Ultrasonic depth gauge. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Indicators, detectors, metal detectors
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Measurement of the depth of the bottom of the water area or - search for sunken objects is possible with the help of an ultrasonic depth gauge, the scheme and a brief description of which are given below.
The principle of operation of the device is based on the reflection of short-term ultrasonic pulses from the river or seabed. In this case, it is not the time of passage of pulses in the water column that is measured (the speed of sound in water is 1500 m/s), but the number of pulses reflected per unit time. The penetration depth of ultrasonic pulses is determined by the radiation power and the sensitivity of the receiving device. In the described device, it does not exceed 20 m.
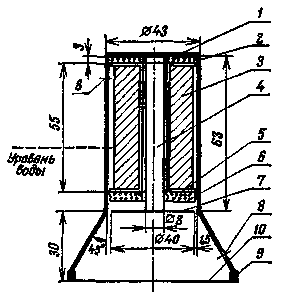
Ris.1
The depth gauge consists of two parts: a magnetostrictive sensor and an electronic unit. The magnetostrictive sensor (its device is shown in Fig. 1) is a nickel rod 4, fixed with a copper ring 1 in the housing 2. A frame 5 is put on the rod with coils 3 wound on it, sealed with a cork gasket 6. Ultrasonic vibrations (their amplitude is maximum at resonance frequencies) of the nickel rod and plate 7 are transferred to the aquatic environment. To exclude fluctuations in the water level in the sensor socket, it is closed with a rubber membrane 0,5-0,8 mm thick, which is held with a bandage 9. During measurements, water is poured into the socket through hole 8.
The electronic unit (Fig. 2) consists of an ultrasonic generator assembled on transistors T1, T2, a modulator on transistors T3, T4, a receiver of reflected pulses T5-T8 and a pointer indicator, the scale of which is calibrated in meters of depth.
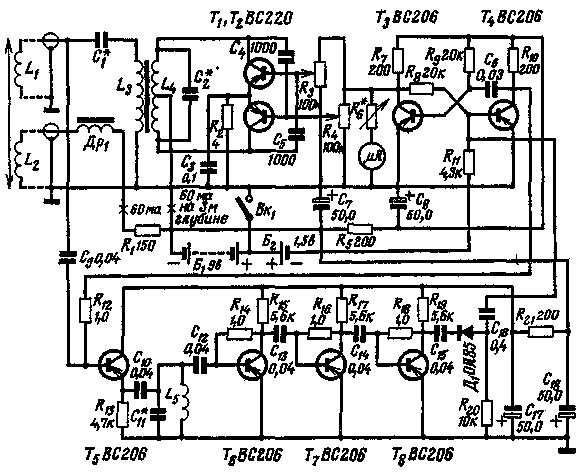
Ris.2
A push-pull generator with capacitive feedback generates ultrasonic vibrations with a frequency of 40 kHz. The generator load is the circuit formed by the L4 coil (it is wound on a closed ferrite rod with a cross section of 2 cm2) and capacitor C2. The specific data of these quantities are not given in the original. They are selected based on the measured (by one of the known methods) inductance of the excitation winding of the vibrator L1 (1500 turns of PEL 0,35), which in turn strongly depends on the quality of the vibrator core. When an atom, it should be borne in mind that the inductance L1 and the capacitance of the capacitor C1 form a series resonant circuit, which is coordinated with the generator circuit using the coupling coil L3. The number of turns L3 is also found empirically. The bias coil L2 has 3000 turns of PEL wire 0,15, its induction value is 0,5 T. In series with L2, the inductor Dr1 is connected, preventing the penetration of ultrasonic frequency oscillations into the bias circuit. The value of the inductance of the inductor is 0,25-0,3 gn.
The multivibrator (transistors T3, E4) is used in the device as a modulator and frequency meter. The time constant of its base circuit is 600 µs. Negative pulses are removed from the collector T3, which control the operation of the ultrasonic generator. The required value of the pulse voltage is set by variable resistors R3, R4. A DC voltmeter with a limit value of 10 V is included in the same circuit, which measures the average value of the pulse voltage. In addition, the multivibrator, together with the transistor T5, performs the functions of an electronic switch that closes the receiver input for the time of sending the probing pulse and opens it when the reflected pulse is received.
The receiver includes an amplifier on transistors T6-T8 and a detector on a diode D1. The reflected pulses received by the sensor (in this case, the reverse magnetostrictive effect is used) are amplified by a three-stage amplifier, at the input of which a selective circuit tuned to a frequency of 40 kHz is switched on, and are detected through a capacitor C16 enter the base circuit of the transistor T4, starting the multivibrator. Since the number of pulses reflected per unit time depends on the depth, when the latter changes, the multivibrator trigger frequency changes.
The initial calibration of the device is carried out at a known depth of 3 m. The vibrator is immersed in water and the current consumed by the generator is set to 4 mA with variable resistors R6 R60 ". The voltmeter reading is calibrated with a mark of 3 m. The current consumed by the generator should decrease from increasing depth.The maximum depth will correspond to the minimum deviation of the depth gauge needle.
Literature
"Radioamater", 1970, N5.
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Indicators, detectors, metal detectors.
See other articles Section Indicators, detectors, metal detectors.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Reverse contraceptive
19.01.2016
One day, German carpenter Clemens Bimek saw a TV show about human anatomy that led him to the idea of a radically new solution to the problem of male contraception. In 2000, he brought his development to patenting, and in 2009 he implanted (with the help of a surgeon, of course) this test device for himself.
The system, called Bimek SLV, uses two shutoff valves that are implanted in the musculoskeletal organ sac. Each valve is made from non-magnetic metal components and a biocompatible polymer used in medical implants. The valves attach to the paired vas deferens and cut into each canal. After implantation, the process of opening and closing the valve occurs by pressing a switch through the skin.
With the valve closed, the spermatozoa are diverted away from the duct and ejected into the surrounding tissue, where they should in theory be absorbed. In order to prevent accidental opening of the valve and, accordingly, an unexpected release of liquid, a safety device is provided in the device, which must be kept pressed to open the valve.
The operation on the inventor was performed under local anesthesia, and he could observe the process. All the past six years since implantation, the device has been working perfectly, and the spermiogram shows that his native ejaculate does not contain spermatozoa. When the rumor about the device spread among the masses, 200 men turned to the inventor, ready to participate in the experiments. Bimek is now working with doctors to prepare the device for clinical trials that are due to begin this year with 25 volunteers.
However, many urologists have raised concerns about the safety of the device. Some suggest a rejection reaction, despite the fact that the materials used in the device have long been used in implants. Others say that scar tissue can form at the junctions of the channels with the device, which will prevent the movement of the ejaculate. And the liquid itself can thicken and become inactive if the valves are kept closed for a long time.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ TOSHIBA 2 and 4 Gigabit Flash Memory Chips
▪ Copper for hospital
▪ The camera leaves traces
▪ Brain implants to control robotic prostheses
▪ New power supplies for LEDs
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers. Article selection
▪ article Russia died from chatter! Popular expression
▪ article What revolves around what: the Earth around the Moon or vice versa? Detailed answer
▪ article Chef of an educational institution. Job description
▪ article DTMF transmitter control scheme by decoder. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Guessing a card from a row. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: