Device for determining interturn short circuits. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Measuring technology
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
A simple attachment to the avometer, the circuit of which is shown in the figure, makes it possible to detect interturn short circuits of up to three or four turns in transformers, chokes and other parts with windings.
The prefix is a low-frequency generator, assembled according to a three-point scheme, with capacitive feedback through capacitors C1 and C2. The role of the inductance of the generator circuit is played by the tested coil. The potentiometer R4 serves to maintain a constant current flowing through the transistor T1, when the internal resistance of the battery supplying the generator changes. Plugs of the avometer probes are inserted into the sockets Gn1 and Gn2. The probe tips are connected to the terminals of the part to be tested. Socket Gn1 is also a power switch. To do this, it is cut along the entire length. The socket halves are closed with a plug inserted into it, the power is turned on. Single-pole plugs, indicated by arrows at the bottom of the diagram, are included in the avometer sockets for measuring alternating voltage.
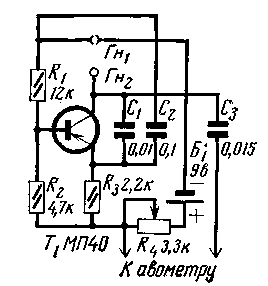
The operation of the device is based on a decrease in the amplitude of the generated voltage when connecting a part with an interturn circuit, since in this case the quality factor of the circuit is significantly reduced. A decrease in voltage is noted by an avometer connected to the device.
The calibration of the assembled device is carried out as follows. Prepare the device for measurements by connecting an avometer and probes to it as described above. Then, a serviceable unified row regulator of the PPC-70 type with a core inserted inside the coil is attached to the probes. By adjusting the potentiometer R4, the avometer shows an alternating voltage value of 1,5 V. Then the probes are disconnected from the PPC-70, the device plugs are removed from the sockets of the avometer, and I measure the collector current of the transistor T1 using the last one. The resulting tone value should be further set using the K4 potentiometer before checking any part. Note the voltage fluctuations. which the avometer will show when connecting other serviceable parts, the avometer readings are tabulated and guided by this table during checks.
Author: V. Dmitriev, Rostov-on-Don; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Measuring technology.
See other articles Section Measuring technology.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Self-degrading plastic from industrial waste
19.10.2020
Scientists from the Fraunhofer Institute for Production Systems and Design Technology (IPK, Germany), in collaboration with partners from the Department of Bioprocess Technology of the Technical University of Berlin, as well as researchers from the USA, Malaysia and Colombia, have developed a process for obtaining plastic from industrial waste that does not require recycling.
A new type of plastic made from recycled waste decomposes quickly in less than a year. A substance that will soon be used for the cleaner production and degradation of mostly disposables is called polyhydroxybutyrate. This innovative material can be produced commercially.
To create it, scientists took the fats remaining after industrial production. Fats contain high levels of minerals. In a special device, bacteria turn the residue into a biopolymer, but this plastic is not yet ready for use, because it needs to harden.
Raw materials must be mixed with chemical additives at the post-production stage. The resulting biopolymer resembles polypropylene in its properties, that is, it can retain heat.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ MAX30102 - pulse and blood oxygen sensor
▪ Construction of the largest neutrino telescope
▪ A new cell type in the human body
▪ Power plant in a button
▪ High-speed optical communication Li-Fi
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Electric meters. Article selection
▪ Article Statistics. Crib
▪ article Who wrote music first? Detailed answer
▪ article Universal stud driver. home workshop
▪ article Brass stamping. Simple recipes and tips
▪ article Norwegian proverbs and sayings. Large selection
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: