
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Active signal splitter for stereo telephones. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
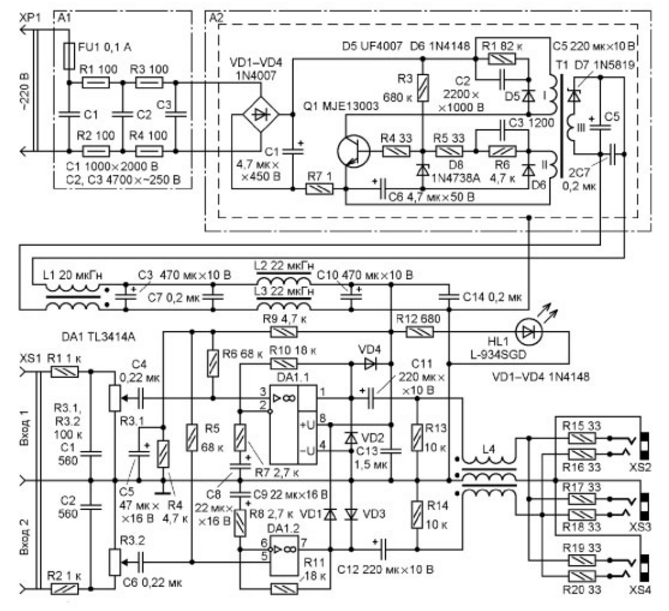
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Audio equipment Many multimedia devices (MP-3 and DVD players, TVs, e-readers, computer tablets, mobile phones) have only one stereo output for connecting headphones or an external amplifier. But what if, together with you, someone else would like to listen to the music recordings on your player or, without disturbing others, watch an interesting TV show with you, which, unfortunately, goes on during a holiday party, and retire somewhere in the place where you would like, there is no possibility? In such a case, a simple active stereo signal splitter will help out, allowing you to connect several pairs of headphones and (or) external AF power amplifiers to one sound reproducing device. The scheme of the proposed active stereo signal splitter is shown in fig. 1. It is a compact two-channel AF power amplifier with a built-in switching power supply. The amplifier is based on the integrated circuit TL3414A - a high-quality two-channel operational amplifier, specially designed for use in AF amplifiers for stereo phones. The AF voltage from the input connector XS1 is supplied to the volume control - a dual variable resistor R3 - through the RC filters R1C1 and R2C2, which prevent radio frequency oscillations from entering the DA1 input. From the sliders of the resistor, the voltage of the AF through the isolation capacitors C4, C5 is supplied to the non-inverting inputs of the op-amp DA1.1 (pin 3) and DA1.2 (pin 5). The voltage amplification factor of the amplifying stages made on them depends on the ratio of the resistances of the resistors R10/R7 and R11/R8 included in the OOS circuit. Since, in addition to common headphones with a resistance of 32 ohms, there are those in which it is much larger (for example, the isodynamic "Electronics TDS-5M", they require several times more voltage for buildup), the voltage gain of the amplifiers on DA1.1 and DA1.2 .6 is chosen equal to approximately XNUMX, which allows using this device as a normalizing amplifier for UMZCH with low sensitivity. The amplified stereo signal from the channel outputs of the DA1 microcircuit (pins 1 and 7) through the coupling capacitors C11, C12, the windings of the noise suppression inductor L4 and the current-limiting resistors R15-R20 is fed to the output sockets XS2-XS4, to which stereo telephones or UMZCH inputs are connected in any combination. The maximum signal swing at the DA1 outputs is about 5,5 V at a supply voltage of 7,5 V. With an input signal amplitude of 0,7 V (such is the MP-3 player in maximum volume mode), the output signal amplitude on stereo phones with a resistance of 32 ohms is - about 2 ... 2,5 V. Diodes VD1-VD4 protect the outputs of the op-amp DA1 from electric shock (this problem has become relevant due to the spread of various devices with switching power supplies). Resistors R13, R14 eliminate the click when connecting stereo phones or UMZCH to a working device.
UMZCH is mounted on a board with dimensions of 120x48 mm (Fig. 2) made of one-sided foil fiberglass. The foil is used as a screen, all connections are made with a thin stranded mounting wire on the opposite side of the board. The foil around the holes for the leads of the parts was removed by countersinking with a drill sharpened at an angle of 90°. The screen is connected to a common wire at only one point - where the terminals of the capacitors C1, C2 and the braid of the shielded wire going to the variable resistor R3 are connected. Chip DA1 is glued to the circuit board on the side of the wiring connections ("under" the capacitor C8). When developing the described apparatus, the task was to create a compact design with an integrated power supply unit (PSU). As a power supply unit, a charger for mobile equipment based on a pulse converter was used, similar to the scheme described in [1, fig. 2)] (marking on the printed circuit board - 4M-2). The main problem when placing an AF amplifier and a pulsed power supply unit in one small case is to eliminate interference from the latter. Thanks to the measures taken (shielding of both devices, the use of LC filters in the power circuits), the problem was successfully solved. On fig. 1 PSU is designated as module A2. The original device has been slightly modified: the oxide capacitor C1 (2,2 uF at 400 V) has been replaced by a 4,7 uF capacitor with nominal voltage 450 V, zener diode 1N4736A (D8) with a stabilization voltage of 6,8 V - zener diode 1N4738A with a stabilization voltage of 8,2 V (this increased the PSU output voltage to 7,5 V), high-voltage transistor MJE13001 (Q1) - more powerful MJE13003 , and the diode 1N4007 (D5) - high-speed UF4007. All parts have been removed from the secondary circuit of the device, except for the Schottky diode D7 and the oxide capacitor C5, in parallel with which the ceramic capacitor 2C7 is connected. An insulating tube is put on the body of the capacitor C5. The maximum load current of the modified PSU, due to the higher output voltage, should not exceed 150 mA (the amplifier at maximum volume consumes about 40 mA when connected to the outputs of three pairs of stereo phones). The current consumed by the PSU from the 220 V network is about 4 mA. The PSU is connected to the network through an R1R4C1C3 noise suppression filter (indicated as module A1 in the diagram). The presence of resistors R1-R4 also reduces the negative consequences in the event of a malfunction of the pulse converter. A voltage of about 7,5 V from the PSU output is supplied to the AF amplifier through noise suppression filters L1C3C7 and L2L3C10C14. The HL1 LED indicates that the device is connected to the network.
Filter A1 is assembled on a small printed circuit board made of one-sided fiberglass foil, the parts are installed on the side of the printed conductors (the distance between the printed conductors with a large potential difference must be at least 3 mm). At the point of connection of the network wire in the board, a cut was made with a width of 1 and a length of 10 mm. Mounting view of modules A1 and A2 is shown in fig. 3 (the first one is on the right, the second one is on the left).
All nodes of the device are housed in a housing with dimensions of 130x130xx35 mm from the ZyXEL OMNI 56K DUO EE modem (Fig. 4), the location of the modules in it is shown in Fig. 5. Modules A1, A2 are glued to its lower wall with Quintol polymer glue. The A2 module is enclosed in a tinned sheet box shield. Its inner surface is coated with XB-784 varnish (available at building materials stores), after which it is pasted over with electrical cardboard impregnated with zaponlak (XB-784 is also used as glue). The screen is connected by a short wire to the negative terminal of the capacitor C10 of the amplifier. When arranging the device in another case, it is desirable to place the A2 module as far as possible from the input stages of the AF amplifier. Fixed resistors - any small-sized (MLT, S2-23, S2-33 or imported), variable R3 - any suitable size dual with a functional characteristic of B and a resistance of 4,7-100 kOhm (if you have a choice, preference should be given to a resistor with a lower resistance ). The author used a miniature sliding variable resistor from an imported car radio. It is fixed on the front panel of the device, its metal case is connected to a common wire, and the terminals are connected to the amplifier board with a five-core shielded wire about 80 mm long. Capacitors C3, C5, C8-C12 in the AF amplifier are oxide K50-68, K53-19 or their imported analogues, the rest are ceramic K10-17, K10-50 or SMD (for surface mounting). Capacitor C13 is installed near the power pins of the DA1 chip, and C7, C14 (and 2C7 in module A2) - between the pins of the corresponding oxide capacitors C3, C10, C5. Capacitors C1-C3 in module A1 are high-voltage ceramic capacitors with a nominal DC voltage of at least 1000 V or AC voltage of at least 250 V. Inductor L1 is wound on a 2000NM ferrite ring with an outer diameter of 12 mm and contains 15 turns of a mounting wire folded in half. Inductors L2, L3 - small-sized industrial production with H-shaped ferrite magnetic cores and windings with a resistance of not more than 1 Ohm. The L4 inductor contains five turns of a mounting wire folded in three on a ring with a diameter of 10 mm made of 2000NM ferrite. Diodes 1N4148 are replaceable by any of 1N914, 1SS244, KD510, KD521, KD522, instead of the zener diode 1N4738A, you can use BZV55C-8V2, TZMC-8V2. LED HL1 - any continuous glow. When replacing a failed Q1 transistor, it is recommended to use serviceable copies dismantled from burned-out CFLs (compact fluorescent lamps). I do not recommend using high-voltage transistors of the MJE13001, MJE13003 and any other types from the xxx1300x series available for sale in the retail network because of substandard and counterfeit transistors that are often found among them. Possible replacement for the TL3414A chip - TL3414AIP, TL3414AID, TL3414AIDR (used in headphone amplifiers built into outdated computer drives for reading / writing CDs). An error-free device starts working immediately and does not require adjustment. However, it should be taken into account that the applied switching power supply does not have overload protection, therefore it is advisable to check the performance of the AF amplifier from a laboratory power source with an output voltage of 7 ... 8 V. If stereo phones have a built-in volume control, it is set to the maximum volume position, and the level is regulated by a variable resistor R3. If volume control is provided in the signal source, a variable resistor R3 is set to the maximum volume position, and the level is adjusted built into the device. This approach in most cases avoids overloading the output stages of amplifiers and minimizes the level of interference and noise. Literature
Author: A. Butov
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ A88W 3D FM2+ Hi-Fi Motherboard for AMD Processors ▪ Budget DC-DC converters Mean Well SPA02 and SPB03
▪ section of the Electrician website. Article selection ▪ article Magnet in the well. Tips for the home master ▪ article Which birds helped the Japanese and Chinese in fishing? Detailed answer ▪ article Watchman (guard) in a bar. Job description ▪ article Checking finger elements. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: