
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Stabilized adapter from unstabilized. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters In shops, kiosks of underground passages, on radio markets, you can buy so-called adapters designed in the form of a network plug. Large ripples of the output voltage and its dependence on the load current make it difficult to power any electronic equipment from them. How to stabilize the output voltage of such adapters is described in this article. To fix the "round" output voltage values, it is easiest to use the KR142EN5 and KR142EN8 microcircuits with the corresponding letter indices [1], installing them on the heat sink in the adapter case and supplementing them with an output capacitor with a capacity of at least 10 μF. If you need a "non-standard" voltage, you should use the chip KR142EN12A [2].
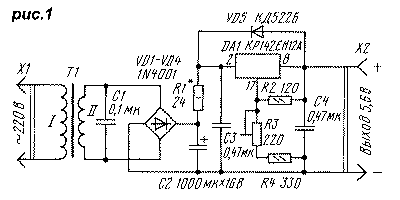
Figure 1 shows a diagram of a charger and power supply for a portable radio receiver, in which four TsNK-0,45 batteries are installed. Capacitor C1 eliminates high-frequency noise that occurs when the rectifier bridge diodes close. The output voltage of 5.6V is set by a trimming resistor R3, and the maximum charging current (about 150 mA) is set by selecting a resistor R1 with a discharged battery connected. The unit is convenient in that the batteries are charged quickly (4...6 hours), and it is impossible to recharge them [3,4].
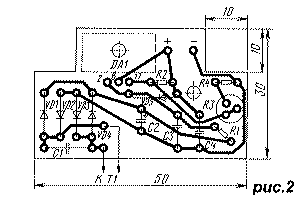
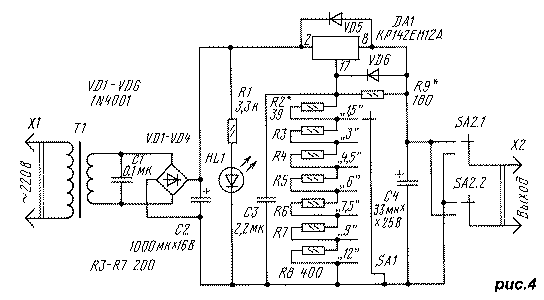
The device is assembled on the basis of the RW-900 adapter [5]. A drawing of the printed circuit board is shown in Fig. 2, and the appearance of the block is shown in Fig. 3. MLT resistors are used: they are installed vertically on the board, R3 - SP3-19a. Diodes VD1-VD4 and capacitor C2 - from the adapter, the rest - RV-6. Capacitor C4 can also be installed with any oxide, but its capacity must be at least 10 μA. Diode VD5 - almost any rectifier or pulse. Chip DA1 is mounted on a ribbed heat sink measuring 10x18x38 mm from an industrial device. For good cooling, six holes with a diameter of 6 mm are drilled in the lower and upper walls of the adapter case (orientation when it is plugged into a wall outlet). If output current limiting is not required, resistor R1 and capacitor C3 can be omitted. In this variant, the maximum output current was 0.5 A at a ripple voltage of about 1 mV. By selecting the resistance of resistors R3 and R4, you can assemble a stabilizer for any output voltage within the limits allowed by the adapter transformer. Using a universal adapter, you can make a stabilized power supply with a switchable output voltage. The scheme of the modified adapter "FIRST ITEM NO:57" is shown in Fig.4. The secondary winding of the transformer T1 is fully used, its taps are insulated. Diodes VD5, VD6 - protective [2].
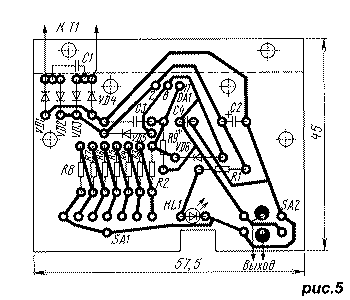
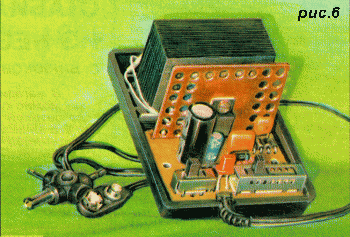
Diodes VD1-VD4, capacitor C2, LED HL1 and switches SA1 and SA2 - from the adapter. Resistors R3-R8 do not have to have the indicated resistances, they can differ in any direction by 1.5 times. It is important that the resistances R3-R7 are equal to each other with an accuracy of 1 ... 2%, and the resistance R8 is twice as large, since they determine the error in setting the output voltages. All elements, except for the transformer T1, are installed on a printed circuit board, the drawing of which is shown in Fig. 5, and the appearance of the device is shown in Fig. 6. For drilling mounting holes and holes for installing switches and LEDs, it is convenient to use the printed circuit board from the adapter used as a stencil. In order to unsolder the switch from the board without damaging it, it is necessary to bend the board by heating several adjacent contacts with a soldering iron at the same time. Moving gradually to other contacts, you can unsolder the entire switch.
The DA1 chip is mounted on a copper plate measuring 52x38x1 mm, which acts as a heat sink. The plate has a flange for mounting on the board, and holes 4 mm in diameter are drilled along its perimeter to provide ventilation. For the same purpose, eight holes with a diameter of 6 mm were drilled in the upper and lower walls of the housing. Setting up the device consists in setting the output voltages without load by a selection of resistors R2 and R9. Resistor R9 can immediately put the resistance indicated on the circuit, and in parallel with it and instead of R2, solder variable resistors with a resistance of 10 kOhm and 56 Ohm, respectively. The resistor connected in parallel with R9 sets the output voltage to 12 V, the resistor R2 - 1.5 V. Since these settings are interconnected, they must be repeated several times. After that, fixed resistors with selected resistances are installed, and the resistor is soldered in parallel with R9 from the side of the printed conductors. The stabilized adapter provided an output current of up to 200 mA. At a voltage of 12 V, the current is limited by the appearance of ripples, at lower voltages, by the temperature of the DA1 chip. An increase in the heat sink surface can significantly increase the output current at low output voltages.
Literature
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Coronavirus vaccine in the form of a patch ▪ Kingston SSDNow E50 Solid State Drives ▪ Cartilage tissue in the joints is not updated throughout life ▪ New York Museum of Natural History will remove all human remains from display
▪ section of the site Visual illusions. Article selection ▪ article Marcus Aurelius Antoninus. Famous aphorisms ▪ article Why was the ship's bell called a rynda? Detailed answer ▪ article Vodyanik black. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Graphic equalizer on LA3607. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: