
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Range shortwave antenna. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
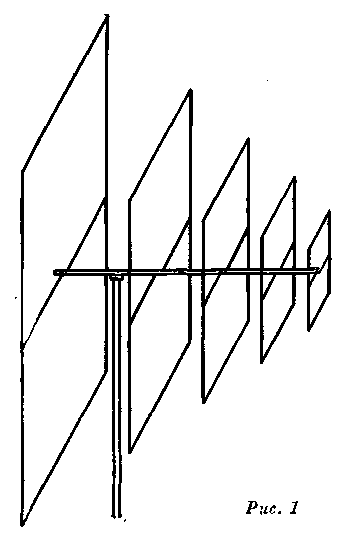
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / HF antennas The article offered to readers provides a description and calculation of a frequency-independent antenna. Until now, this class of antennas has almost never been used in amateur practice. At the same time, the use of such antennas is very tempting, since it allows one antenna system to be dispensed with when operating on several bands (for example, 14; 21 and 28 MHz on KB or 144 and 430 MHz on VHF). Compared with the common "wave channel" antenna, the described system has smaller dimensions in the horizontal plane. Perhaps its only drawback is the need to make elements in the form of frames with a side of 0,5l, which for the 14 MHz range is a construction of impressive size. But such is antenna technology. The eternal dilemma is either large size or low efficiency. Each amateur decides this question based on his specific conditions. As for efficiency, the frequency-independent antenna seems to have an advantage over both the "wave channel" and various "squares". The described antenna was developed on the initiative of a shortwave, who is well known in our country and abroad, a selfless radio sports enthusiast, a former member of the Presidium of the FRS of the USSR Igor Nikolaevich Zhuchenko (UA1CC). The authors and the editors dedicate the article published below to the memory of I. N. Zhuchenko. As a rule, antennas that use shortwave are narrow-band and have a relatively low gain. Therefore, the overlap of amateur bands is 14; 21 and 28 MHz is usually achieved by manufacturing three antennas, and long-distance communication is achieved by increasing the transmitter power or complicating antenna systems. At the same time, the problem of providing long-range communication can be successfully solved without amplifying the transmitter if a highly directional, frequency-independent antenna with a high gain is used. Various authors have proposed a number of design solutions for the creation of frequency-independent (log-periodic) antennas, which have a gain of 9-12 compared to an isotropic radiator. Below is a description of a broadband log-periodic antenna, the increase in the radiation efficiency of which was achieved due to the use of resonant elements made in the form of two-loop frames. The antenna, the general view of which is shown in Fig. 1 consists of a rigidly made two-wire power line and radiating elements arranged parallel to each other along it. The dimensions of the radiating elements and the distance between them varies exponentially with a proportionality factor t. The elements are excited in such a way that the energy radiated by the elements of the active region is added in phase in the far zone (under the active region one should understand a group of vibrators whose geometric dimensions are close to the length of the resonant element 0,25l).
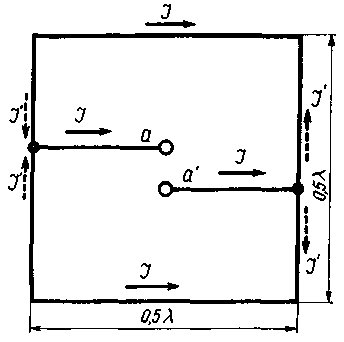
The radiating element has the shape of a square, the side of which is equal to 0,5l (Fig. 2). Quarter-wave jumpers form two symmetrical circuits fed by a two-wire line at points a - a'. The directions of the main currents that form the radiation pattern are indicated by solid arrows. The electromagnetic fields generated by the currents indicated by the dotted arrows cancel each other out. Thus, the resonant element is a three-element in-phase array.
On fig. 3 shows a drawing of an antenna in a horizontal plane. It follows from it that the calculation of the antenna is reduced to solving a right triangle. In passing, we note that the principle of operation of the antenna is not violated under the condition of a reasonable decrease in its longitudinal size, which is of decisive importance in the construction of short-wave antennas.
The dimensions of the shortened antenna are determined by the frequency range. So, to cover the frequency range 14; 21 and 28 MHz, a necessary and sufficient condition is the presence of resonant elements corresponding to the cutoff frequencies. However, in this case, the directional properties of the antenna at 28 MHz will be slightly lower than at 14 MHz, since the active region at the upper frequency will be limited to one element. Therefore, it is desirable to shorten the antenna in such a way that at least two resonant elements work at the upper frequency. Antenna calculation Based on the conditions for ensuring case communication with correspondents, we calculate (or set) the required antenna gain G:
where: E - field strength (receiver sensitivity threshold), mV/m; P - transmitter power, W; r - distance, km.
From the graph in Fig. 4 determine the angular size a. From the graph in Fig. 5 we find the longitudinal dimension L (Lo, L1 or L1 - depending on the selected degree of shortening, where: Lo - total length of the antenna, L1 - minimum possible
the length of the shortened antenna, L2 is the length of the shortened antenna, taking into account the increase in the active zone at high frequencies). From the graph in Fig. 6, we determine the value of the proportionality coefficient m. Here, Gopt corresponds to the optimal gain, and Gopt-D and Gopt-2D correspond to a decrease in gain by 1 and 2 units.
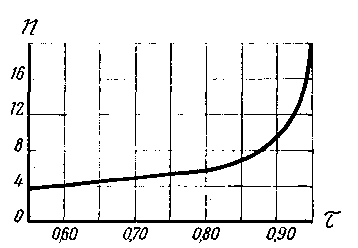
From the graph in Fig. 7 determine the number of radiating elements n.
We calculate the resonant length of the radiating elements: l1=0,25lmax l2=tl1 . . . . . ln=tln-1 We determine the location (distance to the first element) of the radiating elements R along the two-wire line: R1=L R2=tR1 . . . . . R2=tRn-1 In the manufacture of a two-wire supply line, the calculated size L should be increased by 0,13lmax to obtain good matching and eliminate back radiation: 0,03lmax - before the resonant element corresponding to the upper cutoff frequency, and 0,1lmax - after the resonant element corresponding to the lower cutoff frequency . For guidance when choosing an antenna in the frequency range of 14-28 MHz, the table shows a comparative assessment of its geometric and electrical parameters. Table 1
Dimensions corresponding to G=9,5 are shown in fig. 3. Size L2 is taken as L. Antenna patterns are shown in fig. 8.
Antenna design The antenna and two-wire power line can be made of steel or duralumin pipes. The constancy of the wave resistance of a two-wire line is ensured by using insulators made of high-frequency dielectric materials or dry wood well impregnated with drying oil. The wave impedance of the line (taking into account the applied insulator) should be approximately 100 ohms. Excitation of a two-wire line can be carried out by both symmetrical and unbalanced feeders. In the event that the transmitter has an unbalanced output, it is rational to excite with a coaxial cable laid inside one of the pipes of the line. In this case, the initial section of the pipe plays the role of a balancing (matching) transformer. The shielding braid of the cable is galvanically connected to the end of one pipe of the line, and the inner core is soldered to the second pipe. Authors: E. Baranovsky, E. Tumarkin; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Internet cables become sources of electricity ▪ Air conditioning system that does not require electricity
▪ site section Parameters, analogues, marking of radio components. Article selection ▪ article A comrade flies to a distant land. Popular expression ▪ article Which plant flowers become transparent after rain? Detailed answer ▪ article Manufacture of strip lines. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

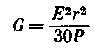



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: