Eight-element antenna of the Wave channel type. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / VHF antennas
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The Czech radio amateur OK1DE designed an eight-element "wave channel" antenna, which effectively operates in the range of 144-146 MHz. The technical characteristics of the antenna are given in the table, the curves for changing the input impedance over the range are shown in Fig. 1, and the radiation pattern in the horizontal plane is shown in Fig. 2.
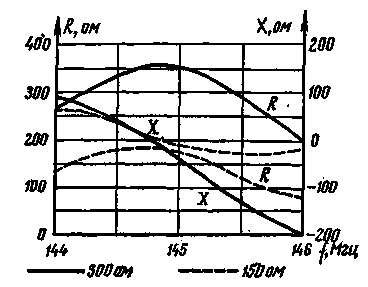
Ris.1
Antenna technical data:
- Number of elements......8
- Gain (compared to conventional dipole), dB.......11-12
- Weakening of the rear lobe, dB.......14±16
- Traveling wave coefficient ....... 0,4-0,7
- Maximum length, m......3,81
- Maximum width, m.......1,135
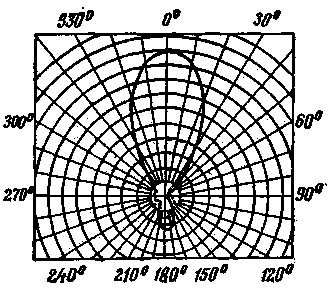
Ris.2
The antenna device and its dimensions are shown in Fig.3. Dimensions are in mm. When building an antenna with dimensions that are given outside the brackets, its input impedance will be 300 ohms. In the event that it is necessary to have an input impedance of the antenna of 150 ohms, some of its dimensions change and are given in brackets. The material for the manufacture of the antenna is duralumin tubes: for all elements with a diameter of 10 mm, and for the rails on which the elements are fixed, with a diameter of 28 mm.
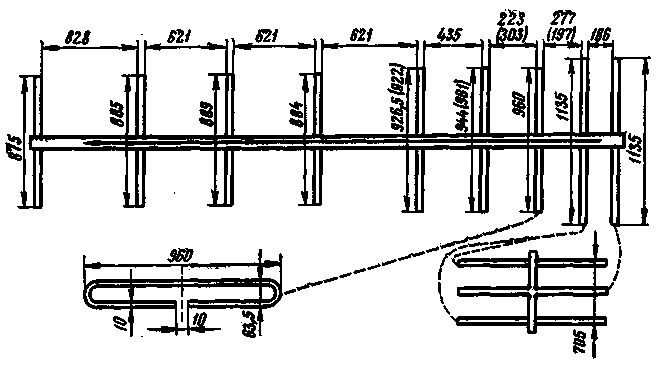
Fig.3 (click to enlarge)
An active loop vibrator is used in the antenna. It is easiest to bend such a vibrator in a cold way as follows. Two rollers with a diameter of 43 mm are machined from solid wood and fixed on a thick board. The distance between the centers of the rollers must be 900 mm. The tube intended for the vibrator is applied to the rollers, strengthened so that it does not move, and bent around the circumference of the rollers.
The antenna elements are fixed on the rail with M3 bolts as shown in Fig. 4. In order to avoid deteriorating the performance of the antenna, all dimensions indicated in Fig. 3 must be strictly adhered to, as well as the thickness of the tubes and the method of fastening the elements and rails.

Ris.4
In order to be able to use the most common cables with a wave impedance of 75 ohms (RK-1, RK-3) for the antenna feeder, it is necessary to connect the loop vibrator of the antenna with an input impedance of 300 ohms U - knee (Fig. 5, a), which is simultaneously with transformation of the input impedance of the antenna will symmetrical it. The transformation of the input impedance of the 150 ohm antenna is carried out using a transformer made of a cable.

Ris.5
Such transformers are described in the article by Kharchenko and Isupova "Incomplete zigzag antenna" ("Radio", 1965, No. 1, pp. 24-27 and page 4 of the tab in the magazine). The length ltr of the transformer for this antenna is 342 mm. To balance the antenna, the feeder with the transformer is laid along the tube of the loop vibrator to the point of zero potential (Fig. 5, b). The outer insulating sheath is not removable from the cable. In this case, it is more convenient to attach the loop vibrator to the rail with the open side up (that is, the side to which the ends of the transformer are attached).
Literature
- Radio No. 2 1966, pp. 57-58
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section VHF antennas.
See other articles Section VHF antennas.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024
The modern world of science and technology is developing rapidly, and every day new methods and technologies appear that open up new prospects for us in various fields. One such innovation is the development by German scientists of a new way to control optical signals, which could lead to significant progress in the field of photonics. Recent research has allowed German scientists to create a tunable waveplate inside a fused silica waveguide. This method, based on the use of a liquid crystal layer, allows one to effectively change the polarization of light passing through a waveguide. This technological breakthrough opens up new prospects for the development of compact and efficient photonic devices capable of processing large volumes of data. The electro-optical control of polarization provided by the new method could provide the basis for a new class of integrated photonic devices. This opens up great opportunities for ... >>
Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024
Keyboards are an integral part of our daily computer work. However, one of the main problems that users face is noise, especially in the case of premium models. But with the new Seneca keyboard from Norbauer & Co, that may change. Seneca is not just a keyboard, it is the result of five years of development work to create the ideal device. Every aspect of this keyboard, from acoustic properties to mechanical characteristics, has been carefully considered and balanced. One of the key features of Seneca is its silent stabilizers, which solve the noise problem common to many keyboards. In addition, the keyboard supports various key widths, making it convenient for any user. Although Seneca is not yet available for purchase, it is scheduled for release in late summer. Norbauer & Co's Seneca represents new standards in keyboard design. Her ... >>
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
Exploring space and its mysteries is a task that attracts the attention of astronomers from all over the world. In the fresh air of the high mountains, far from city light pollution, the stars and planets reveal their secrets with greater clarity. A new page is opening in the history of astronomy with the opening of the world's highest astronomical observatory - the Atacama Observatory of the University of Tokyo. The Atacama Observatory, located at an altitude of 5640 meters above sea level, opens up new opportunities for astronomers in the study of space. This site has become the highest location for a ground-based telescope, providing researchers with a unique tool for studying infrared waves in the Universe. Although the high altitude location provides clearer skies and less interference from the atmosphere, building an observatory on a high mountain poses enormous difficulties and challenges. However, despite the difficulties, the new observatory opens up broad research prospects for astronomers. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Attosecond pulses of light - using a conventional industrial laser
11.09.2020
A team of researchers at the University of Central Florida has developed a new method to produce attosecond pulses of light using light from a conventional industrial laser as input. This achievement opens up the possibility of recording events and making measurements with attosecond accuracy, which, in turn, will allow scientists from various fields of science to study ultrafast phenomena and processes, such as the movement of electrons in atoms or molecules in their natural time frame.
The production of extremely short pulses of light, the duration of which is comparable to the duration of one oscillation of the electromagnetic wave of this light, is usually done using light pulses produced by a high-quality laser, which are passed through tubes filled with noble gases such as xenon and argon. Due to this, already quite short pulses, numbering about a hundred cycles of electromagnetic wave oscillations, are compressed in time.
In the new method proposed by scientists from Florida, the new method practically does not differ from the one described above, except that the tubes through which the light pulses pass are filled not with noble (inert) gases, but with molecular gases, such as nitric oxide, which have linear optical properties. The effect of reducing the pulse duration obtained by scientists arises due to the fact that gas molecules, which have their own electric polarization, under the influence of the electric field of the light pulse, have time to align and turn into a kind of linear resonator.
With the help of the first experimental setup, scientists managed to achieve a reduction in the duration of the initial pulse, which varied in the range from 100 to 1000 cycles, to a duration of 1,6 cycles of an electromagnetic wave. In this method, the key points are the choice of the molecular gas-filler, the frequency and duration of the initial light pulses. With properly selected parameters, which necessarily take into account the inertia of the gas molecules, the new method will be able to reduce the pulse duration to the time of one oscillation of the electromagnetic wave of the initial light pulse.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Monitor NEC MultiSync EA234WMi
▪ Rear view mirror with touchscreen and LTE
▪ Volitronics Success
▪ Intel develops new SSD specifications for ultrabooks
▪ 11nm SoC Snapdragon 675 with support for integrated cameras
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the Garland website. Article selection
▪ article Maiden's memory. Popular expression
▪ article When is Pi Day celebrated? Detailed answer
▪ article Installer. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article LCD from Nokia 3310 on LPT. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Pyroelectric effect. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese





 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: