
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Economical electronic cat. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
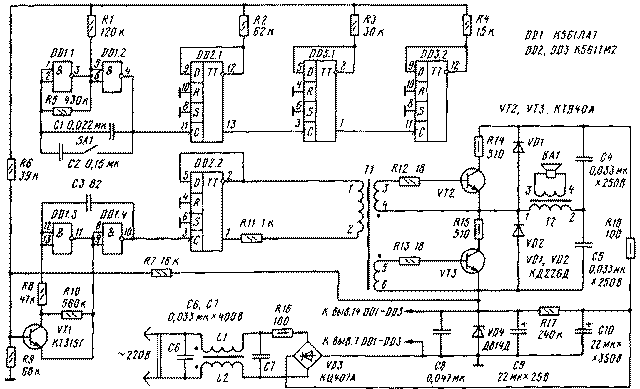
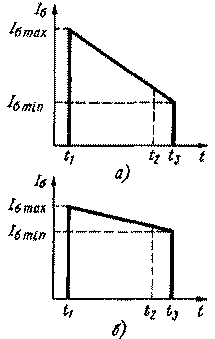
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Home, household, hobby Materials on the fight against rodents with the help of various electronic devices have already been published in the Radio magazine. In the article brought to the attention of readers, a description is given of another device of a similar purpose, which differs from those already known by the ability to work in conditions of significant fluctuations in temperature and humidity, efficiency, and a simple circuit design. It does not require complex measuring instruments when setting up. A schematic diagram of an electronic device for repelling rodents is shown in fig. 1. It consists of a low-frequency generator, a frequency divider, an ultrasonic frequency generator, a square wave signal conditioner, a power amplifier and a buzzer. The LF generator is assembled on the elements DD1.1, DD1.2 of the DD1 chip. The repetition rate of the rectangular pulses generated by it is determined by the values of the resistor R5 and capacitor C1. When the contacts of the switch SA1 are closed, an additional capacitor C1 is connected in parallel with the capacitor C2, which lowers the frequency. To make it more difficult for rodents to adapt to the scaring signal, the position of the SA1 switch must be changed once or twice a week. From the output of the low-frequency generator, the signal goes to a three-digit binary counter-divider, made on the elements DD2.1, DD3.1 and DD3.2 and counting up to 16 in the code 1-2-4-8 (the least significant bit is the output of 3 elements DD1.1 ). Resistors R1-R4 are connected to the outputs of the counter, converting the binary digital code of numbers from 0 to 15 into an analog signal, i.e., into a voltage that varies from zero to a logical unit (12V). Each high bit of the counter is connected through a resistor half the value of the low one. With such a combination of the inclusion of resistors R1-R4, the voltage at the point of their connection is zero when there is a logical zero in all bits. With each switching of the multivibrator DD1.1, DD1.2, this voltage increases abruptly by 1/16 of the supply voltage (Upit). For 16 switching cycles, the counter will reach a state of 1111, and the voltage at the connection point of the resistors will reach a maximum, i.e. Upit. At the next switch, the counter is reset to 0000 and the cycle is repeated. Resistors R1-R4 can be installed on the connectors, which makes it possible to swap them, while each of the 16 states of the counter will correspond to one of the 16 voltage levels. Each combination of these resistors corresponds to a certain sequence of changes in the control voltage. The number of such combinations N is equal to the factorial of the number four: N=4!=1х2x3x4=24. Such a variety of ultrasound modulation laws can also be used to prevent rodents from adapting to the deterrent signal of an electronic device. On the elements DD1.3, DD1.4, an ultrasonic frequency generator is assembled, which is determined by the capacitance of the capacitor C3, as well as the operating mode of the open transistor VT1. The mode depends on the control voltage supplied through the resistor R6 to the base of the transistor VT1. With the ratings of the elements indicated in the diagram and a change in the control voltage from 0 to 12 V, the generator frequency changes from about 50 to 100 kHz. From the output of the ultrasonic generator, the frequency-modulated oscillations are fed to the D-trigger DD2.2, which divides their frequency by 2 and generates a meander-type signal at the output, which is necessary for the symmetrical operation of the output stage. The D-trigger is loaded on the primary winding of the transformer T1, connected to its output through the resistor R11. This reduces the current loading of the flip-flop and improves the performance of the output stage. In more detail, one should dwell on the circuitry of the output stage - a power amplifier, as well as on the method of supplying power to different parts of the device. Considering the conditions in which such devices have to work, it is not advisable to use the traditional power supply circuit (transformer-rectifier-stabilizer). The fact is that small-sized network transformers in rooms with high humidity work unreliably: the magnetic circuit is exposed to corrosion; in the primary winding, the insulation is often damaged and breaks occur, since very thin wire is used for it. As for linear stabilizers, they have a significant drawback - from 20 to 50% of the power is dissipated on the stabilizer itself, which does not meet the requirement of efficiency. That is why it is recommended to use transformerless power supply for such devices. The emitter in such rodent repellers is usually a four-, six-watt high-frequency dynamic head. As the test showed, after a few days of operation, this head is the hottest part. For greater reliability of operation, its power should be about 3 ... 3.5 W. With a supply voltage of 300 V, the current consumed by the power amplifier will be 10 ... 12 mA. The low-voltage part of the device, assembled on the IC, consumes approximately b ... 7 mA. Such current values allowed the low-voltage and high-voltage parts to be connected in series and powered from a common power supply with a voltage of 300 ... 310 V, consisting of a bridge rectifier VD3 and a filter capacitor C10. The power supply of the IC stabilizes the Zener diode VD4. Thus, there is no need to generate an additional IC supply voltage, for example, using a quenching capacitor and a diode bridge. The power amplifier is a half-bridge inverter assembled on transistors VT2, VT3 and capacitors C4, C5 (Moin V.S. Stabilized transistor converters. - M .: Energoatomizdat, 1996). It uses the cheapest of the high-voltage transistors KT940A. The voltage on their collector is close to the maximum allowable, but as tests have shown, this unit is able to work even at a voltage of 335 V. The use of high-frequency transistors partially solves the through current problem. Other measures have been taken to protect against it. So, the inclusion of resistors R14, R15 in the collector circuit of transistors VT2, VT3 limits their currents even with a short circuit in the transformer T2 or load. The power dissipated by the resistors is 0,1 ... 0,15 W, which reduces the efficiency by no more than 5%. Excessive saturation of the open transistor is eliminated by limiting the base current using resistor R11. And this is better than using the base resistors R12, R13 to limit the current, since in the first case the base current during the time the opening pulse is present on it is decreasing. On fig. Figure 2 shows the shape of the base current when it is limited by resistor R11 (Fig. 2, a) and resistors R12, R13 (Fig. 2,6). When the transistor is operating in the key mode, it is necessary that it be in a saturated state Knas = Ib / (Ik / h21e)> 1 for almost the entire duration of the opening pulse. As shown in fig. 2,6, this time corresponds to the segment t1-t2. Only at the end of the pulse (t3-t4) is it necessary to reduce the base current so that the saturation factor Knas approaches 1. This will reduce switching losses in transistors. However, it should be recognized that this method of reducing switching losses is effective only with fine tuning of the output stage, and this is possible with a constant pulse duration (t3-t1=const). Since this condition is not met in the described device, fine tuning of the cascade is also impossible. A small current flows through the resistor R17, which ensures that the device starts when it is connected to the network. Filter L1 L2C6C7 protects the network from interference from the rodent repeller. In the author's version of the device, the printed circuit board contains an IC, a transistor VT1 and associated resistors and capacitors, as well as a Zener diode VD4 and capacitors C8, C9. For the rest of the parts, hinged mounting on a piece of fiberglass was used. Transistors VT2, VT3 are attached to the board with M3 screws and nuts. In the device, MLT resistors of the power indicated in the diagram can be used. Capacitors C4, C5-C7 - K73-17, C9, C10 - K50-29 or K50-35, the rest - any ceramic. For winding chokes L1, L2 and transformer T1, ring cores K12x5x5,5, K12X8XZ, K16x8xb, etc. from ferrite are suitable. Coils L1, L2 contain 20 turns of PELSHO 0,25 wire folded in half. Winding 1-2 of transformer T1 contains 210 turns of PELSHO 0,1 wire, windings 3-4 and 5-6 - 18 turns of PELSHO 0,25 each. Transformer T2 can be wound on ferrite ring cores K20x10xb, K28x16x9, K32X16X8 and even on a W-shaped ferrite magnetic core, for example, from a blocking transformer of an old tube TV. Winding 1-2 contains 200 turns of PELSHO 0,2 wire, 3-4 - 8 turns of PELSHO 0,3 wire. All magnetic circuits are made of ferrite grades 1500NM, 2000NM, 3000NM. Microcircuits K561LA7 and K561TM2 can be replaced with the corresponding ones from the 564 series. Instead of KT940A transistors, it is permissible to use KT854, KT858, KT872 and other high-voltage ones. Switch SA1 - P2K or any other small-sized, dynamic head - 4GDV-1.
To set up the device, an external power supply with a voltage of 20 ... 25 V is required. First, the part that is mounted on the printed circuit board is separately adjusted. The power source (observing the polarity!) is connected to the capacitor C0.62 through a resistor with a resistance of 1 ... 9 kOhm. The operation of the LF generator and frequency dividers can be checked using the LED. The LED cathode is soldered to the negative terminal of the capacitor C9, and the anode through a resistor with a resistance of 5,1 ... 10 kOhm - alternately to the lower (according to the diagram) terminals of the resistors R1-R4. The blinking frequency of the LED should be halved each time. When the contacts of the SA1 switch are closed, the frequency decreases several times. If you have an oscilloscope or frequency meter, check the frequency range generated by the ultrasonic generator. To do this, reduce the frequency of the LF generator by connecting instead of C1 a capacitor with a capacity of 2,2 ... 4,7 μF and instead of R5 a resistor with a resistance of 1 ... 3 MΩ. The frequency is alternately measured at pins 1 and 2 of the DD2 chip. It should take 16 different values, from about 25 to 50 kHz. If necessary, the frequency range can be adjusted using resistors R6-R10: divider R7R9 sets the average frequency; when the resistance of the resistor R6 decreases, the deviation increases; resistors R8, R10 provide uniformity of frequency change. In the absence of measuring instruments, it is possible to verify the operability of the ultrasonic generator by transferring it to the sound range. To do this, an additional capacitor with a capacity of 3 ... 820 pF is connected in parallel with the capacitor C3300 and, using a high-resistance telephone connected to pins 1 and 2 of the DD2 microcircuit, they listen to the frequency with which the trigger switches. After that, having installed the resistor R5 and the capacitors C1, C3 of the ratings indicated in the diagram, they proceed to setting up the device as a whole. The elements of the device have a galvanic connection with the mains, so when setting it up, you must take precautions! The printed circuit board is connected to the transformer T1 according to the circuit diagram. The IC is powered from an external source. Full power is supplied to the output stage by connecting the negative terminal of the capacitor C10 to the emitter of the transistor VT2. If there are no errors in the installation and the parts are in good order, then the output stage will work immediately. You just need to set the desired output power. To do this, measure the voltage drop across the resistor R18, it should be 1 ... 1,2 V. At a lower voltage, the winding 3-4 of the T2 transformer must be increased by 1-2 turns, with a larger one, reduced by the same number of turns. If the transistors VT2, VT3 heat up, you need to reduce the resistance of the resistor R11. After carrying out these operations, the external power source is disconnected from the IC and all connections are made in accordance with the circuit diagram. Author: I. Tanasiychuk, Storozhynets, Chernivtsi region; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Philips BDM4UP 3275K monitor with MultiView ▪ DC-DC converter SPB05 5W in SIP package ▪ Solar panels LG NeON R and NeON R Prime ▪ Three-dimensional image on the monitor screen
▪ site section Frequency synthesizers. Selection of articles ▪ article International Financial Reporting Standards. Crib ▪ article Who was the first to tame a horse? Detailed answer ▪ dryer article. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article Welding - with electronics. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: