the counter DD5. It will switch to state 1, but the DD10 counter will not switch, since its +1 input is connected by the DD8 multiplexer to output 1 of the DD5 counter. After the second reset DD3 counter DD5 switches to state 2 and switches the counter DD10. Each effect will be repeated twice. When the HL4 or HL5 LEDs are turned on, the multiplexer will pass the signal from outputs 2 or 4 of the DD5 counter and, accordingly, the effect will repeat four or eight times. The SB2 button is designed to reset the counters DD10, DD11. Button SB1 is used to stop switching lamps. When you click on it trigger DD4.2 switches from zero to single state. Log. 0 from the inverse output is fed to the input R of the trigger DD2.1, blocking it; the LED HL1 "Stop" turns on. To turn on the "running lights", you need to press the button SB1 "Stop" again From the outputs of the DS1 ROM, the signals go to amplifiers made on transistors VT1-VT8, which control the HL8-HL15 LEDs located on the front panel of the case, and the LEDs of the optothyristors. Optotriacs are suitable instead of optothyristors, then the VD5-VD8 diode bridge is not needed. The main parts of the device are located on a printed circuit board made of double-sided fiberglass (Fig. 2).
Microcircuits of the K555 series can be replaced with similar KR1533 or K155 series. In the latter case, +5 V voltage should be applied to the inputs of the microcircuits through resistors with a resistance of 1 to 10 kOhm (they are shown by a dashed line in Fig. 2). Transistors VT1 -VT8 - any medium power npn structures. Buttons SB1-SB5 - P2K, KM1-1 or others. The codes recorded in the DS1 ROM are shown in the table. The establishment of the machine consists in the selection of resistors in the optothyristor LED circuits for their full opening. It is advisable to connect all the contacts of the SB1-SB5 buttons connected to the microcircuits through resistors with a resistance of 5 ... 10 kOhm to +5 V circuits. Authors: A.Slinchenkov, V.Yakushenko, Ozersk-10, Chelyabinsk region.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Created spider silk using photosynthetic bacteria ▪ ASUS ZenPad 8 (Z380M) and ZenPad 10 (Z300M) tablets ▪ Smartphones can withstand 15 meter drops ▪ How do ants deal with traffic jams? ▪ Reflections on abstract topics lead to inspiration
▪ section of the site Calls and audio simulators. Article selection ▪ Article Garden set. Tips for the home master ▪ article The name of which world-famous corporation arose due to a spelling mistake? Detailed answer ▪ article Buten Khorasan. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: