
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Modernization of AC 35AC-012. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
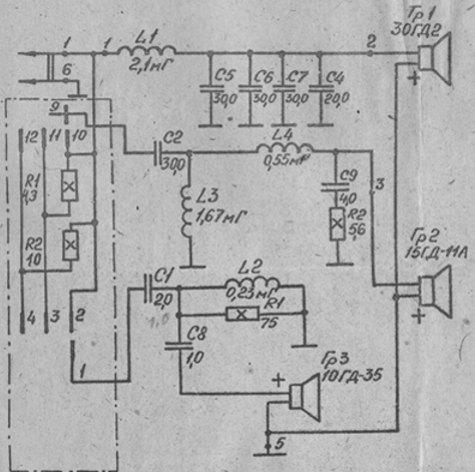
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Audio equipment The first domestic speaker system that meets the requirements for Hi-Fi equipment (the initial letters of the English words high fidelity - high quality, high fidelity of sound reproduction) was the S-90 35AC-012 speaker system: three-way, phase inverter type, 30GD-1 loudspeakers are used , 15GD-11, 10GD-35. Based on this model, acoustic systems 35AC-016 (with a phase inverter), 35AC-018 (with a phase inverter), 35AC-008 (closed), 35AC-015 (with a passive radiator) were created. All of them have similar parameters and differ in appearance [1]. Currently, this one, to some extent, has ceased to satisfy the needs of lovers of high-quality sound reproduction. Taking into account the fact that a fairly wide range of expensive modern acoustic equipment, but not always of high quality, is presented on the current market, we will consider options for refining a pair of S-90 35AC-012 acoustic systems, released in 1985 by the Riga Radio Plant. A. S. Popov, equipped with newer, at that time, developments of LF, MF heads - 30GD-2 and 15GD-11A. The circuit diagram and layout of the AC filter parts are shown in Figure 1.
Capacitors C1, C2, C4-7 used type MGBO-2, C9, C8 - K73-11. The filter elements are mounted on 12 mm plywood with dimensions of 210 x 160 mm. The inductors are installed in a horizontal position and, moreover, L1, L2 and L3, L4 are placed close to each other, respectively. The filter itself is fixed on the back wall inside the speaker cabinet behind the woofer. Chassis Carefully remove the protective grilles of the heads and the heads themselves, the filter and other elements that will restrict access to the inner surfaces of the housing walls. Carry out preventive maintenance. The joints of the walls and the seats under the woofer, midrange speakers are smeared from the inside with a silicone sealing mass. Seal with silicone (if necessary) the gaps between the rear, side, bottom and top walls on the outside of the case, having previously cleaned them of dust, dirt and glue. In order not to stain the veneer finish of the body with sealant, it is closed around the slots with paper construction tape. Excess sealant is removed. After it hardens, a shallow cut is made with a sharp knife under a metal ruler along the edges of the adhesive tape, at the points of its mating with the sealing compound. The tape is removed. The sealant is used to match the body color or transparent. Among many radio amateurs being finalized by the S-90, a common means of combating panel vibrations is to increase their rigidity by using additional "stiffening ribs" (slats), spacers, etc. They also additionally cover the inner walls with a sound absorber. Which is not always justified, since such measures lead to a decrease in the internal volume of the case, which, in turn, reduces and even eliminates the efficiency of the phase inverter. A simple increase in the rigidity of the walls by using additional "stiffening ribs" or thickening the panels only increases the resonant frequencies of the panels and changes the nature of the distribution of their vibrations and radiation, since the number of vibrating surfaces and their sizes change. The thickening of the panels, in addition, increases the weight and cost of decoration. Therefore, for the manufacture of decoration, it is more expedient to use materials that have increased internal losses of vibrational energy during their deformation (increased "internal friction"), as well as a sufficiently high elasticity. Such materials, called vibration damping or vibration absorbing materials, can be applied to conventional panels. Vibration-absorbing materials convert part of the oscillatory energy of vibrations into heat and increase the mechanical resistance of the panels, thereby reducing the amplitude of vibrations. Vibration damping is especially effective at resonant frequencies, when the amplitudes of vibrations and bending or shear deformations increase. The use of a vibration-absorbing coating on acoustic design panels leads to an increase in the overall rigidity of the panel, and therefore it seems possible to reduce the thickness of the panels by 1,5–2 times without fear of an increase in their vibrations [2]. Therefore, a self-adhesive vibroplast with a thickness of 1,5 - 2 mm is applied to the inner surfaces of the walls of the speakers being finalized (a flexible and elastic vibration-absorbing material, which is a polymeric self-adhesive composition duplicated with aluminum foil, Fig. 2, is used to reduce vibrations of car body parts).
For a perfectly tight fit to the surface of vibration-isolating materials, the walls of the housing must be prepared from the inside. Namely, sand with medium grit sandpaper and prime, for example, with nitro-lacquer or PVA glue. After that, the necessary blanks are marked and cut out from a piece of vibroplast (on some materials there is a special marking in the form of molded squares 1 x 1 cm, which allows you to do without a ruler and marker). Bend the corner of the protective film on the workpiece and apply it to the intended place. Attach the edge of the material to the surface and gradually, gently smoothing it, while removing the film, stick the entire piece. The material is finally rolled with a roller, achieving maximum fit. The sound-absorbing coating increases the sound absorption of low frequencies up to 500…1000 Hz. The degree of sound absorption should be proportional to the surface area of the coating. If you fix it on the walls of the case not close, but at a distance of 20 - 50 mm from them, then the sound absorption at frequencies below 500 Hz increases [2]. This condition is met by the manufacturer 35AC-012 - mats with cotton wool in sufficient quantities are located at some distance from the walls (approximately in the central part of the box). Therefore, additionally covering the walls with a sound absorber is not only useless, but also harmful. Rollers or cushions of sound-absorbing material suspended at the geometric center of the loudspeaker give the same results as placing it on the walls of the box.
The construction of the 35AC-012 phase inverter port has the shape of a curved tunnel of an unusual configuration in cross section. This is due to the goal of satisfying the following conditions: rigidity and the absence of resonant overtones in the material of the port. It consists of two glued plastic parts. The places of gluing look around. The cracks found during inspection are filled with dichloroethane. After that, at these points, both parts of the phase inverter port are tightened with clamps and dried - fig. 3. It will also be useful to paste over its walls with strips of vibroplast. After such processing, the plastic of the port becomes hard and deaf. It is recommended to install an Acoustic Impedance Panel (PAS) at the output of the bass reflex port. This technical solution, protected by USSR author's certificate No. 577699, makes it possible to reduce the acoustic quality factor of the loudspeaker head by several times. An acoustic system with such a PAS sounds more natural, without "mumbling" [3,4]. It is known that sound travels much better in solid materials than in air. When playing music, speaker vibrations are transmitted to the floor, and through it to other electronic components of the Hi-Fi system. In order to maintain the high stability and stability of the acoustic systems, not to lose the dynamics and accuracy of the sound stage, and at the same time to avoid the transmission of vibrations from the acoustic systems to the floor, the plastic legs of the speaker cabinet are replaced with rubber ones, truncated cone shape, base diameter 28 mm, height 15 mm. Of course, another option is possible - the use of spikes as supports for acoustic systems. Such a solution, according to the manufacturers of progressive audio equipment, breaks the parasitic mechanical connection of the sound reproducing equipment with the surface on which it is installed. This prevents the spread of unwanted vibrations and their influence on the process of sound reproduction. As a result, high-quality reproduction is provided. Disadvantages - the problem of scratches, which means that it becomes necessary to use patches for spikes, stone slabs, etc., which is not always convenient and justified. There are also one-piece supports (spikes with stands), but they also have an appropriate price. The weakest link The frequency response of the midrange driver 15A - 11A has a sharp drop above 4,5 kHz - fig. 4a, the acoustic quality factor is about 11,8. And the higher the quality factor of the oscillatory system, the stronger it emphasizes the frequencies coinciding with the resonant ones, or close to them. Which, in practice, excludes the possibility of obtaining a full-fledged undistorted sound when it is turned on through a midrange bandpass filter, if the necessary measures are not taken. To eliminate the first drawback, the following method is used.
Soak the dust cap of the head with nail polish remover, you can use solvents 646, 647 and others. Carefully remove it with a scalpel (Fig. 5, b). Remember that due to the strong action of the field of the magnetic system on a steel instrument, careless movements can damage the elements of the speaker! Then wipe with a cotton swab dipped in the same nail polish remover, the glue diffuser. Lubricate the lower part of the horn and the upper part of the voice coil with Moment glue. Dry for 10 - 15 minutes. Again, coat both parts and immediately connect them, pressing lightly (Fig. 5, e). The horns are installed both new and extracted, in the above way, from old speakers (Fig. 5, c).
The glued horn is designed for the 10GDSH-1 dynamic head. For our case, it should be adjusted. Fitting consists in cutting it, while measuring the frequency response of the speaker. To do this, place the speaker on the same axis as the microphone (preferably measuring), within 40 - 50 cm, in the room no closer than 1 meter from walls, furniture, etc. The microphone is connected to the appropriate port of the computer's video card, and the speaker to the amplifier computer speakers. Run the RightMark 6.2.3 program and measure the frequency response. Cut off the edge of the horn, about 1 cm. Measure the frequency response and compare it with the previous one. The operation is repeated until the most even frequency response is obtained in the middle frequencies, thereby increasing their range to 10 kHz (Fig. 6).
The second and subsequent cuttings should be carried out very carefully, cutting off no more than 3 mm. As a result, the side surface of the horn inside was about 7 mm (from the dust cap to the trim edge) - fig. 5, e. Trimming is performed with nail scissors, since they turned out to be the most acceptable tool for this type of work, they have miniature rounded cutting surfaces. The cut edge, to stiffen, is impregnated with BF-2 glue with slightly diluted ethyl alcohol. To eliminate the second disadvantage, acoustic damping of the head using PAS is used. Damping the heads with sound-absorbing material is less effective and, moreover, contributes to an increase in the resonant frequency. In order to increase the effectiveness of the PAS action on a moving system operating in the acoustic design of the head, the damping fabric should be placed as close as possible to the cone. It is most rational to arrange the PAS in the holes of the diffuser holder. To do this, eight identical elements are cut out of thick cardboard with a thickness of approximately 2 mm (Fig. 7, a). The total area of the holes for the head 15GD-11A should be 22 ... 28 cm2. One side of each element is smeared with glue moment. After 5 minutes, they are glued onto a cotton fabric stretched with the help of an embroidery hoop. After 30 minutes, the fabric is trimmed around the elements. The PAS elements are slightly bent and glued into the windows of the diffuser holder (Fig. 7. b). Gluing points are additionally smeared with glue [5, 6]. It is important that the fabric in the holes of the elements is stretched, otherwise there will be no effect from the use of PAS! The use of PAS, i.e. acoustic damper, allows you to slow down the natural oscillations of the diffuser, as a result, the "after-sound" time will be significantly reduced and the sound quality of the speaker will noticeably increase.
The damping effect of the PAS for the dynamic head 15 GD-11A is graphically shown in Figure 8.
The effectiveness of the use of PAS was tested by employees of the Berd Radio Plant. In particular, the harmonic coefficients of the mid-frequency driver 15GD-11A with and without PAS were measured. The measurement results shown in Table 1 show that PAS can significantly reduce the harmonic distortion in the frequency range in which the human ear is most sensitive [7]. Table 1. Harmonic coefficients of the head 15GD-11A
A rubber-fabric suspension, to restore elasticity, is impregnated with an aerosol "Air conditioner and tensioner for drive belts". After such a refinement, the frequency range of the head has significantly increased, up to 10 kHz (!), The linearity of the frequency response of sound pressure has improved and, most importantly, the sound quality of the speaker system as a whole. Crossover filters In passive crossover filters, their design plays an important role, as well as the choice of specific elements - capacitors, inductors, resistors, in particular, the mutual placement of inductors has a great influence on the characteristics of speakers with filters; closely spaced coils. For this reason, it is recommended to place them mutually perpendicular, only such an arrangement allows minimizing their influence on each other. Inductors are one of the most important components of passive crossover filters [1]. It is not recommended to place the coils closer than 100 mm to each other. The simplest way to refine the filter 35AC - 012 (Fig. 1, b) is to reinstall the coils L1 and L3 perpendicular to the base and each other. For this arrangement, plastic corners are used, cutting out from cases of old equipment or boxes. Pay special attention to the base material on which the filter parts are placed. It must be dielectric! In some acoustic systems, 35AC-1, "S-90" 35AC-212, the predecessors of "S-90" 35AC-012, the filter parts are mounted on a steel plate, the magnetic properties of which negatively affect the inductors and, of course, sound quality. No less important elements of the crossover filter are capacitors. Their objective characteristics depend on the design and material of the body, plates, type of dielectric, and quality of manufacture. An important feature of an audiophile capacitor is the use of the "correct" dielectric. The most suitable is polypropylene - an almost ideal material with high stability, low dielectric losses and absorption. Another audiophile dielectric is oil-impregnated paper. Oil-paper capacitors in terms of the loss tangent, and especially in dielectric absorption, noticeably lose to all types of film capacitors. The first of them are appropriate in the low-pass filter circuit for low-frequency heads, and the film ones are in the high-pass filter circuits of crossovers for midrange and high-frequency heads. Polyethylene terephthalate capacitors K73-16, which showed excellent results, both in objective measurements and in subjective examination, are recommended as an inexpensive alternative to specialized audio capacitors [8]. You should not look for capacitors with a calculated capacitance value. It is advisable to use the parallel connection of capacitors of a smaller rating. This approach makes it possible not only to use products that are not in short supply, but also to significantly reduce the parasitic parameters of the equivalent capacitance, significantly expanding the range of suitable types of capacitors. Wirewound resistors PEV-10 used in the filter have parasitic inductance. If you fix them to the base with screws, then the inductance will increase. This is explained by the fact that the material of the screw (steel) serves as the core of the so-called inductor in the form of a resistor. Thus, the PEV-10 resistors are replaced with non-inductive ones or they are fixed with glue, plastic or wooden wedges, etc. The 10GD-35 high-frequency head is shunted with a notch filter tuned to its main resonance frequency of 3 kHz. It is a high quality series LC circuit. The capacitance of the circuit capacitors is 6,6 μF (MBGO and MBM with a tolerance of ± 10% from the nominal value), the coil inductance is 0.43 mH, its winding contains 150 turns of PEV-1 wire 0,8 mm, wound on a frame with a diameter of 22 and a length 22 mm with a cheek diameter of 44 mm [9]. The use, for these purposes, of the filter elements of the acoustic system 10AC - 401 will significantly reduce the costs and labor intensity of the work. The product of the capacitance of the capacitor in microfarads and the inductance of the inductor in mH should be equal to 2,82 (radiolamp.ru/acoustics/3/). If 2,82: 6,6 = 0.43 mH, then for a circuit with an inductance of 0,5 mH, it is easy to calculate the capacitance of the capacitor: 2,82: 0,5 = 5,6 μF. Just need to pick up the capacitors to the required capacity - 5,6 microfarads. Another refinement option is unwinding from an inductor of 0,5 mH, extra turns to the required 0,43 mH. It is convenient to use the RLC - meter. In place of the filter resistor of the acoustic system 10AC - 401 (previously removed as unnecessary), a 2 μF capacitor is reinstalled, and a 4 μF capacitor of the same type, MGBO, is attached in its place. MBM capacitors are soldered to the terminals of the capacitors to set the capacitance of the required value of 6,6 μF (Fig. 9). As a result of the described refinement, overtones, rattling and characteristic "hissing" of the 10GD-35 head are eliminated.
Guides The cable connecting the loudspeaker and the amplifier makes a certain contribution to the sound of the system. Mainly due to the fact that the cable has a certain resistance. The influence of this resistance not only affects the sensitivity of the speakers, but also affects the power distribution between the radiators in the column. To eliminate this effect as much as possible, the cross-sectional area of the wire should be as large as possible, and the length should be as small as possible. In addition, it is necessary that the length and cross section of the wire be the same for all speakers. It is also impossible to exclude the fact that the conductor has a certain inductance, and two closely spaced conductors form a capacitance. In this regard, the twin wire can be considered as an LC low-pass filter. That is, the longer the wire, the stronger the high frequencies will be damped. In practice, the influence of the wire inductance appears only when the cable length is over 50 m [10]. Also, when a current of low-frequency sound signals of a high level flows through an acoustic wire, a strong magnetic field is formed around the cable conductors. This field affects the medium and high frequency audio signal currents flowing through these conductors, as a result of which the sound of the speaker system becomes less clear and transparent. The solution to these problems is to ensure the flow of currents of the low-frequency components of the signal and the currents of its mid-, high-frequency parts along physically separated conductors. To do this, an additional pair of sockets (screw clamps) is installed in the acoustic system, to which the input of the filters of the midrange and high-frequency loudspeakers is connected. Thus, the input of the woofer filter is connected to a separate pair of input terminals [11]. Such a connection is called "bi-wiring" (bi-wiring), i.e. in two pairs of wires to one speaker. The use of two- and three-pair communication cables with a load allows you to significantly reduce the total cross section of the conductors without increasing the mutual influence of the loudspeakers. Such acoustics with a double set of terminals can also be connected to separate amplifiers, which will already be called "bi-amping" (bi-amping), i.e. two amplifiers per channel. In the latter case, they also get rid of the electrical interaction of the emitter sections. As screw terminals, instrument threaded terminals are used. The material of the stud is brass, the thread is M6 x 0,5, the lamb is covered with ABC plastic. The most important criterion for choosing a conductor for an AU is its electrical power. The electrical power P supplied to the loudspeaker is understood as the power dissipated by a resistance equal in value to the nominal electrical resistance Rн, at a voltage equal to U at the loudspeaker terminals: P = U2/Rн. In the practice of designing domestic speakers, two types of power were usually used - nominal (electrical power, limited by the occurrence of distortions exceeding a given value) and nameplate (the highest electrical power at which the loudspeaker can work satisfactorily for a long time on a real sound signal without thermal and mechanical damage, usually 1,5 ... 2 times higher than the rated power). According to the technical documentation "S-90" 35AC-012, the rated power PMr.. = 35 W, nameplate RPassp. = 90 W. The manufacturer of these types of dynamic heads allows their operation with a voltage not higher than 11 volts. In this case, the current I flowing in the voice coil of the woofer will be 2,8 A, and in the voice coil of the midrange loudspeaker - 1,4 A. To calculate the conductor cross section, it is necessary to proceed from the specified current values. Note. The calculation is made in a simplified form, provided that there is only active resistance in the circuit, at which the cosine of the phase shift angle of the current and voltage φ is equal to zero. In a real loudspeaker electrical circuit, there are always inductive and capacitive resistances, called reactive, which introduce temporary changes in current and voltage values. Musical works are variable in nature, both in terms of signal level and frequency, so a current of 2,8 A can theoretically take place, but not constantly and in very short time sections of the musical path, for example, when a bass drum is "thumping". Internal installation "S-90" 35AC - 012 is made of tinned copper stranded wire in PVC insulation with a cross section of 1 mm2, which corresponds to the calculated data, since the current density in the copper conductor becomes 6 - 10 amperes per square millimeter. Note that the voice coils of the loudspeakers are wound with wire of a much smaller cross section: 30GD-1 - 0,1 mm2, 15GD-11A - 0,02 mm2, 10GD-35 - 0,005 mm2. The total cross section of the wires of all coils is 0,125 mm2, eight times thinner than an internal speaker wire! In the power circuits of power amplifiers of the "S-90" era, with a nominal power of 25 to 50 W per channel, fuses (fuses) for a current of 2 to 3 A were provided, and this, first of all, to power the circuit and then the load. The real sound signal is impulsive. On a signal with steep fronts, even at frequencies in the audio range, the skin effect (from the English skin - outer layer, sheath) is largely manifested - the effect of current displacement to the surface of the conductor, which leads to an increase in the effective resistance of the connecting cables. [12]. Low-frequency signals propagate almost throughout the entire volume of the conductor, and the propagation of high-frequency signals occurs mainly in a thin near-surface layer. This skin effect dramatically increases the resistance of the conductor and slightly reduces its inductance. Figure 10 shows the frequency dependence of the impedance of copper conductors of various diameters 1 m long. At f < 1 kHz, the impedance is determined by active resistance, and at f > 100 kHz, inductance plays a dominant role [14]. A copper wire with a diameter of 0,16 mm up to a frequency of 20 kHz does not change its resistance, but has a relatively large value, almost 1 ohm. Significantly reduce the resistance of the conductor and leave it unchanged in the entire audio frequency band will allow the use of several core insulations with a diameter of not more than 0,16 mm. A bundle of enameled wires intertwined in a special way (from German Litzen - strands and Draht - wire) is called a litz wire.
Thus, speaker cables should not only have a minimum resistance and inductance, but also have a minimum skin effect. Connecting loudspeakers, especially MF - HF, is best done with a litz wire or copper wire coated with a thin layer of silver [12]. Silver has the highest conductivity among all metals, and its thin layer, in which, due to the skin effect, most of the current flows, has a strong influence on the active resistance of the conductor. When choosing a mounting wire, it is also necessary to take into account the principle of connecting acoustics through 2 pairs of contacts, which, of course, proportionally distributes power between the LF and MF - HF channels. With equal sensitivity of the heads, the maximum noise (passport) power at the crossover frequency, in our case, is 500 Hz for the LF channel - 56% of the total power, and for the MF-HF - 44%. Between the midrange and tweeters, the power at a cutoff frequency of 5000 Hz is distributed by 41,5% and 2,5%, respectively. Such a division of power cannot be considered unconditional, but gross errors in the calculations can be avoided. Speaker heads differ both in sensitivity and in nominal electrical resistance (Table 2). The difference in each of these parameters leads to the need for an appropriate choice of the voltage supplied to the head in order to obtain a uniform frequency response with respect to pressure [15]. And the voltage supplied to the head is one of the dominant indicators that affect the power. Table 2. Main parameters of the heads used in acoustic systems "S - 90" 35AC - 012
Note. Information about the parameters is taken from many sources, not always exhaustive, and sometimes contradictory (indicated in brackets). It should be noted that, in home acoustic design, the influence of conductors on sound quality is negligible compared to other factors. It is necessary to pay attention to more important elements, the acoustic properties of the room, the correct placement of equipment. Information about the exclusivity of oxygen-free copper cables, from wires with the "orientation" of the surface layer of the conductor, which affects the passage of the sound signal in one direction or another, is nothing more than advertising. The electrical part of the modified system The circuit diagram is shown in Figure 11,a. The filter uses capacitors with a maximum operating voltage of 160 V: K73-11 (C1, C10, C11); K73-16 (C2-4); MBGO-2 (C5 - 9); MGBO-2 and MBM (S13) connected in parallel. Installation is carried out with a single-core copper wire with a cross section of 1 mm2 (extracted from a communication cable with air insulation of each core) and MGShV wire (flexible multi-wire, conductive cores made of tinned copper wire, wrapped with electrical insulating silk with PVC insulation, for intra- and inter-unit mounting of various radio-electronic equipment and devices for a rated voltage of up to 1000 V AC frequency current up to 10 Hz), cross sections 000 mm2(for a low-frequency link) and 0,5 mm2 (only in the filter MF - HF link). The connection between the terminals, the divider, the filter and the RF head is carried out with a wire LEPSHD 500 x 0,05 (round wire 0,98 mm2 with a stranded strand of 500 copper wires 0,05 mm in diameter, insulated with a polyurethane-based varnish, with a two-layer winding of natural silk, recommended for a frequency range of 250 ... 500 kHz, with electrical resistivity, at 20˚C, 0,0158 ... 0,018 Ohm/m). The playback level control can be omitted.
All elements are placed on the plywood of the native filter "S - 90" 35 AC - 012, (Fig. 11, b). Particular attention should be paid to the relative position of the inductors. Details must be rigidly fastened. Connections are made with as short wires as possible, avoiding sagging. Filter elements must not touch. If necessary, for tight mounting, use sealant, ties, insulating tape, etc. Otherwise, as a result of vibrations of the case and air vibrations inside the speaker, the filter parts will rattle and emit unpleasant overtones. The filter is attached to the bottom wall inside the case, thereby minimizing the effect on the inductors of the magnetic field of the woofer. Installing the speakers Before installation, first of all, the woofer and tweeter heads (the midrange head has already been brought back to normal) are inspected for the integrity of the structures, especially in the places of gluing, the absence of mechanical damage to parts, the integrity of the suspensions of the woofer. It can be rubber or polyurethane (35AC - 018). The suspension, made of not very high quality rubber, hardens over time. Polyurethane is destroyed by impurities of sulfur contained in the air. The problem of suspensions is eliminated by replacing them. An alternative solution for an undamaged rubber suspension could be to impregnate it with conditioner and a drive belt tensioner. Replacing suspensions is a very time-consuming job that requires some knowledge and skills. Places of peeling of the centering washer or suspension from the diffuser holder are smeared with glue with the simple name 88, after which the glued surfaces are pressed. It is also necessary to make sure that the voice coil does not touch the elements of the magnetic system. Restoration of the appearance of the diffuser is carried out by simply painting it with a black marker filled with alcohol ink (it says: "alkohol" on it). Some "finishers" use printer ink. This is not the right solution, since it has the properties of quick burnout and rinsing with ordinary water. At the tweeter, the acoustic lens is removed to release the domed cone with the voice coil. Carefully remove it and make sure the integrity of the voice coil. Very often, its turns are separated from the frame during operation. If the specified defect is found, the diffuser with the voice coil is replaced with a new one. For prevention, the voice coil is coated with BF-2 glue, slightly diluted with ethyl alcohol. It is advisable to test the heads with the measurement of the frequency response of sound pressure. Loudspeakers that cannot be repaired are replaced with new ones. Another effective way to reduce vibrations, and therefore unwanted overtones, is to "soft" mount the heads [2]. They are mounted on rubber gaskets. It is necessary that the fastening elements do not come into contact with the diffuser holder. To do this, select a tube of the required diameter, for example, PVC, with a snug fit to the walls of the speaker mounting holes, while ensuring the free entry of screws. If necessary, the holes are drilled to the desired size. Under the nets with decorative rims, rubber washers are also placed at the holes. It should be noted that the bass and midrange heads are mounted in recesses. Therefore, it is necessary to put rubber bands in four places around each speaker, for example, from a bicycle tube, to prevent the side parts of the diffuser holders from touching the case. Facing and decorative elements have a significant impact on the frequency response of speakers. A decorative material that covers the opening of the phase inverter, especially the passage, can have a significant impact due to high oscillatory air velocities. Grilles and shutters can sometimes cause resonant phenomena and additional peaks and dips will appear in the frequency response of the loudspeaker. The front part of the head 10GD-35, around the acoustic lens, is pasted over with felt or thick cloth. This will ensure both its soft fastening and minimization of diffraction, the manifestation of the effect of reverberation of sound waves, which, in turn, will weaken the resonant phenomena between the head and the grating. Acoustic system 35AC-1 has a removable decorative panel. In the technical documentation specified by the AU, it is recommended to remove the panel when listening to high-quality programs, when working at maximum permissible powers. Figure 12 shows the frequency response graphs of the sound pressure of loudspeakers 15GD-11A and 10GD-35 in an open version (white curve) and closed with decorative nets (green curve), provided for by the design of the S-90 35AC-012 speaker system. No special differences are observed. Conclusion: in this device, there is no special need to remove protective decorative nets, since their presence does not affect the frequency response of the heads in the operating frequency range. You should be guided by subjective assessments after listening to a real sound signal through a speaker system with and without decorative grids.
The described technique for finalizing the sound speakers "S - 90" 35 AC - 012 will be useful for reworking loudspeakers and other models, as well as making speaker systems with your own hands. Loudspeaker matching. Almost all modern high-quality acoustic systems (AS) are multi-band, i.e., consisting of several loudspeakers (most often three), each of which operates in its own frequency range. This is due to the fact that, for a number of reasons, it is impossible to create a loudspeaker (SH) with good characteristics in a wide frequency range. Separation filters are used to distribute the energy of the audio signal between the loudspeakers. However, they have a significant impact on such characteristics of a multiband acoustic system as amplitude-frequency (AFC), phase-frequency (PFC), group delay (GD), directivity characteristics, distribution of the input signal power between the radiators, the input impedance of the speaker, the level of nonlinear distortion [ 1] . It is not easy to create a crossover filter, which is subject to the requirements of low non-uniformity of the total frequency response, linearity of the PFC in the passband and high steepness of the slopes of the frequency response of the links. The first of these requirements is due to the sharp deterioration in the characteristics of dynamic heads at the edges of their nominal frequency ranges. This is especially true for mid- and high-frequency heads, in which the overlap of the nominal ranges of reproducible frequencies is, as a rule, relatively large. That is why crossover filters for these heads must have a frequency response with steep slopes: with an octave (relative to the frequencies of the separation of adjacent bands) margin over the nominal range of reproducible frequencies, it is preferable to use filters with a frequency response slope of at least 12 dB per octave. The simplest filter with a slope of 6 dB per octave can only be used if the frequency margin is less than two octaves [16]. The specified condition in the MF, HF sections of the filter of the acoustic system 35AC-012 (S-90) was observed by the developer. The 10GD-35 high-frequency head is connected through a third-order filter (C1, L2, C8, in the diagram of Fig. 1, a of the first part of the article) and provides an attenuation of 18 dB / oct. The 15GD-11A midrange bandpass filter consists of two sections - a second-order high-pass filter (C2, L3) to suppress low-frequency frequencies with an attenuation of 12 dB / oct., and a first-order low-pass filter (L4) to suppress upper range frequencies. The first order filter consists of a single reactive element and provides an attenuation of 6 dB/oct. Such a filter satisfies the requirements when working with a conventional 15GD-11A speaker, which has a natural decay in the frequency response of sound pressure from 4,5 kHz (Fig. 4). If the head has a wider frequency band, then it is necessary to take measures either to increase the cutoff frequency or to change the order of the filter. It is known that the use of an additional cone, which is inserted into the diffuser, increases the upper limit of the frequency range of the speaker to 10-12 kHz. In this case, at high frequencies, the main cone ceases to work due to its relatively flexible connection with the voice coil, and a small cone, rather rigid and light, is put into operation [17]. Therefore, the mid-frequency dynamic head 15GD-11A (20GDS-1-8) with an additional sound-emitting horn has better characteristics compared to the usual one. Namely, the upper limit of the reproducible frequencies is 10 kHz instead of 4,5 kHz (Fig. 6). Thus, the zone of its joint action with the high-frequency emitter 10GD-35 also increases, which can lead to peaks and dips in the frequency response of the loudspeaker due to different phase characteristics of the GG and somewhat worse perception of the scene. The reason for this lies in the design of the 35AC-012 (S90) speaker system filter, which is not intended for a midrange speaker operating in the range up to 10 kHz. To increase the cutoff frequency between MF and HF emitters up to 10 kHz, changes are made in the filter following the example of M. Zhagirnovsky and V. Shorov [18]. To do this, in the crossover according to the scheme in Fig. 1, a, solder the leads of the L4 coil (0,55 mH) and remove it, and install the L2 coil (0,23 mH) in the vacated place, which is included in the filter instead of L4 (this increases the upper limit of the operating frequency band of the midrange head). Then 4 turns are unwound from the L115 coil (the new inductance is 0,1 mH) and installed on the board, connected instead of the L2 coil. Capacitor C1 (2,0 uF) is replaced by a 1 uF capacitor, and C8 (1 uF) by 0,5 uF. Thus, by moving the frequency of the high-frequency filter section from the frequency of the main resonance of the high-frequency head 10GD-35, the quality of its sound is improved. The notch filter (L5, C12 in the diagram of Fig. 11, a) is not used in this case. However, the modified speaker in the above manner, with a good frequency response, also has a very significant drawback - a noticeably degraded directivity characteristic due to an increase in the crossover frequency to 10 kHz [19]. The directivity characteristic, along with the frequency response of the sound pressure, is the most informative in terms of assessing the sound quality of the speakers. At a certain frequency, the length of the sound wave becomes commensurate with the size of the diffuser and even less than it. In practice, this manifests itself as a narrowing of the dynamic head's radiation pattern with increasing frequency. That is, the higher the frequency, the closer to the axis of the head the listener must be in order to hear high frequencies. So for a diffuser with a diameter of 125 cm, the theoretical maximum frequency at which the acoustic radiation pattern is compressed to a narrow beam is 3316 Hz. Usually, at medium frequencies, acoustic system designers try not to force the heads to work above these frequencies and do not accept separation frequencies between midrange and high-frequency emitters above 6...8 kHz [15,20]. The manufacturer of the heads, the Krasny Luch plant, recommended turning on 15GD-11B through a separating filter with a 3rd order low-frequency link - fig. 13. A similar scheme was used for the 20GDS-1L-8 head in the 35AC-001 Cleaver acoustic system.
To change the order of the LF link of the 35AS-012 bandpass filter from the 1st to the 3rd circuit (Fig. 11, a), they are supplemented with a capacitor C'1 with a nominal value of 10 μF and an inductor L'1 - 0,22 mH, as shown in the diagram rice. 14 (changes in the scheme are indicated in red). Thus, the 10GD-35 and 15GD-11A speakers separate the 3rd order high-pass filter into C1, L2, C10 and the 3rd order low-pass filter into L4, C'1, L'1. At the cutoff frequency, the 3rd order low-pass filter is 135˚ lagging and the high-pass filter is 135˚ ahead. As a result, at the crossover frequency, when added in phase and antiphase, the signals are summed with a shift of 90˚. The total frequency response is flat. Adding in phase is preferable because it gives less phase distortion. The slopes of the third-order frequency response have a steepness of 18 dB per octave. With an increase in the steepness of the slopes, the region of joint radiation is reduced and the effect of delays on the total frequency response is weakened [21]. Therefore, the 10GD-35 head is switched on in phase with the 15GD-11A head. The inductor L'1 has 115 turns, wound with a copper winding wire 0,8 mm thick (according to the varnish), on a plastic frame with an inner diameter of 27 mm and a width of 15 mm. It is not recommended to use wire of a smaller diameter, because, in this case, the coil resistance will be more than 5% of the head resistance, which is not desirable. Larger wire is more difficult to wind. For the coil, you can use a frame with other dimensions, optimal, based on the ratio of the coil inductance to its resistance. You can calculate the inductor online [22]. The capacitor is used with a maximum operating voltage of 160 V or more of any of the types K73-11, K73-16, MBGO-2, MBM or other non-polar or several connected in parallel, recommended for audio circuits.
Unlike a woofer, which has a fundamental resonance frequency within its reproducible frequency range, the resonant frequencies of midrange and tweeters, as a rule, lie below the reproducible range, and the lower the better. When removing the frequency response of the loudspeaker by sound pressure (i.e., with a smooth change in the frequency of the signal and its constant level), the resonant properties of the midrange and high-frequency heads do not appear in any way. The real sound signal is impulsive with a wide dynamic range. Therefore, with a sharp decrease in the signal, conditions arise for the continuation of oscillations at the mechanical resonance frequency. Thus, the resonant properties of midrange and tweeters can significantly affect the quality of sound reproduction. Transient distortions, especially noticeable by ear at medium frequencies, are due to the high quality factor of the moving head system at the frequency of the main resonance. They give the sound a metallic tint, deprive it of transparency [23]. The quality factor of the midrange head is quite simply reduced by using an acoustic impedance panel [6], which cannot be applied to the tweeter. To the latter, to attenuate the resonance, a notch filter (L5, C12) [10] is used, the elements of which, in contrast to the PAS, affect the PFC - fig. 15. The use of a 3rd order low-pass filter head in a midrange band pass filter will also make it possible to weaken this negative effect of the rejecting element on the total phase response and frequency response.
At the rejection frequency, the reactances of the coil and the capacitor are equal in value, but opposite in sign, the total resistance vanishes. This factor creates an additional load on the amplifying device, despite the fact that the filter introduces some signal attenuation in this area. If the amplifier does not have sufficient power and overload protection is triggered when operating at extreme levels, it is necessary in series with the circuit, to break the wire at point A in the diagram in Fig. 14, turn on a resistor with a nominal value of 5 ... 10 ohms and a power of 5 ... 10 watts. Series RLC offices are called GG resonant peak canceller. At the frequency of the main resonance, the amplitude of the diffuser oscillation reaches its maximum, while the head resistance is many times higher than the nominal value, and the load on the head increases. The use of compensation (Fig. 16) is a means not only to reduce distortion, but also to protect the GG from overloads [21].
The described filter makes it possible to use in the speakers another mid-frequency or broadband head that is suitable in terms of power, sensitivity and installation dimensions. It is only necessary to choose an RC chain (R2, C11). And when using heads with greater sensitivity, it is also necessary to include an attenuator in the circuit. For subjective examination of the orders of the low-frequency link of the band-pass filter, the circuit is supplemented with two toggle switches. One to switch the filter order, the other to turn off the notch. During the playback of musical programs, the toggle switches alternately switch and stop at the most correct sound of the instruments. Comparative listening to speakers with a low-frequency link of different orders of the band-pass filter showed that the third order is preferable. There are almost no noticeable differences in sound. However, in the section band, the sound with the 1st order filter is a little more pronounced, the midrange and treble emitters seem to be "approaching". This is due to the fact that such a filter has a low slope slope and the midrange head has the ability to work on the high-frequency component. The signal emitting GH in phase is added and amplified, and weakened in antiphase. The influence of the notch filter on the sound quality in the direction of deterioration is not heard. The opinion of radio amateurs that the notch filter introduces distortion, which manifests itself in a decrease in sound pressure in the lower part of the HF range, is a delusion. Exterior design of speakers. The electrical circuit of the upgraded speaker has a "bi-wiring" connection, that is, through two pairs of wires to one speaker. To implement such a solution without violating the authenticity of the design is simple. You should find terminal blocks from old similar systems and mount them, as shown in Figure 17. Passport data given on additional terminal blocks, in order to avoid confusion, must be sealed with a self-adhesive film of the appropriate color or painted over. When selecting threaded instrument terminals, special attention must be paid to the material from which the carrier is made. Products made of steel or, even worse, silumin, widely represented on the market by manufacturers in Asian countries, are unsuitable for use. The most common terminals in instrumentation are made of chrome-plated brass. Well, as the best option - silver and gold-plated.
When connecting via screw terminals, it is also necessary to pay attention to the materials of the contact pairs. Simply joining conductors of different materials can in itself cause galvanic corrosion. The oxide layer formed as a result of corrosion creates additional resistance, unstable contact, which generates unpleasant overtones in the speakers, etc. This is how the difference in the electrode potentials of materials manifests itself. Each current conductor has a certain electrochemical potential. In the presence of atmospheric moisture, when water gets between the metals, a closed galvanic cell is formed, current begins to flow, and just as one of the electrodes is destroyed in the galvanic bath, one of the metals is destroyed in the connection. The electrochemical potential of each conductive material is known (Table 3), and knowing the value, you can accurately determine which materials can be connected to each other. For example, copper and aluminum are connected either by soldering or by bolting, through washers made of carbon steel, duralumin or stainless steel, etc. [24]. Analyzing table 3, it should be concluded that for chrome-plated terminals, the most suitable pair for connection should be either chrome-plated or lead-tin. Table 3. Electrochemical potentials (mV) occurring between connected wires, terminals, etc. (conductors)
Acoustic system 35AC-012 (S-90) has a weight of about 30 kg. In the process of refinement, she acquired, albeit small, but an addition to the indicated weight. Therefore, for ease of use, it is advisable to insert a pocket handle into each side wall (Fig. 18, a), having overall dimensions of 135 x 88 x 76 mm and a seat of 102 x 59 mm. Holes for handles are cut out at a distance of 360 mm from the lower outer edge of the case and 70 mm from the front so that the inner parts of the handles do not touch the midrange head box and the phase inverter port. The shape of the hole should repeat the shape of the handle so that the handle fits as close as possible to the surface of the hole, but without stretching. To cut a hole, it is recommended to use an electric jigsaw with a variable angle of the cutting part. Cutting should be carried out slightly smaller than the required size. Then the holes are adjusted with a rasp, file and (or) sandpaper to the desired size. Before installing the handles and terminal blocks on the walls outside, around the holes made, a sealing non-hardening mastic is applied (sticky viscous mass is used in construction when installing elements of greenhouses, air conditioners, etc.). From the inside of the case, the gaps between the handles and the walls are sealed with plasticine. The handle, inside the case, is pasted over with vibroplast (Fig. 2).
An alternative to the dynamics 15GD-11A. It is known that the weakest link in the 35AS-012 speaker system is the dynamic head 15GD-11A (20GDS-1-8). The results of many years of practice in refining this head in order to improve its sound quality, unfortunately, do not satisfy all lovers of good sound. Many refer to the opinion that the 15GD-11A speakers need to be replaced with heads similar in size and mounting dimensions [25], for example, 4GDSH-1 (4GD-8E), 5GDSH-5-4 (4GD-53), 6GDSH-5 -4, 30GDS-1-8 - fig. 19. However, it is impossible to simply replace the GG with another one, due to the fact that in the acoustic system all the heads, woofer, midrange, treble, are coordinated with each other based on their individual parameters.
It is believed that the amplitude-frequency characteristic of the GG is one of the main indicators for evaluating sound quality. Heads 4GDSH-1, 5GDSH-5-4, 6GDSH-5-4/8 noticeably outperform 15GD-11A in this parameter. The second factor affecting the sound quality is the acoustic quality factor of the head. For 15GD-11A, this indicator is several times higher than for 4GDSH-1, 5GDSH-5-4, 6GDSH-5-4, and the higher the quality factor of the moving system, the higher the distortion in the main resonance frequency region, which negatively affects the sound quality . The main characteristics of diffuser dynamic loudspeakers are shown in table 4. Table 4. Main characteristics of cone dynamic loudspeakers
The main disadvantage of 4GDSH-1, 5GDSH-5-4, 6GDSH-5-4 is relatively low power. But the coefficient of performance (COP) of these heads is much higher than that of 15GD-11A. The efficiency of a dynamic cone loudspeaker is the ratio of the radiated acoustic power to the electrical power supplied. The efficiency of a loudspeaker directly depends on the standard sound pressure or characteristic sensitivity, which are uniquely related to each other and the acoustic power. In other words, in order to create sound pressure of the same level, much less power should be applied to the heads 4GDSH-1, 5GDSH-5-4, 6GDSH-5-4/8 than to 15GD-11A. A change in the energy parameter, input power, twice corresponds to a change in level by 3 dB, four times - by 6 dB. The 75GDN-1-4 low-frequency head has a maximum noise power of 75 W, a characteristic sensitivity level of 85 dB / m (minus 1 dB for filter losses) and a nominal impedance of 4 ohms. The 6GDSh-5-8 mid-frequency driver has a maximum noise power of 6 W, a characteristic sensitivity level of 92 dB/m, and a nominal impedance of 8 ohms. The difference in sensitivity in relation to the woofer is 7 dB - 2,24 times in sound pressure and 5 times (2,342 = 5) in terms of power. Thus, the maximum noise power of the midrange driver, reduced to the sensitivity of the woofer, is 6 W x 5 = 30 W. When operating in the frequency band from 500 Hz to 5000 Hz, the midrange head accounts for only 41,5% of the power, i.e. - 31 W, which almost meets the requirements. If we also take into account the difference in the nominal resistances of GG, 8 Ohm and 4 Ohm, then when these heads are connected to a common source, the sound pressure must be reduced by √. \u1,41d 3 times, i.e., by 89 dB, and take it equal to 85 - 4 \u1d 2 dB. To equalize the sensitivity of the mid-frequency head with respect to the low-frequency circuit, a divider is added (R''20 and R15'' in the diagram in Fig. 2) [11]. It is also necessary to correct the compensator (R6, C5) for changing the electrical resistance modulus when turned on through the separation filter of the 8GDSh-11-8 loudspeaker head. For this, Capacitor C30 is set to 1 uF. According to the same scheme, the 8GDS-15-11 head is also connected, as the most suitable replacement for the 11GD-2A speaker, while putting the capacitor CXNUMX with a nominal value of XNUMX uF.
When installing a speaker 5GDSh-5-4 (6GDSh-5-4) with a nominal resistance of 4 ohms, the circuit is supplemented with just one element - a resistor R''1 with a nominal value of 4,3 ohms with a power of 7 ... 10 W - fig. 21. This will provide both the necessary equalization in terms of the sound pressure of the radiators, and in terms of impedance. Let me remind you that the band pass filter of the 35AC-012 (S - 90) speaker system is designed to connect a midrange head with a nominal impedance of 8 ohms.
It is even easier to implement the connection of the 4GDSh-1 head (by excluding elements L'1 and C'2 from the circuit). The formation of a frequency response decay of 12 dB per octave occurs as a result of the interaction of the transfer characteristic of a first-order filter with a slope of 6 dB per octave (L4) and the natural decay in the frequency response of the 4GDSh-1 head, fig. 22 near the interface [1]. Therefore, it is not necessary to apply a 3rd order low-pass filter in a bandpass filter. The 1st order filter on L4 is enough to provide the necessary attenuation. The HF head 10Gd-35, in this case, is turned on in antiphase to the midrange - fig. 23.
The minimum allowable power PR dissipated by the resistor R''1 is calculated by the formula: PR = Pd(R/Rd), where, Pd is the nameplate power of the speaker; R is the resistance of the resistor R''1; Rd - nominal resistance of the speaker. The real power of the resistor is selected 1,5 ... 2 times more than the calculated one. When mounting resistors, one should not hinder the removal of heat from them [26]. In the development of passive separation filters, their design plays an important role, as well as the choice of the type of specific elements - inductors, capacitors, resistors. In particular, the mutual placement of inductors has a great influence on the characteristics of speakers with filters. If the location is unsuccessful, due to the mutual connection, signal interference between closely spaced coils is possible. Coil connections. Inductors are one of the most important components of passive crossover filters. Currently, many foreign firms use inductors on cores made of magnetic materials, which provide a large dynamic range, low level of non-linear distortion and small dimensions. However, the design of coils with magnetic cores is associated with the use of special materials, so many developers use air-core coils, the main disadvantages of which are large dimensions with low losses (especially in the low-frequency channel filter), as well as high copper consumption; advantages - negligible non-linear distortions [1]. The configuration of a cylindrical coil with an air core is shown in fig. 1.
An alternating magnetic field is formed around a coil through which an alternating electric current flows. If another coil is installed next to such a coil, then part of the magnetic field lines of the first coil will fall on the turns of the second coil, crossing them. The closer the coils are to each other, the more intersections of the lines of force with the turns of the coil. As a result, an electromotive force (EMF) is induced on the second coil, that is, an alternating voltage appears at the terminals of the second coil. The connection of closely spaced coils can be traced with the help of available improvised devices - an audio frequency generator and a multimeter, using the circuit in fig. 2. One of the coils (L1) is connected to the generator, the other (L2) to the multimeter, switched on in the voltmeter mode. A personal computer with an appropriate program and a bass amplifier are used as a generator. Coil L1 to the amplifier should be connected through a resistor R1. The total resistance of the resistor and the inductor must match the output impedance of the amplifier. The generator supplies a signal of the desired frequency and amplitude to the L1 coil (measured with a voltmeter at points A, B in the diagram). The EMF induced on the L2 coil shows the multimeter. The value of the readings varies depending on the distance of the coils and their relative position. If you connect a speaker instead of a multimeter, then the induction EMF of the L2 coil can also be heard.
The test results for various mutual positions of the L1 1,8 mH inductors connected to the generator and the L2 0,43 mH coils connected to the multimeter are shown in Table 1. Table 1. Dependence of the EMF value of induction on the relative position of the coils
As can be seen from the table, the most correct mutual arrangement of the coils is position 4 - orthogonally cylindrical (side) surfaces. A slightly worse result was shown by the placement of coils in position 3 - mutually perpendicular. In position 2, coils should be placed no closer than 100 mm, and in position 1 - more than 100 mm. It should be noted that in position 3 the measurements were carried out at the position of the geometric center O of coil I on the axis of symmetry of coil II. When the center is shifted from the axis, the EMF increases significantly and reaches its maximum when the projection of the center of coil I is on the line of the average diameter D (Fig. 1) of coil II. In other cases, an increase in EMF as a result of mixing coils is not traced, but on the contrary, it decreases. The magnitude of the induced emf depends on the number of lines of force traversed by the turns of the coil. Based on the data obtained, the design of the board of the future filter for the acoustic system begins with the choice of the relative position of the inductors. If there are two coils in the filter, everything is simple, they are placed in position 4. But if there are more, 5, 6 coils, it is necessary to approach them comprehensively. Correctly select not only the mutual position of the coils, but the distance between them. Payments. The implementation of the filter circuit of the upgraded acoustic system 35AC-012 "S-90", shown in fig. 14 in the second part of the article, turned out to be very difficult on a native plywood board due to lack of space for new components. Therefore, a new larger board is made on foil fiberglass. This will allow you to place inductors with minimal mutual influence, streamline the installation of other components, get rid of a large number of connecting wires and jumpers, which, in turn, will facilitate the connection, maintenance and repair of the filter in the future. The most suitable place in the speaker cabinet for the filter base is the inner bottom plane. A board with dimensions of 205x195 mm is placed on it. It is these dimensions that cut out the blank for the main printed circuit board - fig. 3a. The design has one more, additional, board, 155x90 mm in size - fig. 3b. On the main board there are printed conductors of the midrange and high-frequency sections of the filter, on the additional board - the low-frequency section. The preparation of the printed wiring drawing is carried out on a computer equipped with a special Sprint-Layout program. There are no special requirements for the board: conductors should be as short and wide as possible; do not allow bends of conductive tracks at a right angle; circuit elements with the symbol "common wire" are connected in one place. After orienting the coils, they are determined with other components - capacitors, resistors. For the convenience of connecting the filter, places are also provided for knife terminals. When designing in the program, the option of a double-sided printed circuit board is used, i.e., projects of the main and additional boards are placed on one figure. Both drawings are separately printed on a laser printer on coated paper or glossy for printer photo printing. For the main board, the drawing must be in a mirror image. On the metallized sides of the workpieces, previously polished with zero grit sandpaper, drawings are applied and transferred with an iron. After the paper is soaked. The boards are ready for etching. For etching an area of 100 cm2, the most suitable solution for domestic conditions is: 100 ml of a three percent solution of hydrogen peroxide, 50 - 75 g of citric acid, 15 g of sodium chloride. After etching, the printer toner is removed, holes are drilled, and the conductors are carefully tinned. If there is an opportunity to make boards in a more progressive way, use it. Properly manufactured boards should overlap each other with conductor-free surfaces, as shown in Figure 3, c.
Installation. Inductors (Fig. 4) should be inspected and, if possible, measured inductance. If a poor winding density or a large discrepancy between the actual value of the inductance and the declared one is detected, the coils are rewound. The design of the frames of the inductors of the MF, HF links has a hole for fastening in the center of one of the bases. A screw or screw made of magnetic material, which is essentially a core, increases its inductance by 2 ... 3 mH, and from non-magnetic (brass) - on the contrary, it reduces it. Therefore, the use of such fasteners gives a positive effect if the actual value of the coil inductance is 2 ... 3 mH less (greater) than indicated in the circuit. In general, it is not recommended to mount such coils on metal screws. The winding data of the inductors of the "S-90" filter from the manufacturer's factory are shown in Table 2 [27].
The scheme is supplemented with coils with nominal values of 0,22 mH and 0,43 mH. They are calculated based on the dimensions of the frame and the thickness of the winding wire. There are many programs for calculating coils. It is known from practice that not every program gives the correct result. It should be wound 5-10 turns more than calculated. After that, the specified value of the coil is set by unwinding the turns, subjecting it to measurements. It is not advisable to measure the inductance using prefixes to multimeters. They do not take into account the resistance of the coil, as a result - a large error in the measurements. Relatively accurately calculate the coil using the computer program CoilCalc 1.02b. Table 2. Winding data of filter coils 35AC-012
Capacitors and resistors lend themselves to measurements of their denominations, since they have a certain allowable spread of parameters. According to the results of measurements, they are sorted into pairs that are close in characteristics. Each pair is divided into two groups, maximally matched by ratings for one and the second filter. The resulting circuits of the two filters should be as similar as possible to each other. From the terminals of the MGBO-2 capacitors, the supply petals are unsoldered - fig. 5, a. Then they are fixed on the main board. An additional fee is applied from above, passing the leads through the holes - fig. 5 B. Both boards are fastened with threaded studs or couplings - fig. 5, c. The threaded connection must rigidly connect both boards and provide a gap between them of 55,5 mm - the distance from the glass insulator of the capacitor to its lower dimension.
All capacitors for midrange and high-frequency filter sections are installed with Lavsan K73-16 series with an operating voltage of 160 and 250 V. The standards provide for certain ranges of values \u73b\u16bof radio elements (capacitors, resistors), which do not always coincide with those indicated in the circuit. Capacitors K250-10 with an operating voltage of 160V are produced with the largest capacity of 6,8 microfarads, and with an operating voltage of 4V - 3,9 microfarads. Closest to 6,6 uF - 6,8, to 30 uF - 10, etc. Therefore, to set the required capacitance, the capacitors are assembled in parallel. For example: 6,6 uF - three 2,2 uF; 4 uF - three 2,2 uF each; 1,8 uF - XNUMX uF and XNUMX uF. When capacitors are connected in parallel, such an important parameter as the equivalent series resistance decreases. Resistors of the PEV series are replaced with C5-16V or, even better, with OSS5-16V, designed to operate in DC, AC, pulsating and pulsed current circuits with voltages up to 300V, or several film (metal oxide) connected in parallel or in series. The number of resistors is selected based on the required power dissipation. For example, the power dissipation of a resistor R1 at 75 ohms is determined by the formula: Pp \u2d U112 / R, where Pp is the power dissipation of the resistor, U is the input voltage, R is the resistance of the resistor, 75/1,61 \u1,5d 2 W. It is recommended to install power resistors 2 ... 35 times higher than the calculated one. Since the sound signal is pulsed, a 212 W resistor is enough. For example, in the acoustic system 90AC-1 "S-100" a resistor R2 of the OMLT type with a nominal value of 5 ohms and a power of 16 watts is installed. Film resistors have a much lower parasitic inductance compared to PEV and CXNUMX-XNUMXV, and are more suitable for use in audio circuits. And if you use several resistors connected in parallel, the parasitic inductance decreases as many times as the number of resistors installed. Crossover elements operate under the influence of vibrations and increased sound pressure. In order to avoid overtones, or even worse, peeling of the conductive elements of the board, breaking off the leads of massive parts, it is recommended to strengthen them on the board using sealants, glue (silicone, acrylic), ties, etc. After assembly, the board (Fig. 6) is inspected , check, screw connections and tracks are coated with zapon-lacquer. The filter is installed in the provided place in the AC case. Mounting wires are fixed with ties.
Literature
Author: V. Marchenko
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ How to protect yourself from sea robbers
▪ section of the website Basics of First Medical Aid (BFA). Selection of articles ▪ article by Orhan Pamuk. Famous aphorisms ▪ article Why are fly stickers placed in men's toilet urinals? Detailed answer ▪ article Controller of gas facilities. Job description ▪ article Heat pumps for lumber drying. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article The most economical indicators. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Comments on the article: Alexander Dear author, hello! I have an S90 since 1982, I have now installed, when assembling the speakers, 2 tech. errors. The midrange speaker does not breathe, because from the bottom it is hermetically sealed with a cap. Between the cap and the speaker, install 4 bushings, 5 mm high. In fact, raise the speaker above the cap by 5 mm. The midrange speaker will have free play (no compression). Remove the steel mesh from the tweeter, it affects the magnetic field of the speaker and decorative plastic too. Everything is so simple, S90 sang perfectly! Thanks to the designers who came up with such a miracle! You are so well done, you have invested so much work in modernization! I am already 68 years old, I love to solve such riddles! I have Bark 001, I took it from Kharkov from the factory in 1982. Arkady Bogdanovich Useful article.
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
















































 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: