
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Thyristor voltage regulators. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
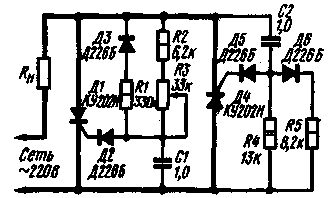
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Regulators of current, voltage, power With amplitude-phase control In the controller, the circuit of which is shown in Fig. 1, two trinistors are used, opening one into positive and the other into negative half-cycles of the mains voltage. The operating voltage at the load Rн is regulated by a variable resistor R3.
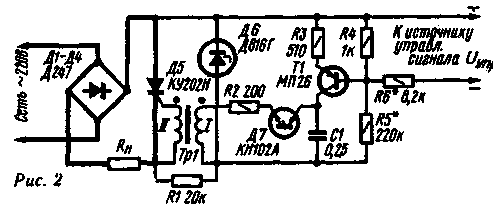
The regulator works as follows. At the beginning of the positive half-cycle (plus on the top wire according to the circuit), the trinistors are closed. As the mains voltage increases, the capacitor C1 is charged through resistors R2 and R3. The increase in voltage across the capacitor lags (shifts in phase) from the network by an amount that depends on the total resistance of resistors R2 and R3 and the capacitance of capacitor C1. The charge of the capacitor continues until the voltage across it reaches the threshold for opening the trinistor D1. When the trinistor opens, a current will flow through the load Rn, determined by the total resistance of the open trinistor and Rn. Trinistor D1 remains open until the end of the half cycle. By selecting the resistor R1, the desired control limits are set. With the values of resistors and capacitors indicated in the diagram, the voltage at the load can be changed within 40-220 V. During the negative half-cycle, the trinistor D4 works similarly. However, capacitor C2, partially charged during a positive half-cycle (through resistors R4 and R5 and diode D6), must be recharged, which means that the turn-on delay time of the trinistor must be large. The longer the trinistor D1 was closed during the positive half-cycle, the greater the voltage will be on the capacitor C2 by the beginning of the negative and the longer the trinistor D4 will be closed. The common-mode operation of trinistors depends on the correct selection of the values of the elements R4, R5, C2. Load power can be any in the range from 50 to 1000 watts. Author: I. Chushanok, Grodno Pulse-phase controlled The regulator, the circuit of which is shown in fig. 2, controlled automatically by Uynp signal. The regulator uses two thyristors - trinistor D5 and dinistor D7. The trinistor opens with pulses that are formed by a chain consisting of a D7 dinistor and a capacitor C1. At the beginning of each half-cycle, the trinistor and dinistor are closed and the capacitor C1 is charged by the collector current of the transistor T1. When the voltage on the capacitor reaches the opening threshold of the dinistor, it will open and the capacitor will quickly discharge through the resistor R2 and the primary winding of the transformer Tr1. A current pulse from the secondary winding of the transformer will open the trinistor. In this case, the control device will be de-energized (since the voltage drop across the open trinistor is very small), the dinistor will close. At the end of the half-cycle, the trinistor will turn off and with the beginning of the next half-cycle, a new cycle of the regulator will begin.
The delay time of the pulse that opens the trinistor, relative to the beginning of the half-cycle, is determined by the charge rate of the capacitor C1, which is proportional to the collector current of the transistor T1. By changing the control voltage Uynp, you can control this current and, ultimately, regulate the voltage across the load. The signal source Uynp can be a bandpass filter (with a rectifier) of a color and music installation, a software device. In automatic control systems, feedback voltage is used as Ucontrol. Resistor R5 must be selected so that when Uynp=0, the trinistor opens in each half-cycle at a time close to the end of the half-cycle. In order to switch to manual control, it is enough to replace the resistor R5 with a series chain of a variable resistor and a constant resistance of 10-12 kOhm. The stabilization voltage of the zener diode D6 should be 5-10 V more than the maximum turn-on voltage of the dinistor. Transistor T1. can be any of the MP21, MP25, MP26 series. Dinistor can be applied types KN102B, D227A, D227B, D228A, D228B. Resistor R1 is made up of two 2 watt resistors. The pulse transformer Tr1 is wound on a ring core with dimensions of 26X18X4 mm, made of permalloy 79NMA (or the same section of ferrite M2000NM1). Winding I contains 70 turns, and winding II - 50 turns of PEV-2 wire 0,33 mm. Interwinding insulation must withstand a voltage close to the mains voltage. Instead of a dinistor in the regulator, you can use a transistor operating in avalanche mode. The operation of transistors in this mode was described in detail in "Radio", 1974, No. 5, pp. 38-41. A diagram of one of these regulators is shown in fig. 3.
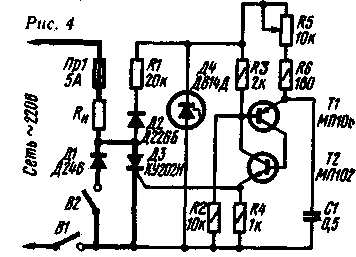
According to the principle of operation, a regulator with a transistor operating in an avalanche mode does not differ from the previous one. The used transistor type GT311I has an avalanche breakdown voltage of about 30 V (with a resistance of resistor R3 equal to 1 kOhm). In the case of using other transistors, the values \u4b\u5bof the elements R1, RXNUMX, CXNUMX will need to be changed. Other transistors can be used in the regulator (Fig. 3), including pnp structures, for example P416. In this case, it is necessary at the transistor T1 (see Fig. 3) to swap the conclusions of the emitter and collector. Resistor R3 in all cases must be connected between the base and the emitter. The load voltage is regulated by a variable resistor R4. Author: Ing. E. Furmansky, Moscow With analogue unijunction transistor In the controller, the circuit of which is shown in Fig. 4, the phase-pulse method of controlling the trinistor is applied. In the control device of the regulator, a transistor analogue of a single-junction transistor (two-base diode) is used. You can read about the operation of unijunction transistors in "Radio", 1972, No. 7, p. 56.
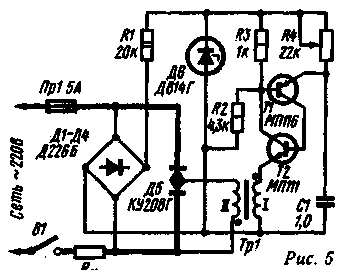
The power circuit of the regulator is built in the same way as that of the regulator published in Radio, 1972, No. 9, p. 55. With open contacts of switch B'2, the effective value of the voltage at the load can be changed in the range from a few volts to 110 V, and with closed contacts - from 110 to 220 V. According to the principle of operation, the control device of the described regulator does not differ from devices on a dinistor or avalanche transistor (Fig. 2 and 3). The power supplied to the load is regulated by a variable resistor R5. Trinistor DZ and diode D1 are installed on a common radiator with an area of 50-80 cm2. Resistor R1 is made up of two 2W resistors. Author: V.Popovich, Izhevsk. On triac The described regulator is built according to the phase-pulse regulation scheme using a triac (symmetric thyristor). The controller circuit is shown in fig. 5. The control device uses a transistor analogue of a n-type unijunction transistor.
When the regulator is turned on (by switch B1), the transistors T1 h T2 are closed and the capacitor C1 begins to charge through the resistor R4 (with which the power dissipated at the load Rn is regulated). The charge continues until the voltage across the capacitor exceeds the opening threshold of the transistor T1. At this point, the transistors open and go into saturation mode. The capacitor quickly discharges through them to the primary winding of the pulse transformer Tr1. The current pulse from the secondary winding opens the triac D5. The threshold for opening transistors is determined by the resistances of the divider resistors R2R3. The pulse transformer Tr1 is wound on a ferrite ring M2000NM1-15, size K20x 12x6. Winding I contains 50 turns, and II - 30 turns of PELSHO wire 0,25 mm. Capacitor C1 - MBM with an operating voltage of 160 V. The maximum allowable load current of the regulator is 5 A. The voltage regulation limits are from several volts to 215 V. Authors: V.Ponomarenko, V.Frolov Voronezh With improved control characteristic In thyristor regulators with pulse-phase control, the voltage on the capacitor of the RC circuit increases exponentially during its charge. With a sinusoidal form of the mains voltage, the control characteristic, which expresses the dependence of the voltage on the load on the resistance of the variable resistor, turns out to be sharply non-linear, which makes it difficult to smoothly adjust the voltage on the load.
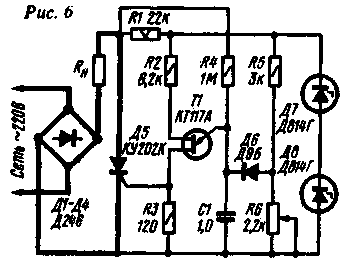
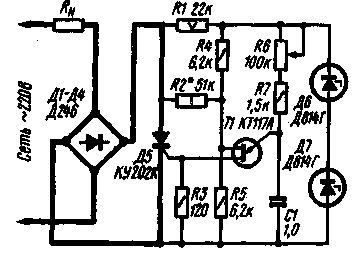
The thyristor regulator, the circuit of which is shown in fig. 6 is largely free from this shortcoming. The regulator uses a unijunction transistor. The improvement in the linearity of the control characteristic is achieved by the fact that the capacitor C1 is charged from the mains voltage (through resistor R4) and simultaneously from a source of constant stabilized voltage (through divider R5R6 and diode D6}. By changing the level of constant voltage with resistor R6, you can control the moment of opening the trinistor and, therefore , voltage on the load Diode D6 eliminates the possibility of discharging the capacitor through the resistor R6. The resistance of the resistor R4 is chosen so that when the resistor R6 is short-circuited, the voltage across the load is minimal. Then, at the lowest (according to the scheme) position of the engine of the resistor R6, the voltage at the load will be maximum. With output voltage stabilization A feature of the described regulator is the ability to stabilize the voltage at the load when the mains voltage changes. The control device is built on a single-junction transistor according to the phase-pulse control circuit (see Fig. 7).
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Google robot to replace service dog ▪ 2kW Great Wall GW-EPS2000DA Power Supply ▪ Photosynthetic engine for artificial cells ▪ Rockets five times faster than sound ▪ 12 new satellites discovered around Jupiter
▪ section of the site Videotechnique. Article selection ▪ article Bad is the soldier who does not dream of being a general. Popular expression ▪ article How can you castle vertically in chess? Detailed answer ▪ article Labor Economist. Job description
Comments on the article: Vladimir Thank you for being. a guest Found, familiarized. Received, works well, thanks
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: