
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
Lightning protection of buildings. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Lightning protection Protection zone lightning rod - this is a part of the space inside which a building or structure is protected from direct lightning strikes with a certain degree of reliability. The surface that forms the boundary of the protection zone has the least and constant degree of reliability. When moving inside the protection zone, the reliability of protection increases. There are two types of protection zone. Type A protection zone has a degree of reliability of 99,5% or higher, that is, the probability of defeat for this zone is 0,5% or less. Type B protection zone has a degree of reliability of 95% and higher. Here the probability of defeat can be 5% or less. The protection zone of a single rod lightning rod with a height of up to 150 m inclusive has the form of a circular cone (Fig. 82).
The top of the cone, depending on the type of protection zone, is determined by the height h0. At ground level, the protection zone is formed by a circle with a radius R0. In a horizontal section, the protection zone at the height of the protected object hx is determined by the protection radius Rx drawn from the lightning rod to the border of the protection zone parallel to the ground surface. In the type A protection zone, the parameters h0, R0, Rx are defined as follows:
In protection zone B:
With known values of hx and Rx, the required lightning rod height h for type B protection zone is determined by the formula
With average thunderstorm activity of more than 20 hours per year (in central Russia it ranges from 20 to 80 hours), it is necessary to arrange lightning protection (lightning rod). This is easy to do after familiarizing yourself with the settlement system. The lightning protection system consists of three elements - a lightning receiver, a current conductor and a ground electrode (Fig. 83).
The lightning rod perceives a direct lightning strike and must withstand large thermal and dynamic loads in order to withstand and not melt. For its manufacture, strip and round steel with the smallest section of 60 mm2 with a length of at least 20 cm is used. The location of the lightning rod is the highest point of the roof, the position is strictly vertical. On fig. 84 shows how to specifically arrange lightning protection for a small house. The down conductor is made of galvanized round steel wire with a diameter of at least 5-6 mm. It is attached to the lightning rod by welding, soldering or bolting, while the contact area should be 2 times the cross-sectional area of the joined parts. The down conductor is laid in the shortest way in the places of the most probable lightning strike (along the roof ridges, along the ledges and edges of the gables), its fastening is carried out with clamps, staples, nails. If the roof of the building is made of flammable material, then the down conductor route should be at least 15-20 cm away from it.
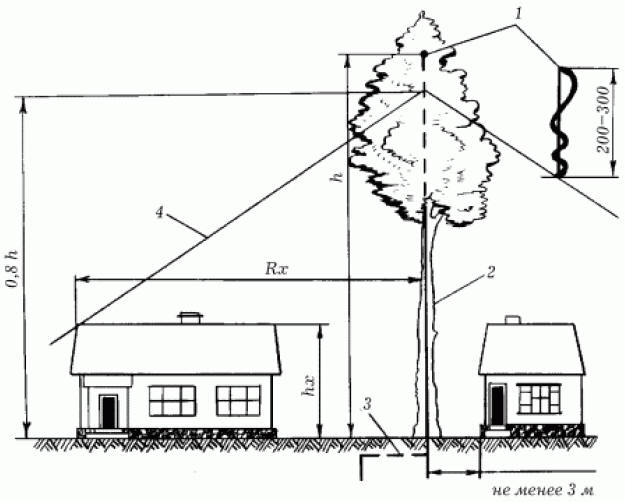
Purpose of the ground electrode - removal of current into the ground, so the electrical resistance of the material from which it is made should have a minimum value. The grounding conductor should be located in such a way that the distance from it to the porch and pedestrian paths is at least 5 m. surrounded by a fence with a radius of at least 4 m. The depth and position of the ground electrode in the ground depend on the type of soil and the level of groundwater in a particular area. With dry soil and a low level of groundwater, the ground electrode is arranged in the form of two rods 2-3 m long, driven vertically into the ground and at a depth of 0,5 m connected by welding with a jumper with a cross section of 100 mm2; a down conductor is welded to the middle of the jumper. Wet or peaty soil and a groundwater level of less than 1,5 m suggests a ground electrode made of metal corners horizontally located in the soil, old springs, etc. Their laying depth is at least 0,8 m (the longer the down conductor in the ground, the more reliable there will be lightning protection). The installation of lightning protection in apartment buildings is the responsibility of construction companies (and they shift this task onto the shoulders of contractors). Currently, lightning rods are not installed on every building under construction, if at least one is on the roof of a high-rise building, protecting a large area from lightning strikes. Therefore, developers first compare the parameters of the building under construction with the scheme of the protective zone of already installed lightning rods, in the event that the new building does not fall into this zone, they install a lightning rod. The owner will have to take care of the lightning protection of a private house. According to the standards existing in Russia, the requirements for the mandatory installation of lightning protection devices do not apply to residential buildings up to 30 meters high. Well, if the law does not require this, then why the extra costs? And now, with the first spring thunderstorms, city houses and country cottages begin to blaze, the owners of which did not take care of their safety. Of course, not all houses that are not equipped with lightning protection catch fire from a lightning discharge, and not even every second one. For example, if the house is located in a lowland, or there are higher buildings nearby, or a neighbor has arranged such a powerful lightning protection that has extended its coverage area to buildings located in neighboring areas, then you don’t have to worry. If none of these conditions is met, then lightning protection should still be arranged. Especially if the roof of the house is covered with metal roofing or metal tiles. The fact is that this roofing material is laid either on roofing material or roofing felt, or directly on a wooden crate; both of these roof base materials are dielectrics; therefore, the roof is completely isolated from the ground. In the metal of the roof, induced atmospheric electricity can accumulate (and during a thunderstorm it is necessary). When the electrical potential reaches a certain level, it needs to be discharged. The human body is a magnificent discharge device. The discharge can reach tens of thousands of volts; if at the same time the current strength is significant, then a person’s touch on an electrified roof can result in death or (at best) loss of consciousness. In addition, the discharge occurs in the form of a spark, which can set fire to both roofing material and wood. The real owner of the house (prudent, reliable, caring) will definitely take care of his house, himself and his loved ones, protecting his house from possible troubles in the form of a fire or electric shock during a thunderstorm. Trees can be used as lightning rods to protect individual buildings from direct lightning strikes. This is possible if the tree is 2-2,5 times taller than the house along with the antenna. The tree should be at least 3-10 m away from the house (Fig. 85).
At its top, one end of a solid piece of wire with a diameter of at least 5 mm is fixed, and the other end is lowered to the ground, buried in the ground and welded to the ground electrode. If the house is located on a site where there are no tall trees nearby, then you can either install two lightning rods at the ends of the roof ridge, or install a mast for a lightning protection device, on which a lightning rod is fixed. It is much easier to arrange lightning protection for buildings with a metal roof. In this case, the roof itself will play the role of a lightning rod, which should be grounded around the perimeter every 20-25 meters. If the house has metal gutters and drains for rainwater, then they can be used as a down conductor; but the grounding conductor will still have to be built. One has only to remember that the resistance of the ground electrode should not exceed 10 ohms. Like any other installation related to electricity, lightning protection requires periodic checking of the reliability of the connections. If, for example, in electrical wiring or electrical appliances, a malfunction of the connections is indicated by a failure in operation, then only a fire caused by a lightning discharge can indicate a malfunction in the lightning rod connections. Of course, you should not wait for this and you should independently check the lightning rod regularly. Author: Korshevr N.G.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Temperature and synthesis of pure polymers ▪ Electronic tablet instead of textbooks and notebooks ▪ Walking stick with echo sounder ▪ Consumed Internet traffic is growing with the diagonal of the smartphone
▪ section of the site Radio - for beginners. Article selection ▪ Article Teaching, learning. Popular expression ▪ article Who first saw the far side of the moon? Detailed answer ▪ article Klubnekamysh. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Thermoelectric generators. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

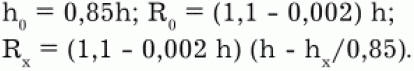

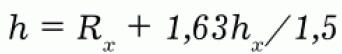



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: