Five-band vertical antenna. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / HF antennas
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The shortwave desire is great to have a set of antennas for each wavelength range, but this is not always feasible due to the lack of space and conditions for placing these antennas. We have to compromise and put multi-range.
The author has tested various types of both horizontal and vertical multiband antennas. The most acceptable were vertical antennas. For a long time, a five-band vertical antenna proposed by Yu. Medinets (UB5UG) was operated. The antenna circuit is shown in fig. one.
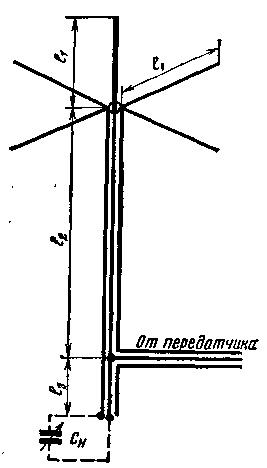
Ris.1
This antenna is quite well described in the literature [1, 2]. The resonant length of the antenna together with the feed line should be equal to 42,5 m, so the length of the radiating part l1 is determined by the expression (all dimensions in meters) l1=42,5-e(l2+l3), where e is the dielectric constant of the dielectric (for most domestic cables with solid insulation made of stabilized polyethylene e=1,51).
Yu. Medinets recommends that the length of the radiating part and counterweights be taken equal to 8,6 m. The emitter can be made of a tube with a diameter of 15-20 mm and, if necessary, reinforced with one or two tiers of guys. The number of counterweights must be at least four, they are made of a cord or copper wire with a diameter of up to two to three millimeters. Without a noticeable deterioration in the performance of the antenna, a metal roof with sufficient geometric dimensions can be used as a counterweight. The antenna is tuned by changing the length of the segment l3 (according to the recommendation of UB5UG l3 = 2,9 m) according to the minimum SWR in the cable coming from the transmitter in the range on which the most active work is expected. So, when tuning the antenna on the 20-meter band with an SWR of no more than 1,3, on the bands of 10,14 and 40 m, the SWR can reach 2, on the 80-meter band - up to 3-4.
Antenna tests showed that it works quite well on the bands of 10,14 and 20 m, satisfactorily on 40 m (a decrease in the length of the radiator affects) and is not very effective in the range of 80 m (the length of the radiator is short and the SWR is high).
The Czechoslovak shortwave M. Shasek (OK1AMS) also uses this antenna [3]. For those cases where the segment l3 can be placed near the transmitter, it marks the possibility of tuning the antenna on each band by connecting a capacitor (See in Fig. 1). Capacitor capacitance does not exceed 450 pF on the 80-meter band and even less on other bands. It should be noted that there is a voltage antinode at the connection point of the capacitor, so the gap between the plates of the variable capacitor must be at least 1-2 mm (depending on the transmitter power). With this method of tuning, the SWR on each range can be no more than 1,5.
When working in competitions, fulfilling the conditions of various diplomas, successful work on 40 and 80-meter bands is no less important than on higher frequencies. In this regard, the antenna was somewhat modified (see Fig. 2). The length of the emitter l1 is increased to 11,2 m, while the length of the supply line is determined by the expression
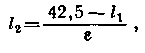
which for a cable with e = 1,51 is 20,6 m.
The antenna is installed on the roof of a small two-story house, made of pipes with a diameter of 45 mm, and reinforced with two tiers of guys. The length of counterweights from a cord with a diameter of 1,4 mm is equal to the length of the emitter.
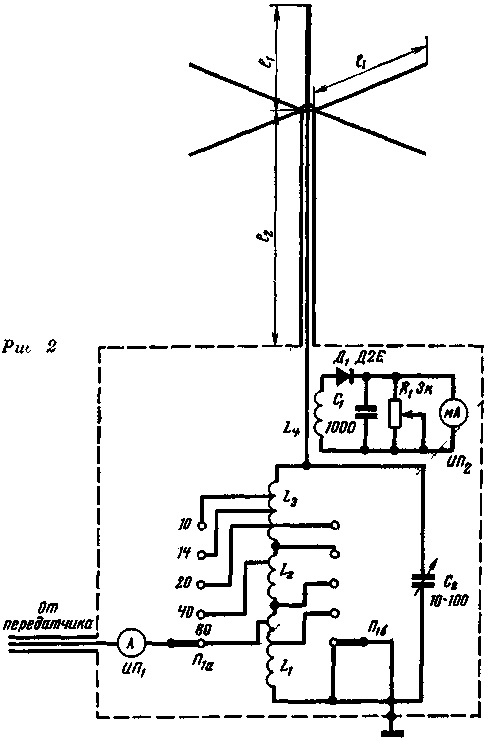
Ris.2
Due to the small distance from the antenna to the transmitter, the use of an additional feeder line was not required. Connecting the feed line directly to the P-loop of the transmitter gave good results, but antenna tuning was difficult due to the fact that with such an antenna feed, it is necessary to provide a voltage antinode at the feed point, which makes matching difficult. In addition, since the antenna is harmonic, higher order harmonic radiation intensity increases with this feeding method.
To eliminate these undesirable phenomena, an antenna unit was made, which is an oscillatory circuit enclosed in a screen and located near the transmitter. The transmitter output via a 75-ohm cable is connected by a P1a switch to a part of the circuit with an input impedance of 75 ohms, which ensures the operation of the feeder in the traveling wave mode with SWR on each of the 5 ranges close to 1. The circuit inductor, consisting of three L1 sections connected in series , L2, L3 is switched by switch P1b.
The first step in tuning the antenna is tuning the antenna circuit with the feeder disconnected from the transmitter. With the help of GIR or GSS with a tube voltmeter, the inductances of the coils are selected for each range at the middle position C2. Rough adjustment of the construction is carried out by selecting turns, fine - by changing the value of the capacitance of capacitor C2. The second stage of tuning is the selection of feeder connection points from the transmitter for each range using an SWR meter of any design.
The final tuning of the antenna is performed according to the maximum readings of the IP2 device, which is weakly connected to the "hot" end of the circuit. As IP1, a high-frequency ammeter with a thermocouple and a measurement limit of 3 a was used. As IP2, a small-sized magnetoelectric device for 5 mA was used. Coil L4 - contains 3 turns of any wire.
The antenna performed well on 40, 20, 14 and 10 meters. It is especially convenient when working with DX, since despite the presence of an additional lobe on the 14 and 10 m bands, the main power is emitted at small angles to the horizon [4]. On the 80-meter band, the antenna works quite satisfactorily.
The use of the antenna unit significantly reduced the level of radiated harmonics. Careful tuning and shielding completely eliminate TV interference. An undeniable advantage is that the antenna is tuned at the workplace. The antenna is grounded but direct current and lightning-proof.
Literature:
1. "Radio", 1960, N 9, p. 44.
2. Sheiko V. P. "Antennas for amateur radio stations", ed. DOSAAF, 1962
3. "Amaterske Radio", 1967, N 2, p. 56.
4. X. Meinke and F. Guvdlach, "Radio engineering reference book" (translated from German), volume 1, State Energy Publishing House, 1960
Author: O. Safiullin (UA4PA); Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section HF antennas.
See other articles Section HF antennas.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Neurons remember taste
29.11.2014
Having taken some filth in our mouth, we quickly remember that next time we can’t eat it - the brain instantly forms a connection between the appearance and smell of bad food and the unambiguous reaction of the stomach. At the very first moment, many neurons respond to food irritation in the brain, but not everyone retains memory. Only a handful of cells store information about unpleasant taste and smell. The question is, how do these cells differ from the rest?
The answer was given by researchers from the University of California at Los Angeles (USA). As often happens, it turned out to be a certain protein called CREB. Those neurons in which its level was elevated remembered the bad taste. CREB stands for cyclic-AMP-response-element-binding protein and it works as a transcription factor: in response to the appearance of the regulatory molecule of cyclic AMP (cyclic-AMP), it binds to certain areas in DNA, enhancing or weakening transcription on them - the synthesis of messenger RNA. A few years ago, Alcino Silva and his colleagues showed that CREB is responsible for the localization of emotional memory in the amygdala—localization in the sense of individual neurons.
At the same time, the researchers suggested that this protein serves as a universal tool that determines which neurons will remember the stimulus and which will not. To test their hypothesis, they conducted a series of experiments with mice that had to try the nausea-inducing solution. The unpleasant taste activated the insular cortex of the brain, but even here a small part of the cells were allocated for information storage, which, as the authors of the work in Current Biology write, contained a lot of the CREB protein. The amygdala and the insular cortex are quite different from each other, but the molecular mechanism that selects cells for memory is similar. So there is every reason to believe that CREB works wherever you need to form a neural memory cell.
Mouse brain cells were modified to synthesize modified CREB coupled to green fluorescent protein. In addition, another gene was introduced into the neurons, which made them sensitive to a substance that turned off neuronal activity. Then the mice were given a taste of salt water, which was also mixed with lithium chloride, which causes nausea. Usually, mice like the taste of salt, but in this version they remembered that salt water would make them feel bad. Three days later, the animals were again offered to taste bad water. Normal mice avoided drinking it, but those in which CREB neurons were turned off forgot the negative experience and drank the nauseating solution again.
Further experiments showed that CREB increased the synthesis of another protein called Arc, whose functions are closely related to the cytoskeleton. It is known about Arc that it is the greater in those neurons that are most excited in response to a stimulus. The role of the cytoskeleton in the formation of memory has been studied for a long time: memorization requires strong nerve chains, that is, strong interneuronal contacts - synapses, and the strength of certain elements of the cellular architecture depends on protein skeletal supports in the cytoplasm.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ London drinks sea water
▪ New Semicube Electronic Platform
▪ CFexpress Type B memory cards
▪ Electronics rules the genes
▪ Virus against girls
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Electrician in the house. Article selection
▪ article Poets are born, speakers are made. Popular expression
▪ article Who are fleas? Detailed answer
▪ article proofreader. Job description
▪ article Security system based on GSM phone. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Desktop air ionizer. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: