Multi-element vertical antenna at 144 MHz. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / VHF antennas
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Readers are offered a description of the design of a multi-element antenna in the range of 144 ... 146 MHz. Its advantages are the original design and low weight. The antenna is placed inside the telescopic fishing rod and it is convenient to take it with you, for example, on a country trip, to the country house, etc. It takes only a few hours of free time to make the antenna. Of course, it can also be performed in a stationary version.
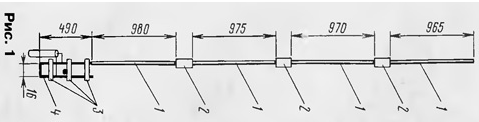
As can be seen from Fig. 1, the antenna consists of four half-wave vibrators 1, located vertically, fed from the end through a short-circuited quarter-wave matching line-transformer 4. Phase-shifting elements 2 provide in-phase switching of the vibrators. The antenna has a vertical polarization and a circular radiation pattern.
The design of the antenna is shown in fig. 2. The author placed it in a part of a plastic rod 4,5 m long. In the figure, for easier reading, the individual elements (knees) of the rod are shown as separate tubes. In fact, they naturally fit tightly into each other, without requiring sealing.
The transformer is made of copper wire with a diameter of 2 mm. To increase the rigidity of the structure, the wire is soldered to three spacer plates 3, made of one-sided foil-coated fiberglass. The foil in the middle of the plates is removed, leaving only at the ends, at the places of soldering to the wire. You can use spacers of a different design and from a different insulating material. A thicker wire is also suitable for the matching line. However, it should be remembered that the ratio of the distance between the conductors of the transformer to their diameter must be 8:1.
Each phase-shifting element of the antenna is a short-circuited quarter-wave segment of a two-wire line - a loop. To reduce the size, they are rolled up in the form of coils. For the manufacture of each loop, a piece of PEV-2 wire with a diameter of 1,4 and a length of 1040 mm is taken, a mandrel made of dielectric material (fluoroplast, plexiglass) with a diameter of 9 ... 10 and a length of 75 mm. The wire is folded in half and, starting from the middle of the mandrel, coil to coil is wound in different directions. The ends of the wires of the windings are passed through through holes, pre-drilled at the edges of the mandrels, cleaned and soldered.
The material for the vibrators is an antenna cord with a diameter of 2 ... 3 mm (for a stationary antenna, a copper wire of the same diameter is used).
Separate elements of the antenna are connected to each other by soldering in accordance with Fig.1.
It is advisable to choose a fishing rod as rigid as possible and with such an internal diameter that all antenna elements could fit inside. In the thinnest knee, the antenna cord is attached with a fishing line with a diameter of 0,7 mm or a suitable elastic cord (Fig. 2).

An RF connector is mounted at the base of the rod. The connector is connected to the matching transformer with a short piece of coaxial cable (50 or 75 ohms). The central conductor of the cable is soldered to the side of the transformer to which the antenna sheet is attached. The cable braid is soldered, respectively, to the opposite. The points of connection of the power cable to the transformer are selected according to the minimum of the SWR meter readings. Measurements are carried out at the maximum distance from the antenna of all foreign objects.
It is desirable to set up a stationary antenna at the place of its permanent installation. In addition, the antenna should be grounded at the base of the matching transformer jumper, and foam rubber cubes should be put on its canvas to eliminate the "rattle" effect (Fig. 2). In case of insufficient rigidity of the rod, additional stretch marks from a nylon cord should be applied, securing them in the region of the second (third) knee.
The antenna, made by the author, has a gain of about 5 dB and an SWR of no more than 1,2 at the edges of the amateur radio band.
Author: G.Bobnev (RA3WQV)
 See other articles Section VHF antennas.
See other articles Section VHF antennas.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Polymer fibers for cooling electronics
14.04.2014
American physicists managed to create special heat-conducting fibers based on polythiophene polymer, which are not inferior in their properties to the best thermal pastes. Such fibers can be used to cool electronics or automotive parts. This is described in an article published in Nature Nanotechnology.
"Polymers are generally not considered as the basis for thermal interfaces, as they decompose at high temperatures. But polythiophene is already used in the production of electronics and high-temperature solar cells. We took advantage of the fact that this compound is resistant to heat due to the nature of the bonds between its molecules,” says Baratunde Kola, a fellow at the Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta (USA).
According to Kohl and his colleagues, one of the reasons for the poor thermal conductivity of polymers is the chaotic arrangement of individual molecular "threads" inside them. Due to the entanglement of the molecules, the so-called. phonons are quasi-particles of vibrations that carry thermal energy in solids.
American physicists solved this problem by using a special technique for growing polythiophene filaments, which made it possible to direct almost all the filaments in one direction, so that there are no barriers to the movement of phonons. In accordance with their methodology, the scientists placed a solution of single thiophene molecules in an electrochemical bath made of porous aluminum. In this bath, the solution is mixed with fluorine, boron and ethyl ether compounds.
If an electric current is passed through this mixture, then single thiophene molecules combine into threads that conduct heat well. According to scientists' calculations, their fibers conduct phonons 20 times better than ordinary polythiophene.
The thermal conductivity of fibers can be compared with the best modern thermal interfaces. In this case, polythiophene filaments can be "smeared" over the cooled surface with a very thin layer. If they are subjected to prolonged heating to high temperatures, they do not lose their properties, which compares favorably with classic thermal pastes.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Hybrid OLED with 111,7 lm/W
▪ High speed 16Gbps interface
▪ Python 480 image sensor from ON Semiconductor
▪ Gesture recognition system based on 60-GHz radio waves
▪ Anti-glare coating improves the efficiency of solar panels
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Amateur Radio Technologies. Selection of articles
▪ article Color marking of domestic semiconductor devices. Directory
▪ article Who was the first Moscow prince? Detailed answer
▪ article Grohotnik. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article 6H13S lamp fixed bias options. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Rules for the installation of electrical installations. Scope, definitions. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: