radio path of the transceiver. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Civil radio communications
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
This block is intended for use in a transceiver with a single frequency conversion. A quartz filter is used as the main selection element [1].

Fig.1 (click to enlarge)
In the receive mode, the GPA signal is applied to the winding 1 of the transformer T1. At the connection point of the windings II and III of this transformer, a signal is supplied from the band-pass filters. On diodes VD1 - VD4, having assembled the first balanced mixer. The IF signal (2 MHz) selected on the L1, C9,05 circuit is amplified by the first IF stage (VT1), filtered by a quartz filter, amplified by the second IF stage (VT2) and then enters the second balanced mixer. It also receives a signal from a reference quartz local oscillator (9,05 MHz). The LF signal is fed through the Dr2S20 to the ULF. An AGC cascade is assembled on the VT3 transistor. R18 adjusts the IF gain. In the transmission mode, relays K1 - K3 are activated. In this case, the signal from the reference quartz local oscillator (1 MHz) is applied to the winding 1 T9,05.
A signal from a microphone amplifier is fed to the midpoint of the winding T1. Carrier suppression is carried out by adjusting the resistor R1. The DSB signal is amplified by transistor VT1. The quartz filter highlights one sideband. The amplified SSB signal (transistor VT2) is fed to the second balanced mixer. The GPA signal is also supplied here. From the midpoint T4, the signal enters the FSS radio frequency of the corresponding range.

Relays - mode switches
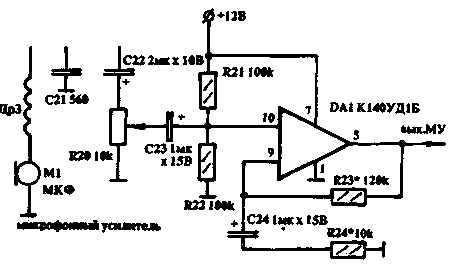
microphone amplifier
Winding data are given in table. one.
| Designations according to the scheme | Number of turns | Wire brand | frame | Core | Note |
| L1 | 10 | PELSHO-0.16 | 5 mm | from SB-12 | Over L2 |
| L2, L3, L5 | 29 | PELSHO-0.16 | 5 mm | from SB-12 | coil to coil |
| L4 | 15 | PELSHO-0.16 | 5 mm | - | Over L3 |
| L6 | 10 | PELSHO-0.16 | 5 mm | - | Over L3 |
| T1 - T4 | 10 + 10 + 10 | PELSHO-0.24 | K7x4x2 | 2 rings 50 HF | coil to coil |
| Dr1, Dr2, Dr3 | 180 | PEL-0.16 | MLT 0.25 1 MΩ | - | in bulk |
A drawing of a printed circuit board and the placement of parts on it are shown in Fig. 2
Literature
1. The best designs of the 31st and 32nd exhibitions of radio amateurs in 1989. Transceiver "Ural-84". - M.: DOSAAF USSR, S.61.
Author: V.Rubtsov (UN7BV ex UL7BV), Tselinograd, Radio Amateur 2/94, p.48-49
 See other articles Section Civil radio communications.
See other articles Section Civil radio communications.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Switches Qnap Systems QSW-2104
05.06.2021
Qnap Systems introduced a series of network switches QSW-2104. The series is formed by the QSW-2104-2S and QSW-2104-2T models. Both of them are six-port - with two 10GbE ports and four 2.5GbE ports, and the difference is that the QSW-2104-2S model has 10GbE ports routed to SFP + fiber optic transceivers, while the QSW-2104-2T model has connectors designed for twisted-pair copper connection.
In the first case, speeds of 10 Gb/s and 1 Gb/s are supported, and in the second - 10 Gb/s, 5 Gb/s, 2,5 Gb/s, 1 Gb/s and 100 Mb/s. The 2.5GbE ports in both cases are designed for twisted pair connection and support speeds of 2,5 Gb / s, 1 Gb / s and 100 Mb / s.
With plug-and-play support, a near-silent passively cooled design, IEEE 802.3az specification compliance, and automatic loop detection and blocking, the QSW-2104 series is "the ideal choice for creating an affordable high-speed networking environment in homes and workplaces." ".
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ 3D ceramic tableware printer
▪ Daylight Savings Time is Dangerous
▪ Ultra-fast FRAME camera
▪ Cold is more dangerous than heat
▪ 60V and 75V MOSFETs for Synchronous Rectification Circuits
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Indicators, sensors, detectors. Article selection
▪ article Like a thief in the night. Popular expression
▪ Article What Space Shuttle Parts Was NASA Buying on eBay in 2002? Detailed answer
▪ article Car mechanic. Job description
▪ article 9 element Swan antenna at 144 MHz. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Production of high power toroidal magnetic circuits at home. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: