
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING About the antenna Five-eighths of a lambda. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
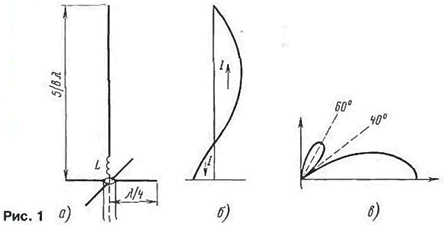
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / VHF antennas A correct statement may be wrong. This is not a pun, but a statement of fact. A correct statement taken out of context can be misleading if, for example, the restrictions under which it is true are not named. Something similar, according to the author of this article, happened with the characteristics of the popular 6λ / 8 antenna. Shortwave and ultrashortwave, as well as among the owners of C-B radio stations, a vertical antenna with a length of 5λ / 8 is popular. It is well known from amateur radio literature and advertising that a vertical emitter with a length of 5λ / 8 gives the maximum directivity pattern lobe pressed to the ground in the vertical plane (in the horizontal pattern is circular) and therefore has the maximum efficiency. The simplest version of the antenna is shown in Fig. 1a. The length of the emitter 5λ/8 is not resonant, therefore it is brought to Zλ/4 by introducing an inductive element into the emitter sheet: a coil L or a segment of a closed line with an electrical length of λ/8. The "reverse" current from the cable braid spreads over quarter-wave balances. They do not participate in radiation, since the currents in them are directed in opposite directions. It is impossible to bend the counterweights down, since in this case the electrical length of the antenna will increase due to the vertical component of the current of the counterweights, which will adversely affect the radiation pattern. Often, the lower output of the inductor in the figure is connected to counterweights. The braid is connected to the same point, and the central conductor of the cable is connected to the coil outlet. In the 27 MHz band, counterbalances are often made shorter than λ / 4, correspondingly increasing the inductance to tune the antenna into resonance. The current distribution in the antenna is shown in fig. 1b. It can be considered sinusoidal with good accuracy. The radiation pattern (Fig. 1c) has a "zero" at an angle to the horizon and an unnecessary side lobe at an even greater angle. This lobe is the payment for the main lobe pressed against the horizon and the mentioned maximum directivity factor. Here, perhaps, in short, that's all. what was known to the author (as well as to other radio amateurs) about this antenna, and ... caused some bewilderment.
The lower section of the emitter did not give rest, where the current is directed in the opposite direction with respect to the current in the upper, half-wave part. After all, it is known that the radiation pattern is formed as follows: the fields from each small segment of the emitter are summed up in any direction, taking into account their amplitudes and phases. In the direction to the horizon, the lengths of the wave propagation paths from all segments are the same and there is no additional phase incursion. The fields from the sections of the upper, half-wave part of the antenna are in phase and add up in amplitude, and the fields from the lower part (where the current direction is opposite) are out of phase and ... are subtracted! From these considerations, it turned out that a shorter - half-wave vertical radiator should work better than a vibrator with a length of 5λ / 8. And if the direction of the current in the lower section of the emitter with a length of 5λ/8 is somehow reversed, then it will be more efficient. To prove this conclusion, it was possible either to calculate the SPV theoretically, or to set up an appropriate experiment. But suspecting that this was all done a long time ago, the author preferred to study the old literary sources. And what did it turn out? For the first time, a vertical antenna-mast with a length of 5λ/8 was described by S. Ballantyne back in 1924 [1]. It was developed as a medium-wave broadcast anti-fading antenna. An additional advantage of this antenna, which immediately became very popular, turned out to be that it really creates the maximum field strength towards the horizon, but only in the class of antennas with a natural (sinusoidal) current distribution along the vibrator located directly above a perfectly conducting surface. Many people remember the first part of the statement well, but the authors of articles in amateur radio literature apparently forgot a little about the second part. In the professional one it is reported [2]: "If special means are taken to prevent a reversal of currents below the upper half wavelength of the radiator, further horizontal gain can be obtained...". In other words, if you reverse the direction of the current in the lower part of the antenna, you will get an additional gain in radiation to the horizon. At the same time, it is possible to further increase the length of the antenna in order to increase the gain. Recall that for a classical antenna with a length of 5λ/8, it is no longer possible to increase the length, since the side lobe of the diagram sharply increases and the main lobe decreases. Having reversed the current in the lower part of the antenna, it is advisable to increase its length by another λ/8 in order to get rid of the matching coil. The result is a well-known in-phase collinear antenna, proposed back in 1911 by Marconi engineer Franklin. The Franklin antenna is a vertical wire divided into half-wave segments, between which coils are connected (Fig. 2, a) or quarter-wave lines (Fig. 2,6). In these elements, the reverse half-waves of the current are "hidden". The currents in the radiating segments turn out to be in-phase (Fig. 2c), which narrows the diagram and significantly reduces the side lobe (Fig. 2d). The bandwidth of such an antenna is a few percent.
The dynamics of the change in the directivity diagram with an increase in the height of the antenna and the number of "floors" (according to Franklin) is illustrated in Fig. 3 borrowed from (2).
The diagrams are given again for the case of a perfectly conducting earth. It is possible to attribute the soil under the antenna to conductors or dielectrics by calculating the loss tangent (the ratio of conduction currents to displacement currents): tgδ = jnp/jcm = δ/ωεε0. For conductors, it is much greater than unity, and for dielectrics, it is much less. The loss tangent depends on the frequency. The same soil will be close to the conductor when working on medium waves, and on high-frequency HF bands and on VHF (the frequency range of interest to us!) It will turn out to be a dielectric. And this will change the phase of the reflection from the ground to the opposite, and in the direction to the horizon it will no longer be the maximum of the radiation pattern, but the minimum. The main lobe of the radiation pattern in this case comes off the surface and is directed at a certain angle to it (the smaller, the higher the antenna is installed above the ground). In other words, when operating over conductive ground, the 5λ/8 antenna actually outperforms the half-wave dipole. This can be explained by the narrowing of the radiation pattern due to the fact that the main radiating part is higher above the surface, which compensates for the decrease in the field due to the radiation from the lower part. If the 5λ/8 antenna is located in open space, then such compensation will not occur, its advantage over the half-wave dipole disappears. The above applies to a lesser extent to multi-storey antenna systems composed of VHF antennas with a length of 5λ/8. Spacing the main, half-wave radiating segments over a greater distance, as in the case of a conductive earth, narrows the diagram and compensates for the loss from the radiation of sections with reverse current. But even in this case, the exclusion of "reverse" segments should give a gain. It is not known if there were disputes between Ballantyne and Franklin about the merits of their antennas. Most likely no. because the antennas were created for completely different purposes. But among radio amateurs such disputes arise repeatedly. I hope that the arguments given in the article will help supporters of common-mode antennas in these disputes. And the practical conclusion reached by the author of these lines is the following. If you decide to make a vertical omnidirectional antenna and at the same time have the opportunity to make it higher than λ / 2, but less than λ, then you will get the greatest positive effect not with the five-eighths lambda antenna, but with the Franklin antenna (see Fig. 2). Literature
Author: V.Polyakov (RA3AAE)
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024 Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024 The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
▪ New Ethernet driver with de-emphasis
▪ section of the Electrician website. PUE. Article selection ▪ article Who dares to say: goodbye through the abyss of two or three days? Popular expression ▪ article What characteristics of a person can elephants determine by his voice? Detailed answer ▪ article Motorcade mechanic. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article Sparking indicators. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: