
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING ISDN network. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Telephony An excerpt from the Cisco Internetworking Technology Overview. Translation by Vladimir Pleshakov. You can find the complete document on the Mark-ITT server, cisco.udm.ru/ITO. Bibliographic reference The name Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) refers to the set of digital services that are made available to end users. ISDN involves the digitization of the telephone network so that voice, information, text, graphics, music, video signals and other material sources can be transmitted to the end user over existing telephone wires and received by him from a single end user terminal. The proponents of ISDN paint a picture of a worldwide network much like today's telephone network, except that it uses digital signal transmission and introduces a variety of new services. ISDN is an attempt to standardize subscriber services, user/network interfaces, and network and internetwork capabilities. The standardization of subscriber services is an attempt to guarantee a level of interoperability on an international scale. The standardization of the user/network interface encourages the development and marketing of these interfaces by third party manufacturers. The standardization of networking and internetworking capabilities helps achieve the goal of possible worldwide interconnection by making it easy for ISDN networks to communicate with each other. ISDN applications include high-speed image processing systems (such as Group 1V facsimiles), additional telephone lines in homes to serve the telecommuting industry, high-speed file transfer, and video conferencing. Voice transmission will undoubtedly become a popular application for ISDN. Many commercial networks are starting to offer ISDN at prices below the tariffs. In North America, commercial Local-exchange carrier (LEC) networks are starting to provide ISDN services as an alternative to the T1 connections that currently carry most of the "wide-area telephone service" (WATS) services. service). ISDN components ISDN components include terminals, terminal adapters (SLTs), network termination devices, line termination equipment, and switch termination equipment. There are two types of ISDN terminals. Dedicated ISDN terminals are called "terminal equipment type 1" (terminal equipment type 1) (TE1). Terminals not designed for ISDN, such as DTEs that predated the ISDN standards, are referred to as "terminal equipment type 2" (TE2). TE2 terminals are connected to the ISDN network through a digital communication line of four twisted pairs of wires. TE1 terminals are connected to the ISDN network via a terminal adapter. An ISDN Terminal Adapter (TA) can be either a stand-alone device or a board inside the TE2. If the TE2 is implemented as a standalone device, then it connects to the TA via a standard physical layer interface (eg EIA2, V.232 or V.24). The next connection point in the ISDN network outside the TE1 and TE2 devices is NT1 or NT2. These are network termination devices that connect a four-wire subscriber installation to a traditional two-wire LAN loop. In North America, the NT1 is a "customer premises equipment" (CPE) device. In most other parts of the world, NT1 is part of the network provided by commercial communications networks. NT2 is a more sophisticated device that is commonly used in "private digital exchanges with access to the public network" (PBX), and performs the functions of Layer 2 and 3 protocols and data concentration services. There is also an NT1/2 device; it is a separate device that combines the features of NT1 and NT2. ISDN has a set number of breakpoints. These breakpoints define logical interfaces between functional groupings such as TA and NT1. The ISDN reference points are "R" (reference point between non-specialized ISDN equipment and SLT), "S" (reference point between user terminals and NT2), "T" (reference point between NT1 and NT2 devices) and "U" (reference point between NT1 and NT1 devices). point between NTXNUMX devices and line termination equipment in commercial communications networks). The "U" breakpoint is only relevant to North America, where the NTXNUMX feature is not supported by commercial networks. On Fig. Figure 11-1 shows "Sample ISDN Configuration". The figure shows three devices connected to an ISDN switch located in a central office. Two of these devices are ISDN compatible, so they can be connected to NT2 devices through the "S" breakpoint. A third device (a standard, non-ISDN-specific phone) connects to the SLT through the "R" reference point. Any of these devices can also be connected to an NT1/2 device, which replaces both NT1 and NT2 devices. Similar user stations (not shown) are connected to the rightmost ISDN switch.
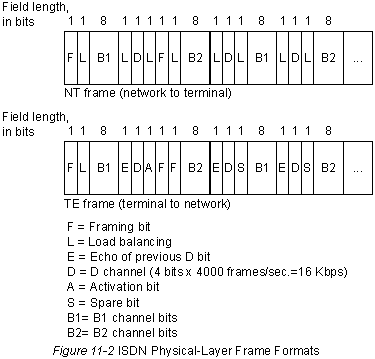
ISDN Services Basic Rate Interface (BRI) services provided by ISDN offer two B-channels and one D-channel (2B+D). The BRI B-channel service is carried out at a rate of 64 Kb/sec; it is intended to carry control and signaling information, although it may support the transmission of user information under certain circumstances. The D-channel signaling protocol includes Layers 1-3 of the OSI reference model. BRI also provides markup management and other overhead operations, with a total bit rate up to 192 Kb/s. The BRI physical layer specification is CCITT 1.430. ISDN Primary Rate Interface (PRI) services offer 23 B-channels and one D-channel in North America and Japan, providing a total bit rate of 1.544 Mbps (PRI-D-channel operates at 64 Kbps). /sec). PRI ISDN in Europe, Australia and other parts of the world provides 30 B-channels and one 64 Kb/s D-channel and a total interface speed of 2.048 Mb/s. The PRI physical layer specification is CCITT 1.431. Level 1 The ISDN Physical Layer (Layer 1) data block formats differ depending on whether the data block is sent out of the terminal (from the terminal to the network) or inward (from the network to the terminal). Both types of physical layer data block are shown in Fig. 11-2 "ISDN Physical Layer Data Block Formats". The data blocks are 48 bits long, of which 36 bits represent information. The "F" bits provide synchronization. The "L" bits adjust the average value of the bit. The "E" bits are used to resolve conflicts when multiple terminals on a passive bus claim the same channel. Bit "A" will enable devices. Bits "S" have not yet been assigned. Bits "B1", "B2" and "D" are for user data.
Physically, many ISDN user devices can be connected to the same circuit. For such a configuration, collisions may result from two terminals transmitting at the same time. Therefore, ISDN provides a means to detect conflicts in the communication channel. When an NT device receives a D bit from a TE, it echoes that bit back to the adjacent E-bit position. The TE expects the adjacent E bit to be the same as the D bit it transmitted in the last transmission. The terminals cannot transmit on the D-channel until they recognize a specific number of ones (indicating "no signal") corresponding to a predetermined priority. If the TE detects any bit on the channel with an echo (E) different from its D bits, it shall stop transmitting immediately. This simple trick is to ensure that only one terminal can transmit its D-messages at a time. After the successful transmission of the D-message, the priority of this terminal is lowered by requiring it to detect more consecutive ones before transmission. Terminals may not be prioritized until all other devices on the line have had a chance to send a D-message. Telephony communications have higher priority than all other services, and signaling information has higher priority than non-signaling information. Level 2 Layer 2 of the ISDN signaling protocol is the Link Access Procedure, D channel, also known as LAPD. LAPD is similar to "High Level Data Link Control" (HDLC) and "Balanced Link Access Procedure" (LAPB) (see Chapter 12 "SDLC and its derivatives" and Chapter 13 "X.25" for more details). about these protocols). As can be seen from the expansion of its acronym, LAPD is used in the D-channel in order to ensure the flow and corresponding reception of control and signaling information. The LAPD data block format (see Figure 11-3) is very similar to the HDLC format; as well as HDLC, LAPD uses a supervisor data block, informational and unnumbered data blocks. The LAPD protocol is formally defined in CCITT Q.920 and SSITT Q.921.
The flag and control fields of the LAPD are identical to those of the HDLC. The length of the "address" field of the LAPD may be one or two bytes. If the extended address (EA) bit is set in the first byte, then the address consists of one byte; if it is not set, then the address consists of two bytes. The first byte of the address field contains a service access point identifier (SAPI) that identifies the main entry at which LAPD services are provided to Layer 3. The C/R bit indicates whether the data block contains a command or response signal. The "terminal end-point identifier" (TEI) field indicates whether the terminal is single or multiple. This identifier is the only one listed above that indicates a broadcast. Level 3
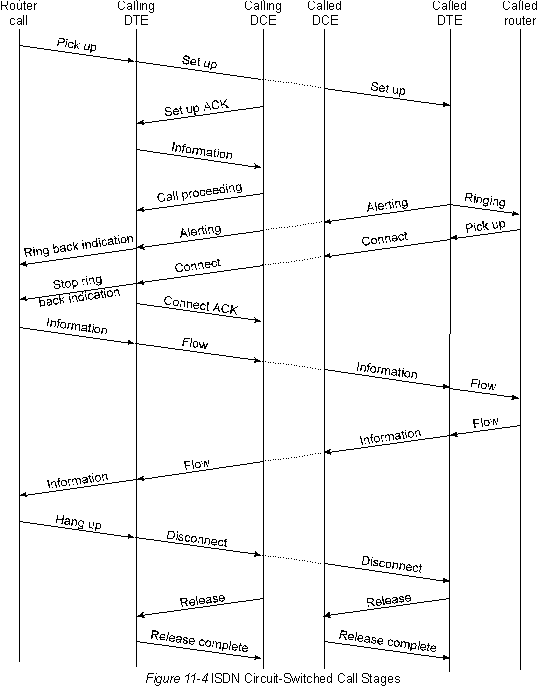
Two Layer 3 specifications are used for ISDN signaling: CCITT 1.450 (also known as CCITT Q.930) and CCITT 1.451 (also known as SSITT Q.931). Together, both of these protocols provide user-to-user, circuit-switched, and packet-switched connections. They define a variety of messages for organizing and completing a call, informational and mixed messages, including SETUP (INSTALLATION), CONNECT (CONNECT), RELEASE (DISCONNECT), USER INFORMATION (USER INFORMATION), CANCEL (CANCEL), STATUS (STATUS) and DISCONNECT. These messages are functionally similar to the messages provided by the X.25 protocol (see Chapter 13 "X.25" for more details). Figure 11-4, taken from the CCITT 1.451 specification, shows the typical stages of dealing with ISDN circuit switching. Publication: cxem.net
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ As temperatures rise, so does the appetite of insect pests. ▪ Water found on distant planets ▪ Application of Ara Modular Smartphone Components for Wearable Electronics ▪ Sony IMX224MQV image sensor with record-breaking light sensitivity
▪ section of the Antenna website. Article selection ▪ article Extender-long-liver. Tips for the home master ▪ article Where did the British fight the French during World War II? Detailed answer ▪ article Working on a chamfering machine. Standard instruction on labor protection
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: