
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Timer with automatic power off and one button operation. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
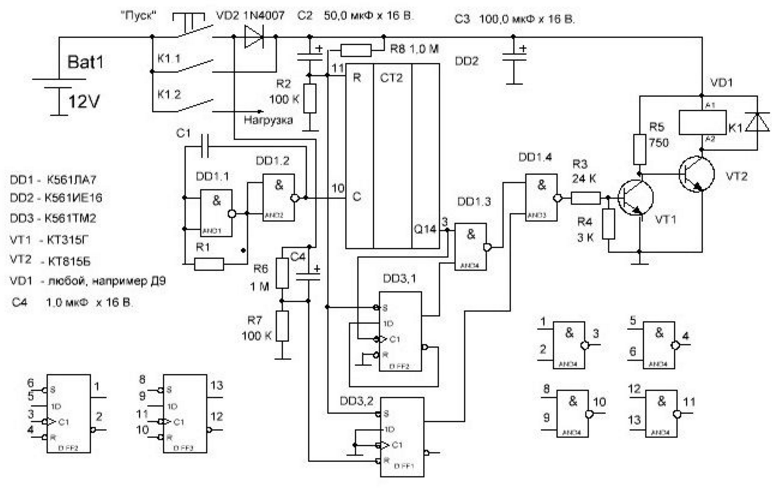
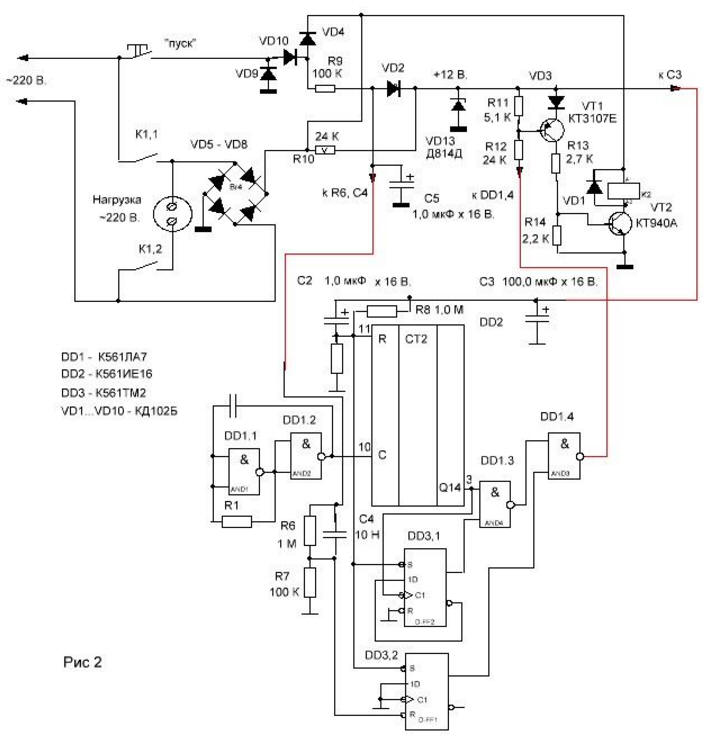
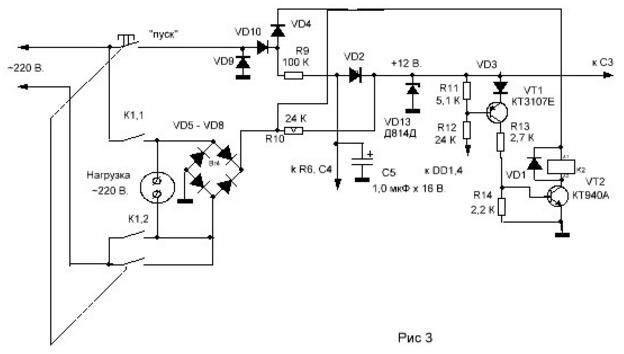
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Clocks, timers, relays, load switches In the initial state, the timer is disconnected from the power supply, by pressing the "Start" button it turns on and turns on the load. At the end of a certain time, it disconnects the load and turns off, from power, by itself. If necessary, the timer can be turned off at any time using the same button. When you press the "Start" button (it is non-latching), relay K1 is turned on along the circuit: Upit., "Start", VD2, K1, VT2. With its contacts, the relay blocks the "Start" button and supplies voltage to the load. Capacitors C2, C4 begin to charge. During their charging, a voltage almost equal to Upit appears on the resistors R2 and R7. those. logical units - 1. 1 with R2 sets the output DD2 to state 0 (voltage 0 is close to zero voltage) and the direct output DD3,1 to state 1, also affects the input S of the trigger DD3,2. At its input R comes 1 from the resistor R7. Because time constant C2,R2 is greater than C4,R7 trigger DD3,2, eventually set to state 1. As C2, C4 are charging, the charge current stops and 2 appears on resistors R7 and R0. The generator starts to work on the elements DD1,1 DD1,2. Its frequency, and hence the exposure time of the entire timer, depend on the ratings of C1, R1. When 3 appears at pin 2 DD1, it will switch trigger DD3,1 to state 0 by counting input C. Next, output 3 DD2 will be 0, then 1 will appear again, which will switch trigger DD3,1 to 1. at both inputs DD1,3 1s, 0 will appear at its output, which affects the element DD1,4. A 1,4 will appear at the output of DD1, which will open the transistor VT1. That, in turn, will close VT2. The relay will de-energize and disconnect the circuit and the load from power. If, without waiting for the relay to automatically turn off, press the "Start" button again, the capacitor C4 will start charging again, which has already managed to be discharged through the resistor R6. A 7 will appear on the resistor R1, which, through the input R, setting 0, will set the trigger DD3,2 to state 0. 0, acting on the element DD1,4, will open the transistor VT1. This will also disconnect the relay, load and circuit from the battery. If the load has an easy start, i.e. the voltage on the circuit (by pulses) does not drop to Upit / 2. then the capacitors C2 and C4 (both) can be reduced by a factor of 500. You can, then, another 10 times, but I would not - why approach the limits of the possibility of microcircuits. Figure 2 shows a timer circuit operating from a ~ 220 V network. The principle of operation of the circuit remained the same. The difference is as follows: When the "Start" button is pressed, the positive half-wave voltage feeds the relay through the circuit: Mains ~ 220 V., "Start" button, diodes VD10, VD4, relay, transistor VT2, diode bridge VD5, VD8. Power supply for the rest of the circuit, with a positive half-wave, through the circuit: Mains ~ 220 V., Start button, diodes VD10, VD4, resistor R10, zener diode VD13, diode bridge VD5, VD8. With a negative half-wave, the relay is powered through the circuit: Mains ~ 220 V, diode bridge VD5, VD8, relay, transistor VT2, diode VD9, Start button. Circuit power: Network, diode bridge VD5, VD8, resistor R10, zener diode VD13, diode VD9, Start button. Turning on, the relay connects the diode bridge VD5 - VD9 with its contacts. Diodes VD2, VD4 prevent the charge of capacitors C4, C5 when the "Start" button is released. Diode VD3 provides reliable locking of the transistor VT1. Capacitor C5 contributes to the charge of capacitor C4, at the moment the "Start" button is pressed, with a constant voltage. By preventing the appearance of pulses setting the trigger to 0, at the input R, with each positive half-cycle. Diode VD2 limits the voltage across capacitor C5. The operation of the circuit is no different from the previous version, with the exception of: At a logical zero, at the output of the element DD1,4, the transistor VT1 opens and opens the transistor VT2. If you use a double "Start" button (with two closing contacts), you can easily make a circuit that has complete galvanic isolation from the ~220 V supply network (Fig. 3).
To improve the operation of the circuit, according to Fig. 2, consider the capacitance ratings C2 - 10 μF, C3 - 50 μF, C4 - 0,68 μF. Attention! The circuit has a transformerless power supply, so touching live parts is life threatening!
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Space cargo delivery using a vacuum tube ▪ The reaction to a cigarette depends on the ideas about its composition. ▪ Nanotweezers extract individual molecules from a living cell without destroying it
▪ section of the site Amateur radio calculations. Article selection ▪ article by Gertrude Stein. Famous aphorisms ▪ article Which star is the brightest? Detailed answer ▪ article Fishing bayonet (anchor knot). Tourist tips ▪ article Parametric sensors. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: