
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Triac regulator with overload protection. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers Improving one of the previously published triac controllers, the author improved its characteristics, supplemented it with an overload protection unit and confirmed his technical solutions with calculations. When establishing a triac controller, assembled according to the description in [1], it was found that it was not possible to enter it into the maximum power mode in the load. The "culprit" turned out to be a generator based on a single-junction transistor KT117A, which produces not one, but several pulses in each half-cycle of the mains voltage. As a result, the capacitor in the power supply circuit of the pulse amplifier did not have time to charge by the beginning of the next half-cycle and the pulse energy was not enough to open the triac. The scheme of the improved regulator is shown in the figure. It not only eliminates the disadvantage described above, but also provides a protection device against exceeding the permissible current value in the load circuit. Unlike the prototype, the pulse generator here is made on a complementary pair of transistors (VT1 KT361G, VT2 KT315G). At the moment when the voltage at the emitter of the transistor VT3, which increases as the capacitor C1 is charging, exceeds the voltage at its base, the generator produces a single pulse. Both transistors open like an avalanche, the capacitor C3 is discharged mainly through the base-emitter section of the transistor VT3. This transistor opens, and the capacitor C5 is discharged through the I winding of the pulse transformer T2. The pulse from the winding II of the pulse transformer opens the triac VS2. Transistors VT1 and VT2 remain open until the mains voltage passes through zero, more precisely, until the voltage on the supply bus drops to 4 ... 6 V. After they are closed, the generator is ready to give out another pulse. The moment of issuing the pulse is determined by the duration of charging the capacitor C3 to the opening voltage of the transistors and depends on the total resistance of the constant resistor R7 and the variable R6. Due to the fact that the generator generates only one pulse in each half-cycle, the discharged capacitor C5 always has the ability to be charged through the VD8 diode for almost a whole half-cycle, with the exception of a short interval when the instantaneous value of the mains voltage is close to zero. With an average charging current izar.sr approximately 9 mA (it depends on the resistance of resistors R1 and R2), the capacitor C5 will have time to charge up to 10 V in a half-cycle (22 ms) (limited by the zener diodes VD2 and VD3), if its capacity is not more than
What is the minimum capacitance of this capacitor? In order for the triac VS2 (TC132-50-6, [2]) to open, the voltage at its control electrode Uy must exceed 4 V for at least t on - 12 μs. The control electrode current iy at this voltage is 200 mA. The resistance of the control electrode circuit Ry can be estimated using Ohm's law:
Taking into account the transformation ratio k of the transformer T2, the voltage and resistance values \uXNUMXb\uXNUMXbreduced to its primary winding are:
From the equation
where U0 \u22d 5 V is the initial voltage on the capacitor CXNUMX, we find
We select the capacitance of the capacitor C5 equal to 1 μF. The overload protection device is made on the trinistor VS1 KU101G. Under the action of the overload sensor signal - current transformer T1 - the trinistor opens, which leads to a decrease in the voltage at the output of the diode bridge VD1 to approximately 4 V. This is less than the stabilization voltage of the KS168A (VD7) zener diode. Therefore, the pulse generator on transistors VT1 and VT2 stops working, the triac VS2 no longer opens. The activation of the protection is indicated by the glow of the HL1 LED. Thanks to the capacitor C1 and the diode VD6, the current through the trinistor VS1 does not stop at the moments when the mains voltage passes through zero and the trinistor remains open. In order to return the regulator with the activated protection to the working state, it is necessary to disconnect it from the mains for a few seconds (the time sufficient for the discharge of the capacitor C1). The voltage on the secondary winding of the transformer T1 is proportional to the current flowing in the primary winding connected in series to the load circuit. The control electrode of the trinistor VS1 receives part of the voltage of the secondary winding, rectified by the diodes VD4 and VD5. Using the trimmer resistor R4, the protection threshold is adjusted. Capacitor C2 prevents it from triggering from impulse noise. The current transformer as an overload sensor is convenient because even at a current significantly exceeding the set protection threshold (for example, when the load is short-circuited), the voltage on its secondary winding remains safe for other elements of the device. This is due to a sharp decrease in the transformation ratio due to saturation of the magnetic circuit. Used in the regulator - current transformer T1 is made of a transformer T-Sh-ZM from a subscriber loudspeaker. Similar can be found in some telephones. The cross section of its W-shaped magnetic core is SM=64 10-6 m2, the average length of the magnetic line is lM = 72 10-3 m. The experimentally determined relative magnetic permeability μ=0,7 103 at an induction of not more than 1 T Saturation occurs at an induction of 1,6 ... 1,8 T. We give the calculation of the current transformer: 1. The field strength required to obtain induction B \u1d XNUMX T,
2. Required ampere turns for this
3. The amplitude of the load current at the maximum power P=2500 W and the effective value of the voltage U=220 V is equal to
4. The number of turns of the primary (current) winding
We accept w1=5. 5. Inductance of the primary winding
6. Inductive reactance of the primary winding at mains frequency f=50 Hz
7. Voltage drop across the inductive reactance of the primary winding
8. For reliable opening of the trinistor KU101, it is necessary to apply a voltage of at least 15 V to its control electrode [2]. This is exactly the voltage amplitude on the secondary winding U2. The number of its turns
Since the device uses a full-wave rectifier (diodes VD3, VD4), the secondary winding of the transformer should actually consist of twice as many turns - 1500 with a tap from the middle. The current flowing through this winding is very small, so the wire diameter is chosen based only on its mechanical strength and the possibility of placing the required number of turns in the magnetic circuit window. The primary winding is wound in one layer over a well-insulated secondary wire with a cross section of at least 4 ... 5 mm2. A wire of this section is very inconvenient to wind, so it is better to use a bundle of a large number of thin wires with a total cross section equal to the required one. The wires of the bundle are connected in parallel. Establishing the regulator comes down to setting the protection tripping current with a trimming resistor R4 and to selecting the value of the resistor R7, on which the upper limit of the power control interval depends (usually 94 ... 97%). The value of R7 is chosen in such a way that in the maximum power mode there are no "skips" of half-cycles due to the non-opening of the triac VS2. To suppress radio interference generated by the controller, use the filter recommended in [1]. Literature
Author: B. Lavrov, St. Petersburg
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Artificial skin for diabetes treatment ▪ Human body for wireless communication
▪ site section Welding equipment. Article selection ▪ article Our little brothers. Popular expression ▪ article Who organized the first zoo? Detailed answer ▪ article Work on cassette folding machines. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article Sources of low-potential heat. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


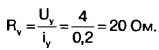







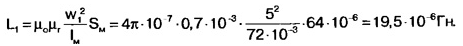



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: