
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Photorelay on a triac. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
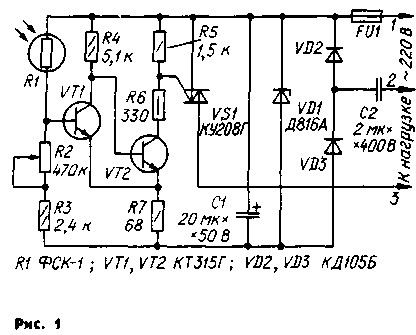
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Clocks, timers, relays, load switches Descriptions of structures for automatically turning on and off lighting depending on natural light have been repeatedly published in various publications, for example [1, 2]. Either electromagnetic relays or a thyristor were used as a switching element in the devices. In the proposed design, this function is performed by a triac. Due to the fact that its operation does not depend on the polarity of the applied voltage, there is no need for a powerful full-wave rectifier. This allows us to simplify the design of the machine and reduce its dimensions. The proposed device is designed to control light sources with a total power of up to 400 watts. The photorelay (Fig. 1) consists of a light sensor (R1), a threshold device made according to the Schmitt trigger circuit (VT), VT2), and a switching element (VS1).
Photoresistor R1 together with resistors R2 and R3 form a voltage divider that determines the base current of transistor VT1. In the daytime, when the photoresistor is illuminated, its resistance is relatively small, so the transistor VT1 is open and saturated, and VT2 is closed. The collector current of the transistor VT2, and, consequently, the current of the triac control electrode is practically equal to zero. The triac is thus closed and no current flows through the load. With decreasing illumination, the resistance of the photoresistor increases and the base current of the transistor VT1 begins to decrease. When a certain value is reached, the transistor VT1 comes out of saturation and starts to close. The increasing voltage drop across the resistor R7 accelerates the closing of the transistor VT1 and the opening of VT2. The triac control electrode current flowing through the open transistor VT2 and resistors R6, R7 keeps the triac open during both half-cycles of the mains voltage. Consequently, the lamps immediately begin to shine at full incandescence. The process of turning off the photo relay occurs in the reverse order. The threshold for operation of the photorelay is set by a variable resistor R2, and the resistor R3 serves to limit the divider current when direct sunlight hits the photodetector. Resistor R6 determines the current of the control electrode of the triac, which, when the transistor VT2 is open, must be greater than the turn-on current of the triac, but less than the allowable collector current of the transistor VT2. Resistor R5 equalizes the voltage at the control electrode and the triac cathode when the transistor VT2 is closed. This ensures reliable switching off of the triac and noise immunity of the photorelay as a whole. The device uses fixed resistors MLT, tuned - SP2-3. Capacitor C1 - any small-sized, C2 - MBGO-2. Transistors VT1 and VT2 - KT315G or KT315E with a current transfer ratio of at least 60. The device is assembled in a round plastic junction box designed for outdoor wiring. All elements are mounted on a round printed circuit board made of one-sided foil fiberglass 1,5 mm thick.The drawing of the board and the arrangement of parts on it are shown in fig. 2. Resistor R5 is soldered directly to the triac terminals, and resistor R6 - between the output of the control electrode and the board. The cathodes of the zener diode VD1 and the triac are connected to each other and to the board by a hanging conductor. The anode threaded leads of these parts must be shortened so that they do not protrude beyond the fixing nuts. The photoresistor is inserted with its leads into tubular racks 25 mm high soldered into the board so that space is made under it for mounting other parts. Sockets of the corresponding diameter from the pin connector were used as racks. The network wires and load circuits are fixed in screw clamps, similar to those used in telephone sets. The clamps are soldered into the board at four points each. The junction box should be selected with a light translucent cover so as not to cut out a special window for the photoresistor. A device assembled without errors and from elements with the type names indicated in the diagram does not need to be adjusted, it is only necessary to set the threshold. Mount the photorelay in such a place that the light from the lamps that it controls does not fall on the photodetector. To prevent water and foreign objects from entering the box, its inlet pipe must be directed downwards, and the lid after installation is sealed with waterproof varnish or glue. Attention! It must be remembered that all elements of the device are under mains voltage, therefore, when repairing and adjusting, safety regulations must be strictly observed. Literature 1. Makedon V. Automatic "keys" of lighting. - Radio, 1974, No. 9, p. 53.
Authors:A. Ivashchenko, N. Kotelenets, Chernihiv; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ How to recover lost memories ▪ Samsung 8Gb DDR4 chips and 32GB DDR4 modules ▪ A new way of presenting and mastering curricula
▪ site section Measuring equipment. Article selection ▪ article Horizontal bar from under the bed. Tips for the home master ▪ article by Tsavo. Nature miracle
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: