Automatic control of the vibration pump. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Home, household, hobby
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The proposed device is intended for automatic control of vibration pumps "Baby", "Brook" and the like for operation in wells (wells) with low water flow or for periodic pumping of groundwater. The machine uses non-contact water level sensors installed directly on the pump's water-lifting hose, which allows it to be used in small diameter wells.
The vibration pump (Fig. 1) with a water-lifting hose is suspended on a metal cable in the well. The hose is equipped with high water level (VU) and low level (NU) sensors. The operation of the device is based on a change in conductivity between the common electrode, which is used as a metal cable for the suspension of the pump, and the electrodes of the sensors located in and out of the water.
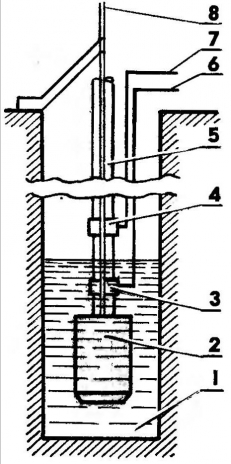
Rice. 1. Placement of the vibration pump in the well: 1 - water in the well, 2 - vibration pump, 3 - low level sensor, 4 - high level sensor, 5 - water-lifting hose, 6, 7 - sensor lead wires, 8 - pump suspension cable - common electrode .
The state of the sensors is analyzed using a logical node on the DD1 chip (Fig. 2).

Rice. 2. Schematic diagram of XP2 automatic device (click to enlarge)
The cycle of operation of the machine proceeds as follows. When the sensors of the upper and lower levels are in the water, the conductivity between the cable and the electrodes of both sensors is large, and when the power is turned on with the SA1 toggle switch, logic 1 levels are set at the inputs R and C of the trigger, which leads to the appearance of the same level at its direct output, causing opening key on transistors VT1, VT2, and the inclusion of relay K1, which connects the pump to the network with contacts K1.3, K1.4.
When pumping water, the pump will turn off only when a logical 1 appears at the input R DD0, that is, when the water drops below the low level sensor. This state of the trigger is characterized by a zero logical value on its direct output, causing the transistor switch to close, turning off the relay and the pump.
After the pump is turned off, the water level in the well begins to rise, and when it reaches the lower level sensor, the value 1 appears at the input R of the trigger, which, however, does not turn on the pump, since there is a logic zero voltage at input C, and up to the upper sensor The water level hasn't risen yet. And only after the rise of water in the well to the upper level sensor, a logic 1 voltage will appear at the input C DD1, and a logic 1 will also be set at its direct output; the transistor switch, relay and pump will turn on: the process of pumping water is repeated.
Resistors R2, R3, R4, R8 are used to set the required logical values at the trigger inputs.
To prevent a short circuit between the cable and the rings, the first one is insulated with three layers of PVC tape in a section 30-40 mm long. The wires are brought out to the connector plug, the counterpart of which is installed on the block box; there is also a socket for connecting the plug of the electric pump. Wires and a cable are tied to a water-lifting hose.
When installing the device in a well with a metal casing, it is necessary to suspend the pump in such a way as to completely prevent the sensors from touching the pipe.
When installing without errors, you do not need to set up the device. For stable operation, there must be a voltage of 3-5 V at the inputs R and C of the trigger (the sensors are in the water). Depending on the resistance of the water layer between the sensors and the cable, the specified voltage is selected using resistor R2. The current through the sensors does not exceed 5-10 mA when the resistance of the water layer between the sensors and the cable is 1,5-2 kOhm.

Rice. 3. Printed circuit board with layout of elements

Rice. 4. Location of sensors on the hose: 1 - low level sensor, 2, 6, 7 - supply wires, 3 - water-lifting hose, 4 - pump suspension cable, 5 - upper level sensor, 8 - PVC tape
The assembled device is checked at home (on the table), having made a sensor mock-up for this purpose and using a suitable vessel with water, and instead of a pump, a table lamp is connected.
Authors: L.Romanov, V.Kireev
 See other articles Section Home, household, hobby.
See other articles Section Home, household, hobby.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive E. coli bacteria for electricity production
17.09.2023
Researchers from the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology of Lausanne (EPFL) have made a significant breakthrough by creating an artificially modified strain of E. coli that is capable of generating electricity from brewery wastewater. This strain has surpassed the effectiveness of even the latest bioengineering developments in this area.
To increase the electrical activity of E. coli to produce electricity, the researchers modified its genome to include instructions for creating protein complexes similar to those found in the bacterium Shewanella oneidensis. This latter is famous for its ability to generate electrical current by oxidizing metals, which can be used, for example, to detect toxic metals, including arsenic.
The engineers successfully integrated all components of the S. oneidensis electrical pathway into E. coli, resulting in twice the efficiency of previously bioengineered strains that only partially replicated the pathway.
However, the question remains whether these bacteria are capable of working in real industrial conditions, and not just in the laboratory. Initial research included analyzing the feasibility of using algae to treat brewery wastewater. Since such plants must treat water containing residues of sugars, starch, alcohol and yeast, it requires treatment before release into the environment to avoid unwanted activation of microorganisms.
The team tested their system, using modified E. coli, on wastewater collected from a local brewery in Lausanne, Switzerland. The modified bacteria successfully treated wastewater in 50 hours.
Thus, the engineered E. coli was found to be much more effective at treating industrial wastewater, even though its ability to generate electricity was still slightly inferior to S. oneidensis, the scientists said.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Serotonin helps burn fat
▪ Fill your cell phone with syrup
▪ 875B Capacitance, Inductance, and Resistance Meter
▪ Prions jump from animals to humans
▪ Smart toilet with electronics and GPS
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the website job descriptions. Article selection
▪ article If someone somewhere we have sometimes. Popular expression
▪ article Why do cactus have needles? Detailed answer
▪ article Maintenance and operation of vehicles on gas fuel. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Acrobatics of lamp cascades. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Moving a bottle and a glass. Focus secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: