
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Three-way speakers with a phase inverter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
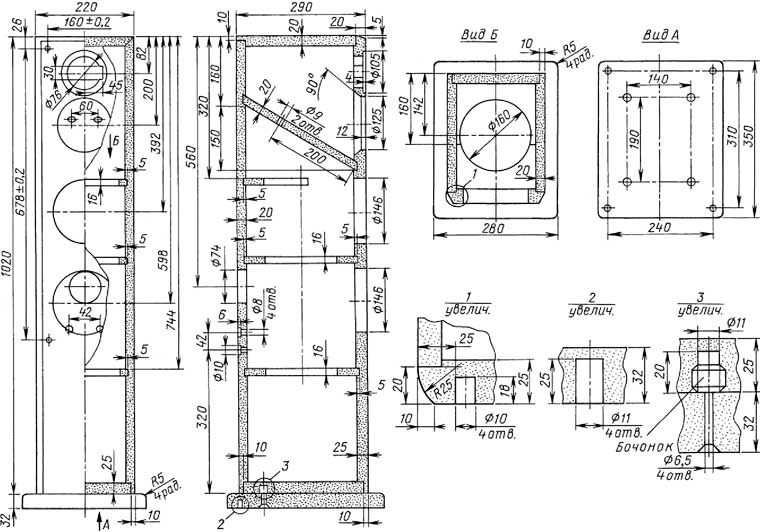
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Speakers The author has been professionally designing and manufacturing exclusive acoustic systems for many years. In this article, he talks about the design of a three-way stereo set of speakers, where high-quality dynamic heads of well-known foreign manufacturers are installed. The crossover also uses high-quality components that improve the fidelity of playback of musical recordings of various genres. This acoustic system was one of the exhibits of the Russian Hi-End 2015 exhibition, where it aroused the interest of many visitors and earned high marks from experts and amateurs during demo listening. The project of this speaker system (AS) was started a long time ago, but the first pair was completed only by the 15th Russian Hi-End exhibition in November 2015. The second pair was recently made with minor changes: the cabinet was simplified and the crossover was slightly changed according to the results listening and measuring. The speakers used dynamic heads: high-frequency Morel ET338-104 [1], mid-frequency Scan-Speak 15M/ 4531K00 [2] and low-frequency SEAS H1215 [3]. The soft-dome tweeter from an Israeli company is distinguished by a very powerful magnetic system and low non-linear distortion. Despite the presence of magnetic fluid in the gap, it has a dynamic sound and reproduces the sound of brass and percussion instruments well. The midrange head with a diameter of 15 cm from the Danish company Scan-Speak in the Reve-lator series has become one of the best midrange heads of all manufacturers. Its moving system has a large linear travel (specifically for a midrange head) and allows for a relatively low crossover frequency. Nonlinear distortions in the operating frequency band are very small: the magnetic system has two linearizing copper rings. The paper cone has special notches that provide a smoother frequency response at the end of the piston mode. Woofers with a diameter of 18 cm (6,5 inches) from the Norwegian company SEAS are ordinary ones with a paper cone, impregnated from the outside. Impregnation provides a smooth decline in frequency response above the operating frequency band. Each speaker has two such heads in total. Acoustic design - with phase inverter (FI). Two 6,5" heads have a slightly larger cone area than one 1215" head. Also on the H800 piston mode extends up to 8 Hz, and on the 600" head of the same company piston mode ends at frequencies above 1215 Hz. HXNUMX acceleration parameter Bl/Mms \u496d 350, and for an eight-inch head it usually does not exceed XNUMX. The required volume for low-frequency heads and the frequency of FI tuning can be estimated in the Unibox Excel (freeware) program (authored by Dane Kristian Kougaard), putting the head parameters from the datasheet into it. This simple and convenient program allows you to take into account many head parameters, various configurations and calculate various designs. When calculating, it is necessary to take into account the estimated active resistance of the low-frequency filter coil. For two H1215s connected in parallel, the calculations show an optimal volume of about 32 liters, and with a phase inverter pipe diameter of 66 and a length of 116 mm, the FI tuning frequency is about 43 Hz. These dimensions correspond to the dimensions of the finished Chinese-made AH-4 phase inverter. Subsequently, the FI pipe was cut to a length of 100 mm. The actual tuning frequency became about 44 Hz. In the prototype speakers, the woofers were installed each in its own compartment, which made it possible to correctly measure. Drawings of the body and its parts (frame for fabric - grill) are shown in fig. 1 and 2.
The case is made of MDF material (sometimes translit MDF is used - a finely dispersed fraction of wood). The front panel and base are 25 mm thick, the other panels are 16 and 20 mm thick. The case is finished with veneer and is attached to a removable base, painted black. Speakers are recommended to be mounted on spikes, for which steel threaded bushings are provided at the base. When an acoustic system is being designed from scratch, mock-up enclosures may be needed to test the design, but in this case (for the exhibition) it was decided to order a finished cabinet in veneer right away. The inclined partition between the midrange and bass compartments in the speaker is made to partially suppress the vertical standing wave in the cabinet and to reduce the volume of the midrange compartment. With a horizontal partition, this compartment turned out to be too large, and in order to obtain the required volume of the bass compartment, it was necessary to increase the total height of the speaker, which was already more than a meter (1052 mm without spikes). The midrange compartment is filled with synthetic winterizer by more than 50%, but the space near the midrange head is free from synthetic winterizer. A loudspeaker filter cannot be calculated correctly without having measured the frequency response of the sound pressure and impedance of each driver installed in the cabinet. Acoustic measurements require a measuring complex. In its simplest form, it is a microphone, a computer sound card, and a computer program for electro-acoustic calculations. I use the measuring complex LMS of the American company LINEARX. It is not currently available, but it is very convenient for measurements and allows you to measure the frequency response in an unprepared room. The complex includes a microphone, PC board and software. There are other measuring instruments, for example, Clio of the Italian company Audiomatica SRL or MLSSA. However, for amateur measurements, such systems are very expensive. A simpler tool is LoudSpeaker LAB 3 by a Swedish author, but it is not free. The program allows you to use a computer sound card with a suitable microphone for this purpose. A complete and relatively inexpensive solution is the ATB PC PRO from the German company Kirchner. Despite a slightly primitive implementation, this computer program allows you to make measurements that are sufficient to make high-quality speakers. On fig. 3 shows the frequency response of dynamic heads, measured by sound pressure, and in fig. 4 - characteristics of their impedance. The frequency response was measured from a distance of 0,5 m along the radiation axis of the corresponding heads. The dotted line is for the tweeter, the dash-dotted line is for the midrange head, the solid line is for the woofer.
The sound pressure frequency response is smoothed for ease of use. The system is not calibrated to measure the absolute value of sound pressure, so the graphs do not correspond to the declared sensitivity of the heads. The signal level is selected based on the convenience of measurements so that system noise does not interfere and there is no large distortion. After measurements, the graphs are exported to a simulator program, which allows you to simulate the frequency response and other system parameters, taking into account the filter. The program also allows you to calculate the elements of the crossover filters and optimize the frequency response. I am using LspCAD 5.25 by Ingemar Johansson. It is quite powerful, but not very difficult to master. There is a later version, but it is not convenient enough. There is also a very powerful LEAP program of the same LINEARX that LMS produced. It is more advanced, but difficult to use. The finished simulation result is shown in fig. 5. The upper graph shows the total frequency response on the axis of the HF head at infinity (thick line) and the frequency response of the heads with their own filters (thin lines). The frequency response cannot be called even, but this is not critical, since the simulator shows a more even frequency response on the axis by 5 degrees. above the axis of the HF head. The lower graph is a characteristic of the speaker impedance and heads with appropriate filters.
The crossover filter circuit for one speaker channel is shown in fig. 6.
The LF crossover uses a first-order filter (inductor L4). The midband is also cut off at the top and bottom by a first-order filter (C2 and L2). The second order filter (dL1) is applied to the high-frequency band. The acoustic and electrical orders of the filter decay usually do not coincide, since the AFC of the heads have their own unevenness in the filter delay band. Therefore, the real declines near the crossover frequencies in the bass bands and are close to the first, in the midrange bands above and HF - closer to the third due to the own frequency response drops of the heads, which are added to the decay provided by the electric filter. In speakers, all heads are connected in phase. Usually, bass heads cannot be reduced by a first-order filter and without polarity reversal - the second order is more often used. Here it was possible at the cost of greater unevenness of the total frequency response. The low filter order means wider head co-operation areas and vertical lobe patterns with narrow center lobes. But speakers with low-order filters sound more natural, cohesive and lively. The R6C5 circuit, together with the L4 coil, forms a plug filter that cuts out a small overshoot in the frequency response of the bass heads, which is audible if special measures are not taken. At the same time, this circuit slightly reduces the slope of the frequency response above the crossover frequency, therefore, to compensate for this decrease in slope, the R7C6 circuit is introduced. The L5C7 circuit (as a notch) eliminates the rise in the impedance of the bass section at frequencies around 75 Hz. This is necessary to eliminate the peak in the frequency response of the loudspeaker, which masks the lower bass. This phenomenon is called "pumping", the term was proposed by SD Batem. Most speaker manufacturers do not take this phenomenon into account, although there are speaker designs that use a similar impedance equalizing circuit. Polypropylene capacitors are used in the crossover, and C1 and C2 are Mundorf Supreme (expensive, black - see photo below). The price of capacitors C2, C3 (an assembly of four) is commensurate with the price of a midrange head, but in a good path, the difference in the sound of speakers with such capacitors is noticeable. To save money, you can replace it with another - Mundorf Msar (white). You can use part Supreme and part MCap (like C4). Capacitor C7 - non-polar oxide (Mundorf Bipolar). Coils - ordinary from winding wire, except for L2 (Mundorf CFC16), which is wound with tape winding (JBSPL wire. Wire diameters for coils L1 and L3 (Mundorf L100) - 1 mm, for L4 (Mundorf L140) - 1,4 mm, for L5 (Mundorf L71) - 0,71 mm (resistance about 4,5 ohms) Coil L5 can be on a ferromagnetic core, and its resistance may differ, in this case, the sum of the resistance of the L5 coil and an additional resistor (not shown in the diagram) should be approximately equal to 4,5 ohms.Resistors in the crossover - metal oxide (Mundorf MResist MOX). On the photo of fig. 7 the crossover is shown assembled. The parts are mounted on the terminals by surface mounting and fixed with hot glue to a panel of MDF, plywood or other material with a thickness of 3 ... 6 mm. The filters are assembled on two panels: together for mid-high frequencies and separately for low frequencies. The low-pass filter panel is attached to the side wall of the speakers in the lower bass head compartment, and the filter panel for midrange and high-frequency heads is attached to the side wall in the upper bass head compartment. The holes through which the wires from the filters to the midrange and tweeters pass must be sealed with plasticine.
Let's see what real impedance and frequency response this crossover provides. On fig. 8 shows the frequency response of speakers in a room, taken from a distance of 1 m along the axis of the HF head. It can be seen that it is similar to the simulation product (see Fig. 4), but turned out to be more even than the simulator predicted. This often happens due to the fact that dynamic heads are considered to be minimum phase by default in modeling and measurements, but in reality, outside the piston mode, this may not be true.
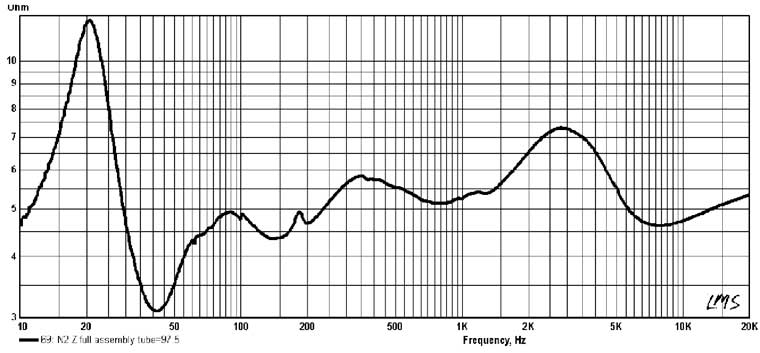
Therefore, it will not be possible to immediately simulate the "correct" filter. Requires filter changes and additional measurements and listening. In reality, the frequency response (smoothed to a third of an octave) falls within a deviation of ±3 dB, if you do not pay attention to the frequency response below 300 Hz, where the room significantly affects. In particular, due to the interference of the direct from the speakers and the signals reflected from the floor, the microphone has a drop in the frequency response in the region of about 200 Hz. When moving away from the speakers, this effect is leveled. Local maxima at frequencies of 34 and 60 Hz are due to standing waves that the microphone perceives at a given point (at 34 Hz - between walls, at 60 Hz - between floor and ceiling). The maximum at 140 Hz was due to reflections from nearby furniture. Given the slight smoothing characteristics, the result is quite decent. On fig. 9 shows the frequency response of the speaker impedance. It practically coincides with that calculated in the simulation. A small peak at 180 Hz is an unsuppressed vertical standing wave in the LF section. Labels at 100 Hz and 1 kHz are generated by software, in reality they are not.
It can be seen that the impedance in the working frequency range does not fall below 3,3 ohms and does not exceed 7,2 ohms (except for the low-frequency hump of the phase inverter). The system can be considered nominally four-ohm, and it can be used with a tube amplifier, as it has a fairly even impedance and a fairly high sensitivity. Speaker Specifications
On the photo of fig. Figure 10 shows the first stereo set of speakers (enclosures along the edges of the stand), manufactured and presented at the Russian Hi-End exhibition in 2015. According to many visitors, with an average cost of components and manufacturing, the quality of the finish of the cases is quite high, and the sound of the speakers is rated as balanced and natural in many musical genres, although, it must be admitted, the author did not have phonograms of "heavy metal" or "rock" there ...
Note. There is a typo in the filter diagram. R6 is not 2.2 Ohm, but 22. To Vladimir: the L3 coil is wound with 1mm wire. All Mundorf coils. The total resistance R5L3 is about three ohms. Literature
Author: G. Krylov
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ New power supplies for LED applications ▪ The lifetime of a free neutron has been measured ▪ Silk-based hybrid transistor ▪ Mold has learned to feel gravity
▪ section of the Electrician website. PUE. Article selection ▪ Argus article. Popular expression ▪ article Wormwood annual. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Automotive VHF FM tuner. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese








 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: