
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING A simple quartz filter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Knots of amateur radio equipment. Quartz filters The quartz filter is currently the most convenient frequency-selective element for the IF path of amateur radio receiving and transmitting equipment. The absence of such a filter makes it difficult to design simple structures with satisfactory parameters. Self-manufacturing of quartz filters from individual resonators requires the availability of measuring equipment and certain experience in such work. In general, it takes time, effort and some funds. As a result, according to the author's observations, only a small part of radio amateurs knows how to make quartz filters. According to the author, ladder quartz filters are the easiest to manufacture and have a high repeatability. Figure 1 shows a diagram of a simple four-crystal ladder filter designed and manufactured according to the technique described in [1]. It requires a small number of resonators and has quite acceptable parameters for use in simple transceiver equipment, for example, described in [2, 3]. The author made filters from quartz resonators from the RSIU A-136 (6,180556 MHz) and A-460 (7,680556 MHz) radio stations without their preliminary selection by parameters.
At the same time, the best shape of the frequency response of the filters was obtained with the same capacitances of the capacitors. On this basis, it can be assumed that when using 34 intermediate denominations of quartz with numbers from 136 to 460 of the "A" series, the same results will be obtained. Probably, this statement is also true for quartz of higher and lower frequencies, as well as for quartz of series "B" from number 283 (6,194444 MHz) to number 601 (7,666667 MHz). If quartz resonators of other types are used, as well as for other frequencies, then it is necessary to use the technique [1] for designing quartz filters, and it is imperative to investigate the frequency response of the resulting filter. Figure 2 shows a printed circuit board (view from the side of the conductors), which is the basis for the design of a quartz filter on resonators from the RSIM radio station. It is made of double-sided fiberglass. On the side of the quartz resonators, only conductors are left along the edges, a longitudinal conductor in the center - from edge to edge, and two conductors corresponding to vertical dashed lines.
Before installing quartz resonators, it is necessary to install side walls with a total height of 53 mm by soldering, of which 10 mm are located below the board. In addition, you need to install internal partitions: longitudinal - in the center (top and bottom) and transverse (only top), shown by dashed lines. The lower longitudinal partition has a cutout at the bottom for the conductor connecting the leads of the quartz resonators B2, B3, C3. The side wall is missing only at the top, opposite the entrance and exit. As a result, the filter is inside a shielded housing, which is very convenient for its use in amateur radio practice as a separate unit. Shielding of the quartz filter is necessary not only because the resonators from the RSIM radio station are made in rather large plastic cases, but also because of the need to eliminate interference and signal penetration from the input to the output due to parasitic connections. In the manufacture of the case, any solderable materials can be used, for example, tin or foil fiberglass. You can find out the frequency of a quartz resonator by its number by referring to [4, 5]. Literature 1. Bunin S.G. Yaylenko L.P. Handbook of a radio amateur-shortwave. - 2nd ed., revised. and additional - K .: Technique, 1984, S. 17-25. Author: E. Solodovnikov, Krasnodar; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Micromax Canvas 6 and Canvas 6 Pro smartphones ▪ Owls and silence of propellers ▪ Restored the spirits of the pharaohs
▪ site section Color and music installations. Selection of articles ▪ article Warm the snake on the chest (in the bosom). Popular expression ▪ article What are primary colors? Detailed answer ▪ article Arabic tea. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Backup power supply. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ read in the Free Technical Library article Experiments with ammonia. Chemical experience
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
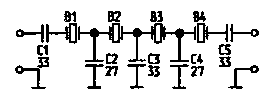

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: