
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Washing machine control. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
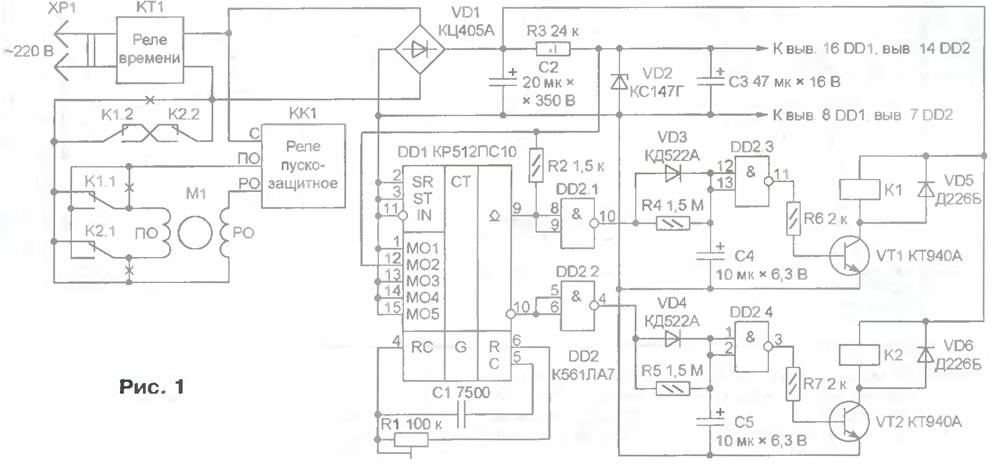
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Home, household, hobby The scheme of the automaton is shown in fig. 1. Electric motor M1, start-up relay KK1 and time relay KT1 - elements of the washing machine. When installing the machine in it, you should cut the previously existing connections in the places marked with crosses in the diagram. As a result of refinement, the M1 engine is controlled by two newly installed relays - K1 and K2. The operation of relay K1 essentially restores the original connections, so the shaft of motor M1 will rotate in the same direction as before the machine was installed. When the relay K1 is released and K2 is activated, the direction of rotation will become opposite as a result of a change in the polarity of connecting the starting winding of the software of the motor M1 to the network. Please note that the contact groups K1.2 and K2.2 are connected in such a way that both when the relays do not work, and when they are simultaneously accidentally or caused by a malfunction, the motor M1 is disconnected from the network. The winding circuits of the relays K1 and K2 are supplied by the mains voltage, rectified by the diode bridge VD1. The output voltage of the stabilizer R3VD2 (4,7 V) is intended for DD1 and DD2 microcircuits. Capacitors C2 and C3 are smoothing. Diodes VD5, VD6 suppress self-induction voltage surges that occur on the windings of relays K1 and K2 at the moments of closing transistors VT1, VT2, protecting transistors from breakdown. While the power is on, the DDI chip's internal oscillator runs continuously, generating pulses at a frequency of 1024 Hz. Connecting the control inputs M01-M05 of the DD1 chip corresponds to a frequency division factor of 122880, and the pulse repetition period at its pins 9 and 10 is 122880/1024=120 s. Mutually inverse signals from these outputs, having an equal duration of pulses and pauses between them, are fed to two identical relay control nodes K1 and K2, thus forcing the motor M1 to change the direction of rotation every minute. Consider the operation of one of the control nodes. The signal at its input is twice inverted by the elements DD2.1 and DD2.3. Thus, at log. 0 at pin 9 of the DD1 chip, the transistor VT1 is closed and the armature of relay K1 is released, with a log. 1 transistor is open the relay has worked. However, the transition between these states occurs at different rates. In the first case, the capacitor C4 is quickly charged through the VD3 diode, so the pauses between setting the log. 0 at the input of the element DD2.1 and the release of the relay K1 is almost non-existent. In the second case, the charged capacitor C4 is slowly discharged through the resistor R4, relay K1 is activated approximately 10 s after setting the log. 1 at pin 9 of the DD1 chip. The delay is necessary so that the shaft of the motor M1 has time to completely stop before changing the direction of rotation. The second control node (elements DD2.2, DD2.4, transistor VT2) works similarly, but with a time shift of half a cycle. The full cycle (50 s - rotation in one direction, 10 s - pause, 50 s - rotation in the opposite direction, 10 s - another pause) is repeated until the time relay KT1 disconnects the washing machine from the mains. Almost all parts of the machine are mounted on a printed circuit board with dimensions of 55x60 mm made of one-sided foil-coated fiberglass (Fig. 2). It is made by cutting the foil with a cutter. Since the power supply of the appliance is transformerless, it must be well isolated from the body of the washing machine and protected from accidental contact. To do this, it is desirable to place the board in a plastic case installed together with relays K1, K2 inside the machine.
Chip DD2 K561LA7 can be replaced by K561LE5. Diodes VD3 and VD4 - on any of the KD522 or KD521, VD5 and VD6 series - on KD208G or KD105B, the VD1 diode bridge - on KTs405V, KTs405Zh or assemble it from KD105B diodes. Instead of KT940A transistors, KT604B, KT605B are suitable. Capacitor C1 - mica K31-11-3 with a tolerance of ± 5%. Oxide capacitors C2 - K50-ZA, C3 - K50-16 or K50-35, C4 and C5 -K53-4 or K53-14. Relays K1, K2 -RP21-003-220 or RP21-004-220 Other relays with a winding operating voltage of 220 V are also suitable, having at least two groups of switching contacts capable of switching 220 V alternating voltage at a current of at least 1 A, for example, MKU48-S (passports RA4.500.236, RA4.501.148, RA4.509.110). When the machine is turned on for the first time, it is necessary to set the required cycle time with the trimming resistor R1. For the capacitance of capacitor C1 indicated on the diagram, the position of the slider of this resistor must correspond to the entered resistance of approximately 65 kOhm. After adjustment, the engine is securely fixed, for example, with a drop of paint. It is even better to replace the tuning resistor with a constant value of the desired value. If between successive starts the washing machine engine does not have time to stop completely or does not start to rotate for too long, the duration of the pauses can be changed by selecting the elements of the R4C4 and R5C5 circuits. Author: E. Zuev, village of Denyatino, Vladimir region.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ MSP-EXP430FR6989 - Extended Development Board for MSP430 with FRAM ▪ Chinese unnamed smartphones fell in price ▪ Sony Reader Daily Edition e-book
▪ section of the site Household electrical appliances. Selection of articles ▪ article by Henrik Ibsen. Famous aphorisms ▪ article How Libraries Originated? Detailed answer ▪ article Eucalyptus spherical. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Riddles about fruits and berries
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: