
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING 1-wire interface. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Computers What is 1-Wire? The 1-Wire single-wire interface, developed in the late 90s by Dallas Semiconductor Corp., is regulated by developers for use in three main application areas:
If the first application is widely known on the world market and has long been deservedly popular, and the second successfully provides the ability to easily reconfigure the functions of semiconductor components with a small number of external pins manufactured by Dallas Semiconductor Corp., then automation systems based on 1-Wire bus have not yet received adequate recognition. Previously, this situation was determined by an extremely limited set of components for organizing applications in the field of automation. However, recently there have been more and more reports and specific examples of using the 1-Wire interface in various fields, more and more developers are showing interest in this technology, which is primarily due to a significant expansion of the range of single-wire components. So what is special about this network standard? Indeed, as a medium for transmitting information over a single-wire line, it is most often possible to use a conventional telephone cable and, therefore, the exchange rate in this case is not high. However, if we carefully analyze the majority of objects that require automation, then for more than 60% of them the maximum service rate of 15,4 Kbps will be more than satisfactory. And other benefits of 1-Wire such as:
Basic principles 1-Wire-net is an information network that uses one data line and one returnable (or earthen) the wire. Thus, to implement the exchange environment of this network, available cables containing unshielded twisted pair of one category or another, and even ordinary telephone wire, can be used. Such cables during their laying do not require any special equipment, and the limitation of the maximum length of a single-wire line is regulated by the developers at the level of 300m. The basis of the architecture of 1-Wire networks is the topology of a common bus, when each of the devices is connected directly to a single backbone, without any cascading connections or branches. In this case, the network structure with one leading or master and numerous followers. Although there are a number of specific methods for organizing the operation of single-wire systems in multimaster mode. The configuration of any 1-Wire network can change arbitrarily during its operation, without interfering with further operation and performance of the entire system as a whole, if the basic principles of organizing a single-wire bus are observed during these changes. This possibility is achieved due to the presence in the protocol of the 1-Wire interface of a special command to search for slave devices (Search ROM), which allows you to quickly identify new participants in the information exchange. The standard processing speed for such a command is ~75 network nodes per second.
Due to the presence of a unique individual address in any device equipped with a network version of the 1-Wire interface (the absence of an address match for devices ever manufactured by Dallas Semiconductor Corp. is guaranteed by the manufacturer itself), such a network has an almost unlimited address space. At the same time, each of the single-wire devices is immediately ready for use as part of a 1-Wire network, without any additional hardware and software modifications. Single-wire components are self-clocked semiconductor devices, the exchange of information between which is based on the control of the change in the duration of the time intervals of pulse signals in a single-wire medium and their measurement. Signaling for the 1-Wire interface is asynchronous and half-duplex, and all information circulating in the network is perceived by subscribers either as commands or as data. Network commands are generated by the master and provide various options for finding and addressing slave devices, determine activity on the line even without direct addressing of individual components, control data exchange on the network, etc.
The standard speed of the 1-Wire network, which is 15,4Kbps, was chosen, firstly, taking into account the maximum reliability of data transmission over long distances, and, secondly, taking into account the speed of the most widely used types of microcontrollers, which should mainly be used when implementing single-wire bus masters. This value of the exchange rate can be reduced to any possible value by introducing a forced delay between the transmission of individual data bits to the line (stretching the protocol time slots). Or increased by switching to a special accelerated exchange mode (Overdrive speed - up to 125Kbps), which is allowed for certain types of single-wire components on a short distance, high-quality communication line not overloaded with other devices.
The single-wire interface uses standard CMOS/TTL logic levels, and most single-wire components can be powered from an external source with an operating voltage ranging from 2,8V to 6,0V. An alternative to the use of external power is the so-called parasitic power mechanism, "the action of which is to use each of the slave components of the 1-Wire line of electrical energy of pulses transmitted over the data bus, which is accumulated by a special capacitance built into the device. In addition, individual components single-wire networks can use the data bus power mode, when the energy to the receiver comes directly from the master via the communication line, while the exchange of information in the network is forcibly stopped.
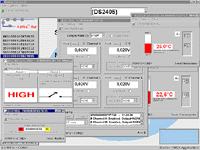
Perhaps the most attractive quality of 1-Wire technology is the exceptional ease of setting up, debugging and maintaining a network of almost any configuration built according to this standard. Indeed, to get started, any personal computer, an inexpensive 1-Wire-line adapter, and a freely distributed Dallas Semiconductor Corp. iButton Viewer software. With this small number of components, control and management of a network of almost any complexity, built on the basis of standard single-wire components, is organized literally within a few minutes. The iButton Viewer program, in this case, allows, with maximum comfort for the developer, to identify any of the slave single-wire devices on the line and check in full the correctness of its functioning as part of the configured network. Organization of leading Separate types of adapters that allow any personal computer to be endowed with the ability to serve as a master 1-Wire network are produced by Dallas Semiconductor Corp. itself. These include adapters for parallel port type DS1410E, for COM port type DS9097E and DS9097U, for USB port type DS9490R. These devices have various functionalities and design features, which provides the designer with maximum design freedom. And the fact that the user has little skills in creating electronic equipment makes it easy to self-assemble the circuit of the simplest 1-Wire-network adapter for a computer from a small number of available electronic components.
Often, it is not a computer that acts as the master of a single-wire bus, but a simple universal microcontroller. Various software and hardware methods are used to organize its interface with a 1-Wire network. From the simplest, when the controller's control program fully implements the 1-Wire interface protocol on one of its functional bidirectional outputs associated with a single-wire line, to options that allow you to free up significant controller resources, thanks to the use of specialized 1-Wire network interface chips. Such microcircuits are connected to the processor, which plays the role of a master single-wire bus, through peripheral input / output nodes that are part of any universal microcontroller. For example, the DS1481 device is designed to be connected directly to the controller's parallel exchange function outputs. And for the organization of the master of a single-wire system based on microcontrollers with a 3-volt power supply, passive DS1482 microcircuits are supplied that perform matching with the signal levels of a standard 1-Wire-line. If the single-wire line master must be organized on the basis of a standard microcontroller UART serial interface node, the DS2480B chip is used, and the DS2490 chip adapts the single-wire line to work from the built-in UBS interface node. Both microcircuits implement the so-called programmable mechanism for active pull-up of the 1-Wire data bus, which provides high-quality signal transmission in long problematic lines and an increase in the load capacity of the master in terms of the number of slave devices it serves. By the way, most of the above-mentioned adapters for personal computers are also built on the basis of such microcircuits. Moreover, taking into account the peculiarities of modern Windows operating environments, the use of these particular components, which are essentially serial-controlled digital automata, provides full-scale real-time single-wire line service. When building complex complete microprocessor systems that have a shortage of computer time for the implementation of the 1-Wire protocol, the most rational idea is to assign a separate task of servicing a single-wire line to a special node of a custom or semi-custom VLSI, for subsequent pairing of such a digital machine through a system backbone, directly with the main processor node. Dallas Semiconductor Corp. even developed a set of recommendations for organizing such a node called DS1WM, which was implemented, among other things, by Xilinx Inc. specialists. as a complete case study for the programmable tunable matrices of the Virtex and Spartan families. Moreover, Dallas Semiconductor Corp., which is also known as a supplier of high-speed controllers of the MCS51 clone, releases a specialized communication microcontroller DS80C400, which contains a 1-Wire protocol support machine built into the chip with the ability to implement an active pull-up mechanism.
Quite promising is also the direction associated with the use of handheld computers (or PDAs (Personal Digital Assistant)) of the popular PalmOS, Handspring and WinCE/PocketPC platforms for servicing single-wire components, including those operating as part of 1-Wire networks. At the same time, to connect the PDA to a single-wire bus, specialized serial port adapters are used, which are characterized by low consumption and are based on circuit solutions using the above-mentioned 1-Wire-line interface chips. It is this approach that is currently the most rational when organizing autonomous and mobile 1-Wire systems. The problem of preparing software for managing the line master when servicing 1-Wire networks does not seem to be unsolvable either. Dallas Semiconductor Corp. iButton TMEX SDK, a professional developer software package, is freely distributed, which is a universal tool for professional programmers, which greatly simplifies the process of creating programs for servicing single-wire devices connected via standard types of adapters to personal computers equipped with the Windows operating system. It contains a set of debugged drivers and utilities for implementing a full-scale 1-Wire protocol. The iButton TMEX SDK package uses a special standardized programming API as an environment for interacting with the developer. In addition, from the fttp server of the Dallas Semiconductor Corp. campaign. A number of examples of 1-Wire protocol implementation for some of the most popular types of microprocessors are freely available, as well as ready-made libraries of single-wire interface functional software modules for various software platforms. Driven Single-Wire Components
Single-wire slave components containing a 1-Wire interface are available in two different styles. Either in MicroCAN packages, similar in appearance to a disk metal battery, or in conventional PCB mount packages. The MicroCAN case is hollow inside. It performs the function of protecting the semiconductor crystal of a single-wire microcircuit contained in it, which is connected to the outside world only through two, isolated from each other, halves of the case, which are essentially pads for connecting a single-wire line. As a rule, iButton devices are supplied in such "tablet" cases. Components that are intended for use in 1-Wire networks are packaged in plastic cases used to make transistors and integrated circuits. This approach is explained by the fact that, unlike iButton devices, single-wire devices for 1-Wire networks often have more than two outputs. In addition to the outputs that are required for data exchange over a single-wire line, they have additional outputs necessary to provide them with power and organize external circuits connecting such devices with automation objects, such as sensors or actuators. The simplest single-wire slave components are the silicon serial number DS2401 (or a modified externally powered version of this device, the DS2411) and the DS2405 1-Wire controlled dongle. The first of these devices is often used as an electronic tag that allows you to identify the state of, for example, a mechanical switch switching the data line of a single-wire interface. Using the DS2405, you can remotely implement the simplest functions of switching external equipment by changing the state of the controlled key relative to the return conductor of the 1-Wire line.
However, the most popular driven components, with perhaps the largest number of applications, are by far the DS18S20 type digital thermometers (better known as the discontinued DS1820, which is no longer in production, but managed to become an international brand). The advantages of these digital thermometers from the point of view of the organization of the highway, in comparison with any other integrated temperature sensors, as well as good metrological characteristics and good noise immunity, bring them to the forefront when building multi-point temperature control systems in the range from -55°С to +125° WITH.
They allow not only direct monitoring of temperature in real time, but also due to the presence of a built-in non-volatile memory of temperature settings, they can provide priority signaling to the line about the fact that a controlled parameter goes beyond the specified values. Also, more advanced devices DS18В20 are supplied, the conversion speed in which is determined by the bit depth of the result, which is programmed by the line master directly during their maintenance. The digital code read from such a thermometer is a direct result of the measured temperature value and does not require additional conversions. And their uncalibrated, but at the same time cheaper version, under the designation DS1822, seems to be the best solution for developers of low-cost multipoint temperature control systems. For customers using only the parasitic single-wire power mode, the Dallas Semiconductor Corp. campaign. produces economical two-terminal devices - DS18S20-PAR, DS18B20-PAR, DS1822-PAR. The Russian company Rainbow Technologies received a certificate from the State Standard of Russia on approval as measuring instruments, including single-wire digital thermometers DS1822, DS18B20, DS18S20, DS1920, manufactured by Maxim Integrated Products, Inc., which includes Dallas Semiconductor Corp. To confirm this fact, there is a document stating that these types of devices are registered in the State Register of Measuring Instruments under No. 23169-02 and are approved for use in the Russian Federation.
A four-channel single-wire ADC of the DS2450 type and a two-channel single-wire counter combined with a buffer memory of the DS2423 type make it possible to solve problems related to the digitization of analog and pulse-time signals. The first of these devices essentially solves the problem of servicing analog information sources in 1-Wire networks, which include most of the currently produced sensors of various physical quantities (pressure, weight, voltage, humidity, current, illumination, acceleration, the same temperature). , but in ranges inaccessible for registration through the use of digital thermometers, etc.). The second device can successfully serve many types of pulse sensors used in technology (various optical counters, speed sensors, output signal from flow meters, capacitive humidity sensors included in the driving circuits of controlled pulse generators, radiation level counters, integrating voltage-to-frequency converters etc.). But still, the most irreplaceable "building blocks" underlying the foundation of single-wire automation networks are universal dual addressable transistor switches of the DS2406P type (the modern version of the well-known DS2407P devices).
On the basis of these devices, a lot of applications can be implemented, and, first of all, control units for logical states (levels) and service circuits for dry contact sensors, as well as various key circuits. Thus, it is thanks to the use of these components that discrete information is collected from geographically dispersed sensors (door monitors, valve position contactors, any sensors with a YES / NO output, such as position, passage, presence, fire and burglar alarm sensors, etc. .). Similar devices provide switching control of any types of power equipment that have two operating states: on / off (heaters, air conditioners, motors, fans, valves, etc.). In addition, the DS2406P's bi-directional, individually programmable pins can be used to provide a slow serial interface between the local MCU and a 1-Wire network. Despite the low speed when implementing this method of information exchange over a single-wire network, when one data bit is transmitted in two standard packages, this solution is acceptable and reliable enough for a large number of specific applications. However, the Dallas Semiconductor Corp. as a standard "bridge" for exchange between any circuits built on microcontrollers of various types and 1-Wire networks, it is recommended to use a specialized two-port DS2404 static memory. Since the memory array of this device can be accessed both from the side of the single-wire bus and from the side of the slave serial interface controlled by the microcontroller, the exchange of information between the network master and the slave intelligent device solving any local problem is quite easy. Moreover, due to the presence in the DS2404 microcircuit of an additional real-time clock and calendar unit, it is possible to supply the data stored by the processor in a common memory array with individual timestamps. Based on the real-time clock node of the DS2404 crystal by Dallas Semiconductor Corp. two more components are being produced that are very useful for building single-wire automation systems. These are the DS2415 and DS2417 devices. Using any of these devices, you can organize a cheap clock / calendar with a single-wire network interface. In addition, the second device, due to the presence of a separate interrupt output in its composition, can also additionally control the switching of external equipment in time or provide synchronization of the operation of other devices with the processes occurring on the 1-Wire line. Significantly expands the capabilities of single-wire networks for analog control of dispersed, including power, equipment, the digital potentiometer DS2890 equipped with a 1-Wire network interface. Using this device, you can create a wide variety of remote shockless control systems, thanks to the ability to smoothly change the analog control signal in 256 gradations.
With all the variety of single-wire components, it is obvious that the most versatile of them is the unique DS2408. This is an individually bidirectional eight-bit freely bit-programmable 1-Wire I/O port that allows you to implement any interface between an external device of arbitrary modification and a single-wire line. This device has a bi-directional external clock output that provides hardware clocking for transmitting or receiving data. The use of the DS2408 chip makes it possible to provide control via a 1-Wire bus: lumped bidirectional input / output on 8 independent channels, driving light-dynamic, liquid crystal indicators and displays of various types, scanning matrix keyboards and discrete sensors of various types, and also allows you to implement a truly full-scale interface with various types of microcontrollers, both in serial and parallel mode.
Some components of 1-Wire networks contain an array of permanent (one-time filled by the user) or non-volatile memory of one size or another. This allows you to store special service information related to the use of a particular component and the peculiarities of its use (identifier, territorial location, calibration coefficients, dimension, default settings, etc.) directly in the single-wire device. Thanks to this, to organize the operation of each new single-wire network, it is not necessary to prepare separate special software, it is enough to have one standard program that is reconfigured depending on the specifics of a particular system (of course, if the memory of all components of a 1-Wire system is filled in accordance with certain, pre-defined stipulated rules). If during the operation of the system it is required to store additional amounts of information, the developer has at his disposal special single-wire devices containing both permanent (DS2502/ DS2505/ DS2506) and non-volatile (DS2430A/ DS2432/ DS2433) memory of various sizes.
A number of components of the iButton family in MicroCAN packages can also be used as part of 1-Wire networks as single-wire slave devices that solve specific problems of identification, accumulation, storage and transfer of information. For example, to implement the identification procedure in industrial automation systems, it is usually sufficient to use common wearable electronic tags DS1990A. And multi-point temperature monitoring can be easily performed by a network of several DS1921 # devices or otherwise TERMOCHRON devices, each of which registers temperature values measured at certain pre-set time intervals and stores the information received in its own non-volatile memory, essentially being a "programmable temperature tape recorder. To solve the problem of transferring data accumulated by an autonomous 1-Wire system to a personal computer, various iButton devices are produced, which in this case play the role of so-called transport tablets. Such devices primarily include non-volatile memory devices, including the composition of its design is a lithium battery. This is a whole series of tablets "from DS1992 (1Kbps) to DS1996 (64Kbps), and among them, of course, a modification of DS1994 (4Kbps), which additionally contains a real-time clock node, convenient for generating timestamps of stored data or to organize autonomous resource loggers.
In addition, devices with electrically erasable memory such as EEPROM modifications DS1971 (32 bytes), DS1973 (512 bytes) and DS1977 (32 Kbytes) can be used for the same purposes. When moving large amounts of information, it is convenient to use the transport "tablet" in conjunction with a USB port adapter of the DS9490B type, which provides a high transfer rate when exchanging data between the iButton device and a personal computer. If we are talking only about solving the problem of accumulating and storing data in a 1-Wire network, any of the above transport "tablets" can be easily included in such a network. At the same time, to connect devices in MicroCAN cases to the conductors of a single-wire line, special latches of the DS9100 or DS9098P type are used, or simpler clips of the DS9094 type. From the point of view of the circuit implementation of a single-wire interface and the stability of operation on problematic lines, all slave single-wire components historically differ from each other, while being divided into groups: 1. DS2401, DS2405 - the first devices with a 1-Wire interface in plastic cases, are completely similar in circuitry to the first models of iButton devices that were oriented to work on short buses (until 1994), 2. DS1820, DS2407P, DS2450, DS2404, DS2415, DS2417, DS1920 etc. - the second version, specially oriented to work on long lines (before 2000, these components are now mostly discontinued), 3. DS18S20, DS18B20, DS1822, DS2438, DS2406P, DS2409, DS2890, DS1973 etc. - the third option, more resistant to collisions on the 1-Wire-backbone compared to the previous one (since 2000), 4. DS2411, DS2408, DS1921#, DS1977, etc. - the last version of the most reliable 1-Wire-interface circuitry (since 2003). Communication line and topology An important role in the construction of 1-Wire networks is played by the execution of a single-wire communication line. As a rule, such lines have a structure consisting of three main conductors: DATE - data bus, RET - return or ground wire, EXT_POWER - external power supply not only for serviced slave devices, but also for circuits of sensors and controls external to them. Depending on the method of laying, interfacing with slave devices and the materials used in laying, in accordance with the following Table, there are three main quality options for organizing 1-Wire networks, each of which implies the use of special technology and accessories when implementing the line.
Often, when organizing complex single-wire networks, in order to facilitate the wiring of a communication line, reduce its length or reduce the electrical load on the line due to the reduction of devices simultaneously working on it, it is necessary to provide a tree-like or beam structure of the trunk, which differs significantly from the structure of the common bus. For this, branches of 1-Wire networks of one or more levels are used. The main element in the construction of such branches is either a conventional addressable key of the DS2406 type, which provides branching due to switching the return wire of a single-wire line, or a specialized DS2409 branch switch that directly switches the 1-Wire line data bus. The latter option is more preferable. components on a disconnected branch driven by a branch remain always active. Alternate maintenance of the network by the master of each of the branches, with the other branches disabled, allows you to significantly increase the total length of the line and the number of slave devices on it. If the organization of a 1-Wire-system based on a personal computer is associated with special difficulties, the most optimal is the use of an intelligent adapter for a COM-port of the LINK type. It is implemented on the basis of a microprocessor. At the same time, the device, fully emulating the operation of the popular DS9097U adapter manufactured by Dallas Semiconductor Corp. from the side of the serial port, and thus supporting all the software previously developed for personal computers, thanks to its own built-in intellectual resources, implements a preferential mode of operation of single-wire devices on problematic 1- Wire-lines in a difficult interference environment. LINK greatly improves the active pull-up mechanism on the line, which allows you to really get ideal exchange signals with cable lengths of more than 300 meters and the number of accompanied single-wire components greater than 100 pieces, and the use of digital filtering algorithms by the processor of the device greatly improves the resistance of the served single-wire line to electromagnetic interference. Applications Numerous facts speak about the recognition of a single-wire bus as an international standard and the seriousness of this interface on the part of venerable developers and manufacturers of electronics. For example, there is practically no universal microcontroller, in the literature on the application of which the methods of organizing a single-wire line master on its basis would not be discussed.
The American company Embedded Data Systems, LLC (successor of PointSix, Inc.) is most consistently defending the line on the use of 1-Wire-network technology in the field of automation. It can be said that this campaign has made a name for itself by introducing and promoting the achievements of the single-wire bus in the field of automation. And this, despite the fact that the main area of its activity is not the automation of greenhouses and not the creation of fire alarm systems, but the development of tools and systems for servicing high-tech branches of mechanical engineering and the chemical industry, and even the creation of unique experimental and scientific equipment. This is confirmed by the widest range of products manufactured by the company (a variety of probes for measuring high and low temperatures, humidity, pressure and acidity sensors with special functions, special optical sensors, information collection boards, interface devices with various analytical equipment, and much more), and each of the devices contains elements of single-wire technology.
Promising examples in the field of application of 1-Wire technology for automation, of course, include the activities of such well-known global manufacturers as SYSTRONIX or AAG Electronica. LLC.
The lines of complete tools, as well as numerous examples of their use, and the high sales rating of the supplied products, indicate the success and relevance of the single-wire bus concept used by these companies to solve a wide variety of distributed automation problems.
Another example that clearly demonstrates the possibilities of single-wire bus technology in practice is the project for the construction of fully automatic weather stations (1-Wire Weather Station), which was developed jointly by PointSix, Inc., AAG Electronica LLC, Dallas Semiconductor Corp. and Texas Weather Instruments, Inc. At the beginning (back in the mid-90s), several experimental systems were created based on a leading personal computer with a DS9097U adapter, which is the heart of the complex, from three DS18S20 thermometers that perform temperature control, a DS2438 microcircuit for servicing an air humidity sensor, a component DS2423 to determine the wind speed and 16 electronic labels DS2401 that determine its direction. These first weather systems were installed and successfully tested during long-term operation in the state of Texas. Moreover, some of them were equipped with additional single-wire solutions that ensured the control of signals from sensors: barometric pressure, lightning discharges, precipitation on the surface, solar activity, soil moisture, etc. The data from all sensors, recorded by each of these systems, was received by a personal computer and transmitted via the Internet in real time to the central operator console, where the weather data of the region was received and archived, obtained through the analysis of information from several territorially dispersed stations. After the successful completion of the Texas Weather Instruments Inc. For several years already, it has been successfully trading in ready-made fully automatic weather stations that do not require human maintenance. Moreover, the popularity of such devices is so great around the world that Dallas Semiconductor Corp. was forced to start production of a specialized WS-1 chipset, which includes a set of single-wire components, the minimum required to build such a station. A complete set of such systems for numerous users from all over the world, including boards for self-assembly, certified mechanical and structural elements, is carried out by AAG Electronica LLC. Quite a promising area in which the advantages of 1-Wire networking technology are fully exploited, and to which the Dallas Semiconductor Corp. campaign pays special attention. is the management of autonomous chemical power sources - batteries. Management here means - first of all, strict and complete identification of energy sources, storage in the memory of each individual electronic device built into the battery of its manufacturing features and individual technical characteristics, the most complete monitoring of their main operational parameters throughout the entire service life, as well as the formation correct control action associated with the restoration of the charge of the serviced autonomous energy source.
The choice of a battery recharging algorithm largely depends on proper management and knowledge of the history of battery operation, which is directly related to the efficiency of use and the service life of many types of batteries. To do this, each of the batteries of multi-element energy structures (especially for mobile devices and uninterruptible power supplies) is supplied with an individual single-wire component, essentially turning into an intelligent system element of autonomous power supply. A number of microcircuits manufactured by the company are associated with this direction. Dallas Semiconductor Corp. today dominates the market of intelligent service systems for autonomous power sources, while professing a new integrated network approach to the problem of energy elements management. At the same time, 1-Wire solutions are used, which allow organizing a multipoint bus for servicing charge management and control devices, which makes it possible to accompany not only individual energy sources, but also entire batteries made up of many separate similar elements. Moreover, such devices are able to provide not only identification or the simplest temperature control of batteries, but also full-scale monitoring of their main parameters (voltage, current, discharge, short circuit control, etc.) throughout the entire period of operation. The results accumulated by such devices are stored in the built-in non-volatile memory either in the form of a histogram (DS2436) or in the form of an array of sequential readings tied to time stamps (DS2438).
Currently, the Dallas Semiconductor Corp. produces a range of precision crystals for monitoring, management, protection and charge recovery control of autonomous power supplies of various types and purposes (DS2720, DS2740, DS2751, DS2770, etc.). These include, among other things, crystals of the DS276# family, which, unlike other modifications of similar devices that require external piping using precision and stable passive components, provide higher accuracy in controlling the current consumed by the monitored battery. This is achieved, among other things, due to the built-in calibrated resistive circuit (shunt) made according to a special semiconductor technology, as well as due to the presence of a special hardware-software pre-calibration mechanism in the composition of such devices. Limitations and interfacing with industrial networks Of course, 1-Wire networks have their own niche for use in building automation systems. It makes no sense to seriously use them to transmit large amounts of information, when building, for example, video surveillance systems or high-speed exchanges related to servicing fast processes, or to compare the capabilities of single-wire networks with such powerful industrial network interfaces as ProfiBus, FeldBus, LonWorks, CAN, Industrial Internet, etc. It is even possible to formulate the main restrictions for today for the use of systems based on single-wire 1-Wire networks in the field of automation:
As can be seen from the remarks given in parentheses, even these obvious difficulties for 1-Wire networks are not insurmountable. Moreover, there are approaches that allow organically integrating slow single-wire geographically dispersed structures into such productive networks as CAN and Industrial Internet. This is achievable through the use of special hardware and software solutions implemented on the basis of modern microcontrollers, as well as a unique Dallas Semiconductor Corp. campaign tool. - TINI devices (Tiny Internet Interface). TINI400 is an entire microsystem based on a central processor, implemented on a high-performance network microcontroller DS80C400, which combines the resources of a number of the most common network interfaces, such as: RS232, 1-Wire, CAN 2.0B, Ethernet, not to mention the possibility of using a parallel sixteen-bit synchronous backbone, as well as autonomous nodes for organizing standard local serial I2C and SPI interfaces. In addition, the TINI400 board contains 1MB of Flash program memory, 1MB of SRAM, a real-time clock node, a lithium battery, and a silicon identification number. The TINI400 runs a powerful operating environment that includes support for TCP/IP and the Java Virtual Machine, which has been carefully developed and tested on the previous generation of TINI, the TINI390 board. The latter is determined by the fact that the software support technology for TINI390 has been developed over the years by Dallas Semiconductor Corp. together with employees of Sun Microsystems, Inc., while being a completely open project. This approach allowed us to have the most effective feedback from end users, which helped to identify and eliminate most of the software deficiencies. And now on the website of Dallas Semiconductor Corp. you can find all the necessary documentation and software development tools, which greatly facilitates the construction of local single-wire remote monitoring and control systems based on the TINI device, combining the advantages of fast and productive, but expensive, and slow, but cheap and efficient interfaces. In conclusion, it is necessary to once again note the absolute efficiency and rationality of using 1-Wire technology in building control and management automation systems for a variety of dispersed equipment, when high speed maintenance is not required, but significant flexibility and scalability are required at low implementation costs. Publication: cxem.net
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ 56Gbps In-System Interface Receiver ▪ Biometric lenses make vision three times sharper ▪ Generation of electricity from moving trains ▪ LDB - DC-DC Buck-Boost LED Driver Series
▪ site section Computer devices. Article selection ▪ article Remote control. History of invention and production ▪ article What is a hormone? Detailed answer ▪ article Foreman. Job description ▪ article Protection system UMZCH. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

























 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: