
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Pre-terminal amplifier for powerful triode output stages of tube UMZCH. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Tube Power Amplifiers The pre-terminal amplifier described here is designed to operate in high-power tube UMZCH with triode output stages built according to a push-pull circuit and operating in classes AB1 and B1. When designing high-power tube audio-frequency amplifiers based on triodes operating in amplification classes AB1 and B1 one has to face the difficult task of providing the required signal voltage range (Upeak-peak) on the control grids of the output lamps. This is due to the fact that for high-power triodes, when operating in the above modes, a high bias voltage is required. For example, in a push-pull output stage on 6C33C triodes at an anode voltage of 250 ... 270 V and a quiescent current of 110 ... 150 mA, a bias voltage of 110 ... characteristics). In this case, the terminal amplifier must provide a voltage swing on the output lamp grids, respectively, 140 ... 6 V. In a push-pull output stage on GM-33 triodes at an anode voltage of 220 ... 280...70 V. With such a bias voltage, the terminal amplifier must ensure the signal voltage swing on the grids of the terminal lamps is already 1400...1600 V! And this is taking into account the resistance and capacitance of the grid circuits of the output lamps, on which the final amplifier is loaded. One of the common solutions to this problem is the use of an interstage step-up transformer, which is also a phase inverter. But the manufacture of a high-quality interstage transformer is a very laborious and difficult task. Since this transformer operates in relatively high-resistance circuits, its parasitic parameters greatly affect the frequency response. Buying a ready-made high-quality transformer will be very expensive. In addition, the range of such transformers produced by some companies is very limited due to low demand. As an alternative, I propose a pre-terminal amplifier circuit (Fig. 1), which, at appropriate anode voltages, provides the necessary "buildup" of powerful push-pull output stages on triodes. The end-of-line amplifier is assembled on 6N8S double triodes and, at an anode supply voltage of 500 V, provides two antiphase signal voltages U at the outputpeak-peak = 300 V, and if necessary, with the maximum anode supply voltage of 600 V for such lamps, it will provide a signal voltage swing of up to 400 V at the output.
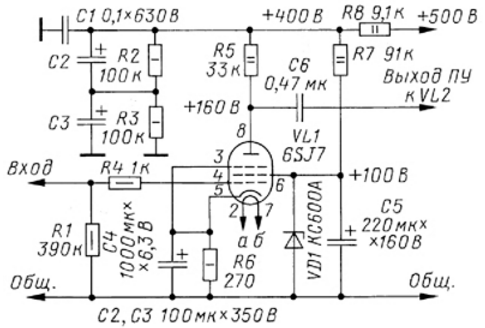
"How so? Are you out of your mind?! 6H8C and 600 V anode voltage!" - the inquisitive reader will exclaim. Don't be afraid. I explain: in most publications such as "Handbook of radio amateurs", "Handbook of radio tubes", "Electronic devices", as well as on numerous Internet resources for a 6H8C lamp, the maximum anode voltage of 330 V is really indicated. And only in very rare cases the word "constant" is added ". In the official reference books of the State Standard, it is indicated that 330 V is a constant, long-term voltage at the anode of this lamp. Under the signal, it can change and reach 660 V at the peaks of the signal. Thus, in the static mode of a correctly calculated resistive cascade, the voltage at the anodes of the lamps will not exceed 330 V at an anode power supply voltage of +600 V. The only thing to note is that such a cascade must necessarily have a delay in turning on the anode voltage after turning on the filament voltage. The input stage of the amplifier is assembled on a double triode VL1, the halves of which are connected by a cascode. With this inclusion, the first stage has a gain equal to 60. Resistors R6 and R7 form a circuit for automatically generating the bias voltage of the lower cascode according to the triode circuit. Resistors R8 and R10 set the voltage on the grid of the upper triode of the cascode, and capacitors C4 and C5 are blocking for the signal. Resistor R7 is trimmer, they set the input stage mode, the load of which is resistor R5. Resistor R1 serves to drain the reverse current of the control grid, and resistor R4 is necessary to prevent possible parasitic self-excitation. The supply voltage of the input stage is reduced to 400 V by resistor R9 due to the current consumption of the lamp VL1. This resistor, together with capacitors C1-C3, forms a smoothing filter for powering the input stage. Resistors R2, R3 equalize the voltage across capacitors C2, C3. The second stage of the pre-terminal amplifier, which also performs the function of a phase inverter, is assembled on two double triodes VL2 and VL3 and is a differential amplifier with a current source in the cathode circuit. The gain of the driver stage is 8. To reduce the internal resistance of the VL2 and VL3 lamps, pairs of triodes are connected in parallel. The signal through the interstage capacitor C6 is fed to the grid of triodes VL2. A feedback signal is applied to the grids of VL3 triodes from the tuning resistor R21. A field-effect transistor VT1 is used as a stable current source, and the resistor R15, in addition to increasing the resistance of the current source, serves to unload the transistor in terms of power. Since the bias source voltage for high-power lamps, which reaches 100 V or more, is usually used as the supply voltage of the current source, a significant amount of power is dissipated in the transistor. In order not to install a large area heat sink, a significant part of the power can be dissipated by a resistor in the drain circuit of the transistor. Resistor R14 sets the current of the zener diode VD1, which provides a fixed voltage at the gate of the current source transistor, and the trimmer resistor R20 regulates this current, which determines the mode of operation of the differential amplifier. The current adjustment range sets the resistor R19. The differential amplifier triode loads are resistors R11, R12 and R16, R17, and R13 and R18 are leakage resistors for the differential amplifier triode grids. Capacitor C8 - blocking. To eliminate the AC background from the cathode heaters in the filament circuit, resistors R24 and R25 formed an artificial midpoint, connected by AC capacitor C11 to a common wire. With a divider on resistors R22 and R23, the filament circuit is shifted relative to "zero" by +60 V. The common wire of the circuit from the artificial midpoint and its bias circuit must be connected to the common wire of the amplifier at the "zero" point of the power supply. With a bridge rectifier circuit, this will be the negative terminal of the bridge, and with a full-wave with a midpoint, it will be the midpoint of the anode winding of the mains transformer. The ratings of the elements and the voltage values in the above diagram are indicated for the anode power +500 V. In this case, the maximum signal voltage at the antiphase outputs of the pre-terminal amplifier (Upeak-peak) is 300 V. The adjustment consists in establishing the static modes of the amplifier cascades. Lamps VL2 and VL3 must be paired with the same gain (with both halves connected in parallel). Resistor R7 must be set to a voltage of 1,2 V at pin 6 VL1. Resistor R20 sets a voltage of 270 V at the anodes VL2 and VL3. The amount of feedback is set depending on the circuit of the output stage, the lamps used in it and the required damping factor of the speakers. In most cases, with triode output stages, the feedback depth is set to about 6 dB. The cascade provides full output voltage at a signal level at the input ieff equal to 500 mV. If more voltage is required at the output of the pre-terminal stage, the anode supply can be increased to +600 V so that the maximum signal voltage at the anti-phase outputs (Upeak-peak) reached 400 V. The values of some amplifier resistors at this supply voltage are as follows: R9 - 22 kOhm, R15 - 10 kOhm (4 W), R20 - 150, R22 - 270 kOhm, R23 - 2 kOhm. Capacitors C9, C10 - for a nominal voltage of 800 V. The voltage set by the resistor R20 on the anodes VL2 and VL3 is 330 V. The rest of the ratings and voltages remain unchanged. The resistances of resistors R15 and R20 are taken from the condition that the negative supply voltage of the current source is -230 V. If such a level of "buildup" of the output stage is necessary, it will obviously not be less. Resistor R15 can be made up of two 20 kΩ (2 W) resistors connected in parallel. In the first stage, instead of a double triode, a pentode can be used, as shown in Fig. 2. The most suitable pentode with an octal base for preliminary amplification of the audio frequency is the 6Zh8 pentode. However, in the "open" version of the amplifier, not everyone likes lamps with a metal cylinder. In this case, you can use the imported pentode 6SJ7-GT. It is practically an analogue of the domestic 6Zh8 pentode, but has a glass container.
Most of the elements in the cathode, grid and anode circuits of the cascade, as well as in the power circuit, have the same purposes as in the double triode cascode circuit. To stabilize the voltage on the screen grid of the pentode, a Zener diode VD1 was used. Resistor R7 sets the zener diode current, and capacitor C5 is a blocking capacitor. The resistance of the resistor R8 is indicated for a supply voltage of +500 V. In the case of a power supply of the pre-terminal amplifier with a voltage of +600 V, the value of the resistor R8 must be 18 kOhm. Author: O. Razin
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Operate better during the day ▪ Brain cells exchange batteries ▪ A luminous bandage will warn about the inflammation of the burn ▪ Converting carbon dioxide to alcohol
▪ section of the site Audio and video surveillance. Selection of articles ▪ article Big Brother. Popular expression ▪ article Which diacritic began to be used as a decoration by rock bands? Detailed answer ▪ article Determining the sides of the horizon by buildings. Travel Tips ▪ article Motorcycle burglar alarm. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Useful thread. Focus secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: