Soundtrack - without wires. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Audio equipment
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
When the soundtrack of television programs interferes with others, you have to use headphones that are included instead of the dynamic head of the TV. There is a more radical way - to connect a frame from a wire stretched along the plinth of the room to the TV instead of a head, and listen to transmissions on a miniature AF signal receiver mounted on headphones.
To get rid of the wires connected to the TV, the author of the published article offers another option - the transmission of 3H signals over the air. By the way, this option will allow you to equip a radio, tape recorder, or any other sound source with a silent listening system.
It is best to implement the proposed system in the VHF band, where it is easy to make a micropower VHF transmitter, and receive its signals on an existing small-sized VHF receiver or player with a VHF band.
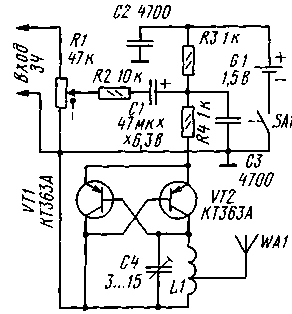
The diagram of a micropower VHF transmitter with frequency modulation is shown in fig. 1. It is a single-ended multivibrator with an L1C4 frequency setting circuit. This scheme is well known to radio amateurs involved in the design of transceiver equipment; it is used in the design of smooth range master oscillators (GPA).
A distinctive feature of generators based on this circuit is the ability to operate at high frequencies at very low currents and voltages.
One galvanic cell with a voltage of 1,5 V is used as a power source for the transmitter. The direct current through the transistors is set by resistors R3, R4. A change in this current leads to a slight change in the frequency of the generated oscillations, therefore, in order to obtain frequency modulation, a 1-hour modulating voltage from the signal source is supplied to the current-setting circuit from resistor R1 through capacitor C2 and resistor R3. The deviation value is regulated by a variable resistor R1, and since it is combined with the SA1 switch, the transmitter is also turned off by it.
The transmitter power is low - less than 1 mW, so it will not create any interference with the radio reception of neighbors, at the same time it is enough for confident reception of its signal within the room. With a supply voltage of 1,5 V, the current consumption is 0,42 mA, which indicates high efficiency and the ability to work from one battery for a long time. The normal deviation is obtained when a 3H signal with an amplitude of 100 mV is applied, the input impedance is 10 kOhm, so you can connect the transmitter to the line output of a TV, tape recorder, radio, etc.
The transmitter remains operational when the supply voltage is reduced to 0,8 ... 0,9 V, i.e. almost until the battery is completely depleted, and the current consumed in this case is 0,07 ... 0,1 mA. A piece of copper wire with a diameter of about 1 mm and a length of 20 cm to 1 m is used as an antenna. The longer the antenna, the larger the zone of reliable reception of the transmitter signal.
All parts of the device are placed on a printed circuit board made of double-sided foil fiberglass. The parts are installed on one side, and the second is left metallized and connected to a common wire along the circuit board in several places. The battery is attached to the same side.
In the device, you can use a variable resistor SPZ-4, SPZ-3 with a power switch, fixed resistors - MLT, S2-33, oxide capacitor - K50, K53, tuning - KT4-25, the rest - KM, KLS, KD. For the VHF-2 range (88 ... 108 MHz), the L1 coil contains seven turns of PEV-2 0,8 wire wound on a mandrel with a diameter of 3,5 mm with a tap from the middle.
Adjust the transmitter in the following sequence. First, choose the range in which it will work - it depends on the receiver used. Then the receiver is tuned to the part of the range that is most free from broadcast radio stations and interference. The transmitter is connected to the line output of a tape recorder or TV and the capacitor C4 tunes it to the frequency of the receiver. Resistor R1 sets the most acceptable frequency deviation, which provides normal volume and minimal distortion. If the volume is not enough even with the upper position of the resistor R1 slider according to the diagram, it will be necessary to reduce the resistance of the resistor R2.
Then they check the coverage area and, if it turns out to be small, increase the length of the antenna to 0,7 m.
The transmitter is placed in a housing (possibly plastic) of suitable dimensions, and a shielded wire with an appropriate connector is used to connect to a TV, tape recorder or other signal source.
If you do not have a small-sized VHF receiver, it is easy to make it using domestic K174XA34, KXA058 microcircuits or their imported counterparts. Several variants of such receivers were described in [1-3].
Literature
1. Gerasimov N. Dual-band VHF receiver. - Radio, 1994, No. 8, p. 6-8.
2. Makarov D. VHF receiver-pack "MARLBORO". - Radio, 1995, No. 10, p. 41-43.
3. Semenov B. A simple VHF receiver. - Radio, 1996, No. 10, p.22,23.
Author: I. Nechaev, Kursk; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Audio equipment.
See other articles Section Audio equipment.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Autonomous fighting robots of the Pentagon
20.06.2013
As part of a pilot initiative called the Autonomous Research Pilot Initiative, work has begun to involve young scientists in the process of creating ground, air and underwater robotic systems with a new level of autonomy. Currently, seven government research groups have already received a total of $45 million to develop new algorithms and equipment that dramatically increase the independence of combat robots. In particular, technologies are being created that will allow combat vehicles to act as a single swarm, continuously exchanging information with each other. Thanks to this, even robots with a primitive "brain" will be able to perform complex tasks, such as continuous monitoring of the region, with automatic distribution of resources within the swarm.
The researchers also plan to improve sensors that provide autonomy, in particular sensors that allow you to move independently over any terrain and quickly respond to changing conditions. The main goal of this program is to give robots the ability to respond to other moving objects (targets) in a rapidly changing environment. Simply put, robots will be able to detect various objects and events and react to them jointly or one by one. This does not always require powerful artificial intelligence, for example, a school of fish moves as a single organism without the use of highly intelligent analysis.
In total there will be 7 different directions in which combat autonomous systems will be improved. So far, special attention is being paid to a group of small cheap robots - this is the direction the US military considers the most promising. Indeed, a swarm of even the simplest autonomous robots can perform a fairly wide range of combat missions, for example, "find a given target, accompany it, carry out target designation." In addition, a swarm of cheap robots is more cost-effective than powerful universal machines. At the same time, robots like the Atlas humanoid terminator will also continue to improve - they will be assigned especially complex and responsible tasks that more primitive machines cannot cope with.
In the coming years, robots will begin to dominate the battlefield, not with the help of high-tech humanoid terminators, but with swarms of small UAVs and ground vehicles that will quickly locate a target, hit it with miniature ammunition or give target designation to artillery and aircraft. Other areas of the Autonomous Research Pilot Initiative include the creation of environmental perception systems, automatic driving systems for armored vehicles, and rapid target acquisition and acquisition.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Chickens talk about geographical discoveries
▪ Smartphone providing free unlimited communication
▪ Female neurons are thinner than male ones.
▪ Cat language inspires scientists to discover new things
▪ DIY robot
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Security and safety. Article selection
▪ article Organic synthesis. History and essence of scientific discovery
▪ article Why King Henry VI of England banned the game of golf? Detailed answer
▪ article Fuel dispenser. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Radiotelephone interface for simplex radio stations. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article BOURNS MULTIFUSE resettable fuses. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: