Economical thermostat. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
For the preservation of vegetables in the autumn-winter period of the year, we use a container (a box with a double bottom), heated inside by incandescent lamps. The set temperature in it is maintained by a heat stabilizer made according to the scheme shown here. The operational amplifier K153UD2 (DA1) used in it, which works as a comparator, ensures the constancy of the set air temperature in the "vegetable store" with an accuracy of 1°C.
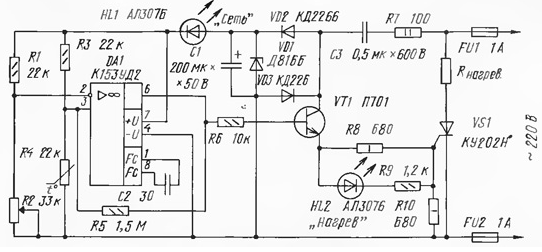
The principle of operation of the device is based on the imbalance of the measuring bridge, consisting of resistors R1 - R3 and a temperature sensor - thermistor R4. The bridge is powered by DC voltage stabilized by the Zener diode VD1.
The variable resistor R2 sets the response threshold of the electronic part, corresponding to the temperature of storing vegetables - from 0 to +10 ° C (it is assumed that the external air temperature is lower than inside the container). In this case, the voltage at the inverse input of the DA1 chip becomes less than at its direct input. The operational amplifier converts this voltage difference into a control current that opens the transistor VT1. When opening, the transistor turns on the trinistor VS1, and it, in turn, turns on the heater Rheating in the anode circuit. At the same time, the HL2 LED lights up, signaling that the heater is turned on.
Two or three incandescent lamps with a total power of about 200 W provide heating of the air in the vegetable store to the temperature set by the resistor R2. Its increase leads to a decrease in the resistance of the thermistor R4, balancing the measuring bridge and, as a result, disconnecting the heater from the network. When the air cools to a given temperature, the resistance of the thermistor increases to the nominal value and the described process is periodically repeated.
A distinctive feature of the proposed thermal stabilizer is the supply of its electronic part with half-wave mains voltage. So, with a positive half-wave of alternating voltage on the upper (according to the circuit) wire of the network, the current flows through the circuit: fuse FU1 - limiting resistor R7 - capacitor C3 - diode VD2 and charges the filter capacitor C1 to a voltage of 27 V, corresponding to the stabilization voltage of the zener diode VD1, and then through the HL1 LED ("Network" indicator) to power the DA1 chip and the measuring bridge to the FU2 fuse. With a negative half-wave of alternating voltage on the same mains wire, the current passes through fuse FU2, diode VD3, capacitor C3, resistor R7 and fuse FU1. It is easy to see that at this time, the transistor VT1, turned on by the emitter follower, is closed, there is no, therefore, the control current of the trinistor VS1 (the requirement for technical specifications is met). When using half-wave power and pulsed control of the trinistor, the incandescent lamps burn in full, which increases the efficiency and reliability of the device during operation.
Briefly about the details of the heat stabilizer. The temperature sensor (R4) is a thermistor MMT - 4 with a nominal resistance of 22 kOhm. Transistor P701 (VT1) can be replaced by any of the KT801, KT807, KT815, KT817, KT819, KT603, KT608 series. We will replace the K153UD2 (DA1) operational amplifier with any similar one, including those from other series. Variable (or tuning) resistor R2 can be of any type. The parameters of other elements of the device are indicated on its diagram.
Author: V. Velichkov, Perm
 See other articles Section Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers.
See other articles Section Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive rogue galaxy
06.02.2019
An unusual dwarf galaxy has been discovered. The uniqueness lies in the fact that it is too isolated from others, writes Digital Trends. It is located 30 million light-years from the Milky Way and two million light-years from the nearest large galaxy, NGC 6744, making it possibly the most isolated small galaxy ever discovered.
The dwarf galaxy Bedin 1 was accidentally discovered by a team of astronomers from the European Space Agency through the Hubble telescope. It was named after Luigi Bedin, an astronomer at the Italian National Institute of Astrophysics, who leads the team that made the discovery.
There are only a few billion stars in an open galaxy. For example, there are about 250 billion of them in the Milky Way.
They found it while studying a cluster of stars in another galaxy NGC 6752. Initially, they wanted to explore the cluster itself, but then switched to another object - a dwarf galaxy was discovered behind the star cluster. She looks underdeveloped, which is why she was hiding in plain sight all the time.
Astronomers now believe that other such galaxies may be hiding behind the light of star clusters. To detect them, you will need another WFIRST telescope. But NASA is just about to launch it into orbit.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Window to the brain
▪ Rain water power plant
▪ Multi-level ROM memory cells
▪ The coldest place in space
▪ Artificial intelligence has created a new material
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the website Residual current devices. Selection of articles
▪ article Great initiative. Popular expression
▪ article What are violin strings made of? Detailed answer
▪ article coachman. Job description
▪ article Household electrical appliances. Directory
▪ article Power amplifier on KP904. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: