
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING ZSK angle meter - prefix to the multimeter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
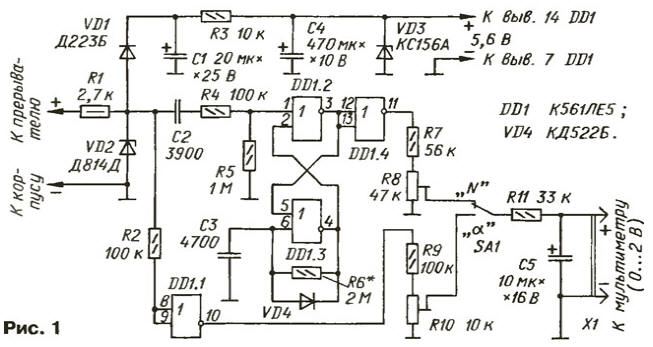
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Automobile. Ignition When adjusting the contact ignition system of an automobile engine, it is necessary to measure the speed of its crankshaft and the angle of the closed state of the contacts (ZSK), which characterizes the width of the gap between the contacts of the interrupter. The devices described in the journal for this purpose [1-3] display the result of the measurement on the scale of a pointer microammeter. Now many radio amateurs have digital multimeters of the M830, M832, M890 series, etc. A simple attachment to such a multimeter will allow you to conveniently and with great accuracy measure the rotational speed up to 2000 min-1 and the ZSK angle within 30 ... 60 degrees. The prefix is easily connected to the multimeter. After turning it off, the device is ready for use for its intended purpose. The attachment scheme is shown in fig. one. The device is assembled on just one digital chip DD1. Its power node consists of a decoupling diode VD1, a charging capacitor C1 and a voltage regulator R3VD3 with a smoothing capacitor C4 connected to a voltage limiter R1VD2. The prefix is powered by voltage pulses taken from the contacts of the breaker in the process of measuring one or another parameter. As a result of two-stage stabilization (R1VD2 and R3VD3), fluctuations in the supply voltage of the microcircuit do not exceed 3% when the duty cycle of the pulses from the chopper changes from 4 to 1,25. On the elements DD1.2, DD1.3, a single vibrator is assembled that generates pulses with a duration of about 8 ms. Voltage pulses, limited by the VD2 zener diode, are fed to the C2R4R5 short pulse shaper (resistor R4 is current limiting), which start the single vibrator with each positive edge of the input pulse sequence (i.e., when the contacts open). The pulses formed by a single vibrator of the same voltage and duration pass through the buffer element DD1.4, the voltage divider on resistors R7, R8 and the SA1 operating mode switch in the "N" position shown in the diagram to the integrating circuit R11C5. Capacitor C5 generates a constant voltage proportional to the engine speed. If the SA1 switch is moved to the lower position according to the scheme ("a"), then the R11C5 circuit will be connected through the voltage divider R9R10 to the inverter output DD1.1. The input of the inverter through the current-limiting resistor R2 is connected to the same zener diode VD2. Each contact closure causes a low-level pulse to appear at the inverter input. Since the ZSK angle is constant and does not depend on the pulse repetition rate, the voltage across the capacitor C5 will be proportional to the ZSK angle at any crankshaft speed. The voltage across capacitor C5 is measured with a digital multimeter. connected to connector X1. Instead of K561LE5 in the set-top box, you can use the same microcircuit from the K176, K564 series. Zener diode VD2 can be used for any voltage within 9 ... 12 V, and VD3 - for a voltage of 4,5 ... 7 V (KS147A, KS168A). Diodes VD1 and VD4 - any low-power silicon. Capacitor C5 is desirable to choose with a minimum leakage current. The details of the console are placed on a board with dimensions of 40x35 mm. The leads of the parts are passed through the holes. The installation is made with an insulated wire. The board is reinforced in a plastic case from the network power supply of an active television antenna. The SA1 operating mode switch - MT-1 microtumbler - is mounted on the housing cover. It is necessary to solder flexible conductors with insulated crocodile clips at the ends to the input of the set-top box. A view of the installation of the attachment is shown in fig. 2.
If the radio amateur has a multimeter from the DT-890 series, in which the distance between the centers of the sockets is approximately 19 mm, then the pins on the power supply housing must be connected to the output of the set-top box - they will definitely fit into the "COM" (common) sockets and "DCV" multimeter. When measuring, the multimeter's limit switch must be set to "2000 mV". To establish the set-top box, its pins are connected to the multimeter sockets, and a sinusoidal voltage of 3 ... 12 V with a frequency of 15 Hz or a sequence of rectangular pulses is supplied to the input from the 30H generator. The switch SA1 of the set-top box is set to the "N" position, and the trimming resistor R8 achieves the reading "900" on the multimeter scale, which corresponds to 900 min-1. When the generator frequency is increased to 50 Hz, the multimeter should show "1500" ± 20 mV. If necessary, the position of the slider of the resistor R8 is corrected. It is advisable to check the multimeter readings at other frequency values: at 20 Hz it should show "600", and at 40 Hz - "1200". Now the prefix is \u1b\u1bconnected to the breaker of the four-cylinder engine and make sure that it works correctly. An increase in voltage by 1 mV at the output of the attachment corresponds to an increase in the rotational speed by XNUMX min-XNUMX. After that, the switch SA1 of the console is moved to position "a". Rectangular pulses with a duty cycle of 2 ("meander") are fed to the input, and the trimming resistor R10 achieves readings of "45" on the set-top box (45 mV). When connecting the input of the set-top box to the breaker of a running engine, the multimeter will show the angle of the ZSK. An increase of one degree in the ZSC angle corresponds to an increase in voltage of 1 mV. The set-top box can be set up without a signal generator by supplying an alternating voltage of 15 ... 25 V with a frequency of 50 Hz to its input from the secondary winding of a step-down network transformer. In the "N" mode, with a tuning resistor R8, the set-top boxes set the indication "1500" on the multimeter display. In mode "a", the engine of the tuning resistor R10 is rotated until the indication "45" appears on the multimeter display. The measurement error of the parameters with careful calibration of the attachment does not exceed 3%, which is quite enough to ensure the normal operation of the internal combustion engine. It should be borne in mind that the settling time of the readings of a multimeter with an attachment is approximately 3 ... 4 s due to the relatively slow charging of the capacitor C5 of the attachment and some inertia of the operation of these models of multimeters. By the way, instead of a multimeter, you can also use an ordinary pointer avometer with a large input resistance - at least 50 kOhm / V. Literature
Author: I.Potachin, Fokino, Bryansk region
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024 The threat of space debris to the Earth's magnetic field
01.05.2024 Solidification of bulk substances
30.04.2024
▪ Makeup and pop culture made people afraid of clowns ▪ Stem cells for muscle regeneration ▪ NEC P and V Series Digital Signage Displays
▪ section of the site Household electrical appliances. Selection of articles ▪ article by Bhagwan Shree Rajneesh (Osho). Famous aphorisms ▪ article Are the timing of the seasons shifting? Detailed answer ▪ article Doctor of the day hospital. Job description ▪ article Electric octopus. physical experiment
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: