
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Automatic lighting control. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Lighting It's no secret that sometimes we forget to turn off the light, say, in the bathroom or in the utility room, and it burns uselessly for hours. In order to save electricity, it is desirable to equip the room with an automatic switch that protects it from our carelessness. Then, when entering the room, the light will turn on, and when leaving, it will go out. The machine is connected in parallel with the existing switch, which has to be used while cleaning the premises. The automaton can be made according to the description in [1], but, using the proposed idea, I developed my own version of the design (Fig. 1), which has been operating in my apartment for several years.
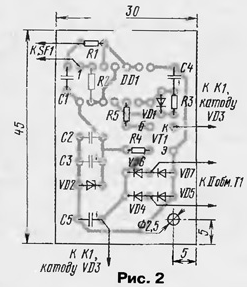
The machine works like this. When you connect it to the network at the output of the counting trigger, made on the elements DD1.1, DD1.2 [2], there is a low logic level, and the output of the inverter DD1.3 - high. Thanks to the integrating circuit R3C4, this level is transmitted to the input of the inverter DD1.4 only after about seven seconds. All this time, relay K1 turns on, which, with its contacts K1.1, supplies voltage to the EL1 lamp, and it lights up. As soon as the inputs of the inverter go high, the lamp goes out. The machine is ready to work. The sensor of the machine is a reed switch (sealed contact) SF1 with closing contacts, installed vertically on the top of the door frame. Opposite the reed switch there should be a permanent magnet, and between them there should be a steel corner fixed on the door. While the door is closed, the contacts of the reed switch are open, the machine is in standby mode. As soon as the door is opened and the room is entered, the corner moves to the side, the contacts of the reed switch are closed. The counting trigger "fires", a high level appears at its output, which is inverted by the DD1.3 element. A low level appears at the output of this element, due to which the previously charged capacitor C4 quickly discharges through the VD1 diode and the output circuits of the DD1.3 element. As a result, the input of the inverter DD1.4 is low, and the output is high. The transistor VT1 opens, the relay is activated, the lighting lamp flashes. When the door is closed, the steel corner blocks the magnetic flux, the reed switch contacts open, but the trigger state does not change. When the door is opened again and people leave the room, the closing contacts of the reed switch change the state of the trigger to the opposite. As a result, the transistor closes, the relay releases, the light goes out. If it is necessary to do some work in the room, for example, cleaning, the light is turned on with the SA1 switch, the automation does not work (that is, it practically works, but does not affect the lighting lamp). About the details of the machine. Reed switch - any of the KEM series with closing or switching contacts. Capacitor C4 - with a low leakage current, for example, K53-14; C3, C5 - K50-16, K50-35; C1, C2 - KM-5, KM-6. Diodes VD1, VD3 - any of the series KD521, KD522, zener diode VD2 - any with a stabilization voltage of 8 ... 10 V. Transistor - any of the series KT608, KT801 or KT603A, KT603B. Relay - for actuation current up to 40 mA at a voltage of not more than 12 V, for example, RES-32 passport RF4.500.335-01. The relay contacts must withstand 220 V and the current of the incandescent lamp. Transformer - industrial or home-made with a voltage on the secondary winding of 9 ... 10 V at a load current of at least 50 mA. Most of the parts are mounted on a printed circuit board (Fig. 2) made of one-sided foil fiberglass. The board with the rest of the parts, except for the reed switch, is placed in a plastic case of suitable dimensions, and the case is fixed on the wall near the door.
In the absence of a reed switch, it is permissible to use the microswitch 3 (Fig. 3) installed inside the bracket 4, for which a groove is hollowed out in the door frame 7. The microswitch is fixed with screws (or nails) 5, and the conductors from it are led out through the hole 6. A pusher 2 is placed in the door 1 of such a length that, when the door is closed, it reliably presses the button of the microswitch.
Literature
Author: E. Zuev, village of Denyatino, Vladimir region.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Next generation visual processor Movidius Myriad 2
▪ section of the site Lecture notes, cheat sheets. Selection of articles ▪ article Better late than never. Popular expression ▪ article When did the first stoves appear? Detailed answer ▪ Malva article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Home weather station. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: