AF power amplifier (80 watts). Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Transistor power amplifiers
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The AF amplifier has very low coefficients of harmonic and intermodulation distortion, it is relatively simple, able to withstand a short-term short circuit in the load, and does not require external elements for thermal current stabilization of the output stage transistors.
Main Specifications
Maximum power at a load with a resistance of 4m, W. . . 0
Nominal frequency range, Hz. . . 20...20 000
Harmonic distortion at maximum
output power 80 W, %, at frequency:
1 kHz. . . 0,002
20 kHz. . . 0,004
Intermodulation distortion factor, % . . . 0,0015
The maximum frequency at which the maximum
power is reduced by 1 dB, kHz. . . fifty
Output slew rate
voltage (without capacitor C2), V / μs. . . 40
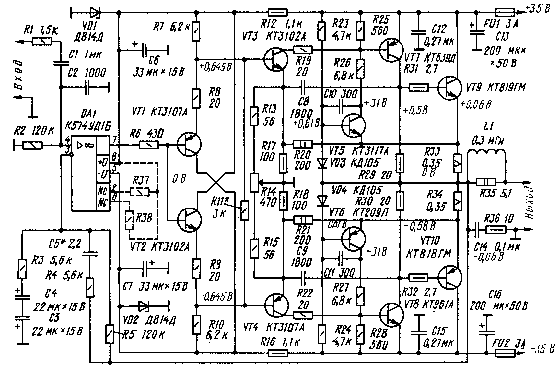
Fig. 1
The circuit diagram of the amplifier is shown in fig. 1. Changes have been made to the output stage. To increase its input resistance, transistors VT1, VT2 are introduced into the AF amplifier. This facilitated the operation of the op-amp DA1 and made it possible to ensure a stable base-emitter voltage of transistors VT3, VT4 when the temperature changes. In addition, the amplifier is supplemented with a cascade on transistors VT5, VT6, which, together with current sensors R33, R34 and output stages on transistors VT7-VT10, form two current generators in idle mode, which eliminates the cutoff of the emitter current of the transistors of the final stage and reduces switching distortion. The latter, as is known, favorably affects the spectrum of harmonics.
In addition to these changes, a deeper local OOS was introduced into each arm of the output stage by increasing the resistance of resistors in the emitter circuits of transistors VT3, VT4, which made the output stage more linear. Since the resistors R20, R21 are connected to the current sensors R33, R34, a rather rigid thermal stabilization of the quiescent current of the transistors of the final stage is obtained. . The presence of current sensors R20, R90, deep DC feedback and current-limiting resistors in the base circuits of transistors VT150, VT180 leads to the limitation of their collector currents to an acceptable value during short circuits in the load. Resistor R33 sets the symmetry of the shoulders of the output stage.
No other changes were made to the amplifier. Nonlinear distortions were measured with an S1-68 oscilloscope using a ZCh GZ-118 signal generator (Kg - about 0,002%) and a precision double T-bridge included in the generator set. The measurements were carried out according to the method described in the article by Yu. Mitrofanov "Economic mode A in a power amplifier" (see "Radio", 1986, No. 5, pp. 40-43). The coefficient of intermodulation distortion was measured according to the recommendations given in the article by V. Kostin "Psychoacoustic sound quality criteria and the choice of UMZCH parameters" (see "Radio", 1987, No. 12, p. 40-43). When testing the amplifier with a pulsed signal, no spikes were observed at the output voltage.
Author: G. Bragin; Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Transistor power amplifiers.
See other articles Section Transistor power amplifiers.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
Exploring space and its mysteries is a task that attracts the attention of astronomers from all over the world. In the fresh air of the high mountains, far from city light pollution, the stars and planets reveal their secrets with greater clarity. A new page is opening in the history of astronomy with the opening of the world's highest astronomical observatory - the Atacama Observatory of the University of Tokyo. The Atacama Observatory, located at an altitude of 5640 meters above sea level, opens up new opportunities for astronomers in the study of space. This site has become the highest location for a ground-based telescope, providing researchers with a unique tool for studying infrared waves in the Universe. Although the high altitude location provides clearer skies and less interference from the atmosphere, building an observatory on a high mountain poses enormous difficulties and challenges. However, despite the difficulties, the new observatory opens up broad research prospects for astronomers. ... >>
Controlling objects using air currents
04.05.2024
The development of robotics continues to open up new prospects for us in the field of automation and control of various objects. Recently, Finnish scientists presented an innovative approach to controlling humanoid robots using air currents. This method promises to revolutionize the way objects are manipulated and open new horizons in the field of robotics. The idea of controlling objects using air currents is not new, but until recently, implementing such concepts remained a challenge. Finnish researchers have developed an innovative method that allows robots to manipulate objects using special air jets as "air fingers". The air flow control algorithm, developed by a team of specialists, is based on a thorough study of the movement of objects in the air flow. The air jet control system, carried out using special motors, allows you to direct objects without resorting to physical ... >>
Purebred dogs get sick no more often than purebred dogs
03.05.2024
Caring for the health of our pets is an important aspect of the life of every dog owner. However, there is a common assumption that purebred dogs are more susceptible to diseases compared to mixed dogs. New research led by researchers at the Texas School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences brings new perspective to this question. A study conducted by the Dog Aging Project (DAP) of more than 27 companion dogs found that purebred and mixed dogs were generally equally likely to experience various diseases. Although some breeds may be more susceptible to certain diseases, the overall diagnosis rate is virtually the same between both groups. The Dog Aging Project's chief veterinarian, Dr. Keith Creevy, notes that there are several well-known diseases that are more common in certain breeds of dogs, which supports the notion that purebred dogs are more susceptible to disease. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Improving Quantum Computing
11.07.2021
The computational capabilities of today's supercomputers may be staggering, but quantum computers are expected to outperform even the most powerful of these machines. Thanks to the huge amount of memory and speed of operation, quantum computers will be able to solve problems that are currently beyond the power of any processor.
European researchers working within the EU-funded Magnum and microSPIRE projects have developed a potentially new qubit system using the rotation of so-called "holes".
Semiconductors consist of artificial quasi-particles, which are a collection of electrons and holes. Holes are usually called carriers of a positive charge equal to the elementary charge in semiconductors. Although holes are not true particles, they share many properties with electrons. They interact when they come close to each other, and they also have the quantum mechanical property of spin.
Holes in materials such as metalloid germanium are excellent candidates for spin qubits. The scientists built a nanostructure from various layers of germanium and silicon, which allowed them to confine the holes to a two-dimensional region.
Scientists at L-NESS stacked several different mixtures of silicon and germanium just a few nanometers thick on top of each other. This made it possible to limit the holes with a germanium-rich layer in the middle. Tiny electrical wires, called gates, were added on top to control the movement of the openings by applying voltage to them. As a result, electrically positively charged holes responded to the voltage and could move very accurately within their layer.
The research team used this technique to bring the two holes as close to each other as possible, which would help them interact as they rotate and form a spin qubit. More importantly, they were able to create a qubit from two interacting hole spins using less than 10 millitesla of magnetic field strength.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ All dumps of Seville
▪ Mobile phones with 3-megapixel cameras will appear this year
▪ Light signals of stars
▪ Car Wi-Fi will improve road safety
▪ Autonomous hydrogen energy source in container design for shipping
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the Antenna website. Article selection
▪ article Factors of human survival in the wild. Basics of safe life
▪ article Which animals cannot recognize their usual food away from their trees? Detailed answer
▪ Chufa article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article LEDs and their application. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Charger Tourist. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: