
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Triac controller with feedback. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers In a device designed to control the power of an active load, the author used feedback not only to stabilize the output voltage, but also to limit the duration of the pulses that open the triac. The controller circuit is shown in fig. 1. The triac VS1 included in the load circuit is controlled by an electronic key on transistors VT1 and VT2. The opening voltage is supplied to the control electrode of the triac, if the logic level at the output of the element DD1.4 is low. The integrator on the DD2.3 element, operating in a linear mode, generates a linearly falling voltage (Fig. 2, a), which, using resistors R21, R22, is added to the feedback voltage, the sum is fed to the input of the DD2.4 element. As soon as it becomes less than the switching threshold of this element, a high one will appear at its output, and a low logic level will appear at the output of the DD1.4 element, which will lead to the opening of the triac VS1.
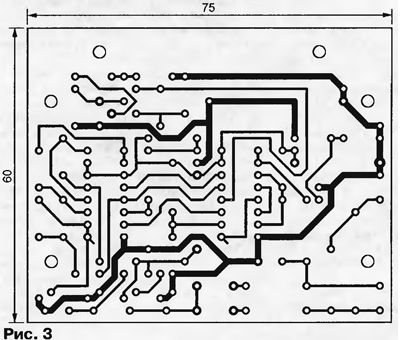
A node of resistors R6 - R9 and logic elements DD1.1, DD1.2 controls the voltage on the triac, the waveform of which is shown in fig. 2b. If the absolute value of this voltage is less than a certain value, the logic level at the output of the element DD1.2 is low, otherwise it is high. The "positive" and "negative" thresholds are equalized by selecting the resistor R9. Since the voltage drop across the opened triac VS1 is close to zero, a low level at the output DD1.2 along the chain DD1.3 - DD2.2 - DD1.4 - VT1 - VT2 leads to the termination of the current in the triac control electrode circuit. As a result, the pulse duration on this electrode will only slightly exceed the minimum required to open the triac. At the same time, the low level at the output of the DD2.2 element through the VD7 diode resets the sawtooth voltage generator on the DD2.3 element. A new cycle of generator operation will begin when the voltage on the triac changes polarity and exceeds the triggering threshold of the control unit. Another function of this node is to stop the supply of opening pulses to the triac if the load is disconnected from the regulator. This happens automatically, since there is no voltage between the main electrodes of the triac. An output voltage detector is assembled on the elements R3 - R5, VD4, VD5. The oscillogram of the signal emitted by the resistor R3 is shown in fig. 2, c. Its constant component is proportional to the average rectified value of the voltage across the load. In a proportion depending on the position of the trimmer resistor R10, the output voltage of the detector is summed with the manual adjustment voltage coming from the variable resistor R11, and filtered using capacitors C3 and C4. The negative voltage feedback loop is closed through the amplifier on the element DD2.1, operating in linear mode. Capacitor C5 serves for additional filtering. The primary winding of the current transformer T1 is connected in series to the load circuit. The voltage drop across the resistor R27, shunting the secondary winding of the transformer, is proportional to the load current. When its instantaneous value is greater in absolute value than on the engine of the tuning resistor R10, the VD6 diode opens and a signal is sent to the control circuit that reduces the output voltage. Socket X1 is used to connect an external commutator, for example, a contact thermometer, to the controller. Closing nests 1 and 3 of the socket sets a low logic level at input 2 of the DD1.3 element, which blocks the triggering of the triac and leads to a load disconnection. Protective resistors R13 - R15 limit the current flowing through the external control circuits to a safe value. Capacitor C6 protects against interference and interference. The power supply unit of the regulator consists of a quenching capacitor C1, shunted by a resistor R1, a limiting resistor R2 and a rectifier based on diodes VD1, VD2 with a storage capacitor C2. The output voltage of the rectifier - approximately 16 V - is directly used only to power the control circuits of the triac VS1. For the rest of the regulator nodes, the voltage is stabilized by the Zener diode VD3. After applying the mains voltage, the resistive divider R17R18 maintains a high logic level at the input 12 of the DD2.2 element until the capacitor C2 is charged to approximately 10 V. This prevents false opening of the triac until the regulator starts to operate normally. The regulator is assembled in an aluminum alloy housing measuring 135x85x50 mm. A three-pin mains plug and a similar socket for connecting the load are installed on the case. The grounding contacts of the plug and socket are electrically connected to the housing. Almost all parts of the regulator are mounted on a 75x60 mm printed circuit board located inside the case, made of one-sided foil-coated fiberglass. A drawing of the board from the side of the printed conductors is shown in fig. 3, the location of the elements from the side of their installation - in fig. 4.
The VS1 triac is mounted on an aluminum corner, the second "shelf" of which, 5 mm thick, has reliable thermal contact with the regulator body, but is electrically isolated from it by a 0,05 mm thick polyimide film gasket, lubricated on both sides with heat-conducting paste. The quality of the insulation must be checked with a megohmmeter with a test voltage of at least 1000 V. The magnetic circuit of the transformer T1 is assembled from two "half rings" from the standard SHL6x10. The primary winding is a power wire passed through the window of the magnetic circuit, the secondary winding is 1000 turns of enameled wire with a diameter of 0,1 mm. In the manufacture of a transformer, you can use the recommendations from the article by I. Nechaev "Indicator of power consumption" ("Radio", 2000, No. 11, p. 59). Variable resistor R11 and socket X1 are mounted on a bracket mounted on a printed circuit board. Resistors R13 - R15 with one output are soldered directly to the contacts of the X1 socket and are protected by PVC insulating tubes. The second terminals of the resistors are connected to the corresponding pads on the board. Resistor R16 - C3-14, the rest are constant - MLT, tuned - SPZ-19a. Variable resistor R11 - SPZ-9 or PPZ-40, a handle made of insulating material is put on its axis. Capacitor C1 - K73-17 for 630 V, C5, C6 - ceramic K10-17, KM or film, C7 - from the K73 series or ceramic group TKE no worse than M1500. Oxide capacitors - K53-18 for a voltage of at least 16 V (C2) and 6,3 V (C3, C4). Other types of oxide capacitors can be used, including aluminum K50-35. In the latter case, you will have to change the location of some pads and conductors on the printed circuit board. Diodes VD1, VD2, VD6, VD7 - series KD102 or KD522, zener diode VD3 - domestic production or imported for a stabilization voltage of 5,6 V. Diodes VD4, VD5 must be designed for a reverse voltage of at least 400 V, for example, KD209, KD105 s any letter index. The LED can be any, operating at a current of up to 15 mA. Transistor VT1 can be of the KT361 series (with indices A, B - E), KT3107 (A - D, I, K), KT209 (G - M), KT203B; VT2 - KT815, KT817 with any letter index or KT801B. K1LA561 is suitable as a replacement for the DD7 chip, but selection of the R9 resistor may be required to achieve output voltage symmetry. The triac must have a voltage class not lower than the fourth. In addition to that indicated in the diagram, the performance of triacs TS 112-10 and TS142-80 was checked. Starting to establish the regulator, the engines of the trimming resistors are set to the following positions according to the scheme (see Fig. 1): R10 - to the right, R3 - to the middle, R11 - to the top. A load is connected to the output - a 100 W incandescent lamp - and an AC voltmeter. For greater safety when setting up, it is recommended to connect the regulator to the network in such a way that its common wire (positive terminal of capacitor C2) is connected to the neutral wire of the network. Rotate the axes of the tuning resistors with a screwdriver with a handle made of insulating material. With the above position of the adjustment controls, the triac is closed, there is no voltage at the load, the HL1 LED is lit, indicating that the regulator is connected to the network. Rotating the axis of the tuning resistor R23, control the signal at the output of the element DD2.3 using an oscilloscope. The minimum value of the sawtooth voltage should be 0,4 ... 0,6 V higher than the voltage at pins 7 of the DD1 and DD2 microcircuits. If there is no oscilloscope, a DC pointer voltmeter measures the supply voltage of the microcircuits between pins 7 and 14 of one of them. Then turn on the voltmeter between pins 3 and 14 of the DD2 chip and the resistor R23 achieve its readings within 40 ... 45% of the previously measured supply voltage. The trimmer resistor R10 sets the lower, then R3 - the upper limits of the output voltage regulation. Having briefly connected a load to the regulator with a power slightly more than permissible during prolonged operation, set the engine of the tuning resistor R27 to a position at which the set output voltage begins to decrease. The permissible load current depends on the type of triac used and in this case should not exceed 10 A. Author: A.Abramsky, Novosibirsk
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ XNUMXD images can be touched ▪ Single-phase bridge rectifiers 4GBUxxLS ▪ Record-breaking short pulses of light received ▪ Compact amateur 4K camcorder Sony Handycam FDR-AX100E
▪ section of the site Microphones, radio microphones. Article selection ▪ article Love all ages are submissive. Popular expression ▪ Maniot article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Elastic rubber lacquer. Simple recipes and tips ▪ article Electricity and our health. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: