Chips K174KN1, K174KN2. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Application of microcircuits
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
K174KN1
Designed to work in the program selection unit of television receivers with electronic channel selectors as an eight-channel voltage switch.
Housing type 238.16-2
The mass of the microcircuit is not more than 1,5 g
Functional diagram
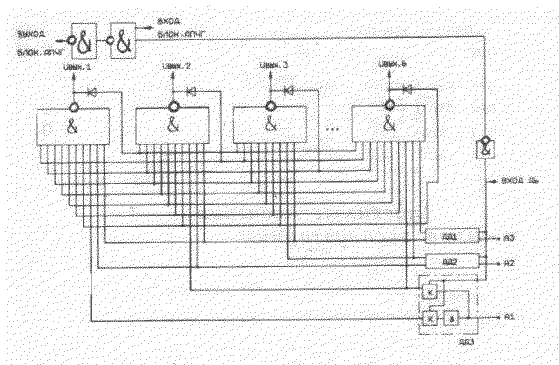
DD1, DD2, DDZ - logic diagram
o - inversion
& - multiplier of the "AND" function
Pin assignment
| 1 |
Blocking input APCG |
| 2 |
1 channel output |
| 3 |
General conclusion |
| 4,5,6 |
Output 3, 5, 7 channels |
| 7,8,9 |
Entrance A1,A2,AZ |
| 10 |
Supply voltage |
| 11, 12, 13, 14 |
Output 8, 6, 4, 2 channels |
| 15 |
Remote control input |
| 16 |
APCG blocking output |
Main technical characteristics under normal climatic conditions
|
No more |
| Consumption current, mA |
8 |
| Analog output leakage current, uA: |
|
| channels 1-8 |
4 |
| on conclusion 16 |
3 |
| Input current, mA: |
|
| high level |
0,5 |
| low level |
0,5 |
| Residual voltage, V: |
|
| channels 1-8 |
0,5 |
| on output 1 6 |
0,5 |
Maximum permissible values of operating modes
Possible change in ambient temperature from minus 10 to plus 70°C.
|
no less |
No more |
| Supply voltage |
10,8 |
13,2 |
| Switched voltage, V: |
|
|
| on pins 1-8 |
10,8 |
33 |
| at pin 16 |
- |
13.2 |
| Input voltage of control inputs, V: |
|
|
| high level |
10,8 |
13,2 |
| low level |
0 |
4,0 |
| Switched current, mA.: |
|
|
| at pin 1 6 |
- |
15 |
| channels 1-8 |
- |
20 |
Typical switching circuit in a control unit with push-button and remote control with random access
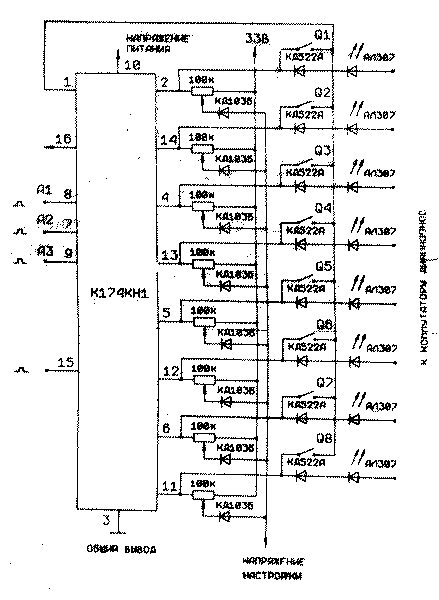
Switching of the microcircuit is carried out by closing the selected output with pin 1 in the push-button control mode for at least 1 ms, or with a three-digit binary code on pins 7, 8, 9 in the remote control mode in the presence of a control voltage at pin 15. The state of the microcircuit is saved after the control switches are turned off. voltages from the indicated inputs.
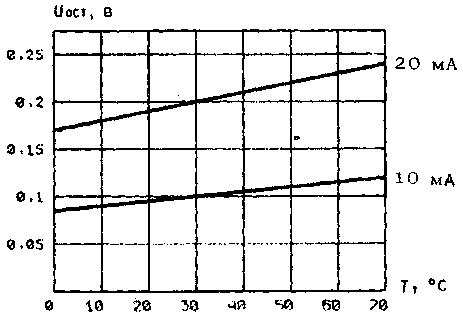
Residual stress versus temperature
environment at various switching currents
K174KH2
Designed to work in the program selection unit of television receivers with electronic channel selectors as a voltage switch for eight outputs, controlled by outputs and a three-digit binary code by address control inputs, as well as allowing the ring switching mode of channels by a sequence of pulses applied to its control input.
Housing type 238.16-2.
Macca microcircuits not more than 1,5 g
Functional diagram

DD1, DD2, DD3 - logic circuit (click to enlarge): o - inversion; & - multiplier of the "AND" function
Pin assignment
| 1 |
Blocking input APCG |
| 2 |
Channel 1 output |
| 3 |
General conclusion |
| 4,5,6 |
3,5,7 channel output |
| 7,8,9 |
Entrance A1, A2, AZ |
| 10 |
Supply voltage |
| 11,12, 13,14 |
8,0,4,2 channel output |
| 15 |
Remote control input |
| 16 |
APCG blocking output |
Main technical characteristics under normal climatic conditions
|
No more |
| Consumption current, mA |
10 |
| Analog leakage current |
|
| output, uA: |
|
| channels 1-8 |
4 |
| on conclusion 16 |
3 |
| Input current, mA: |
|
| high level |
0,5 |
| low level |
0,5 |
| Residual voltage, V: |
|
| channels 1-8 |
0,5 |
| by conclusion. 16 |
0,5 |
Maximum permissible values of operating modes
Possible change in ambient temperature from minus 10 to plus 70°C.
|
no less |
No more |
| Supply voltage, V: |
|
|
in a mode that allows both local and
remote control |
10,8 |
13,2 |
| in local control only mode |
9,0 |
13,2 |
| Switched voltage. AT: |
|
|
| at pin 16 |
1 |
13,2 |
| channels 1-8 |
9,0 |
33 |
| Input voltage of control inputs, V: |
|
|
| high level |
10,8 |
13,2 |
| low level |
0 |
4 |
| Switched current, mA: |
|
|
| channels 1-8 |
- |
20 |
| at pin 16 |
- |
15 |
Typical switching circuit in the control unit with push-button and remote control with random access and ring count
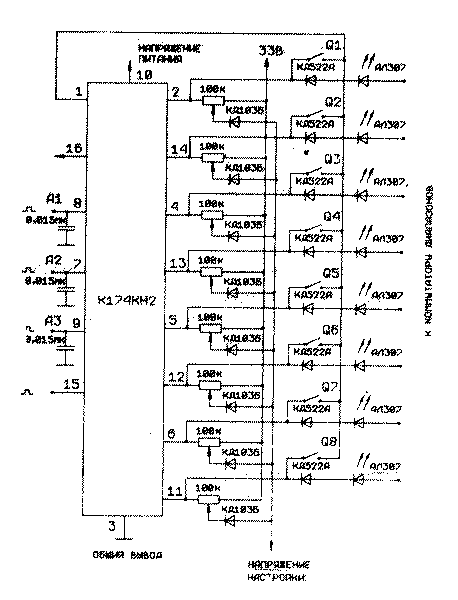
Switching of the microcircuit is carried out by closing the selected output with pin 1 in push-button control mode for at least 1 ms, or with a three-digit binary code on pins 7,8,4 in remote control mode in the presence of a control voltage at pin 15, a sequence of single pulses on pin 15 in the ring switching mode of channels, and the capacitors on pins 7,6,9 are connected only in the last of the modes. The state of the microcircuit after switching off the control voltages of the indicated inputs is saved.
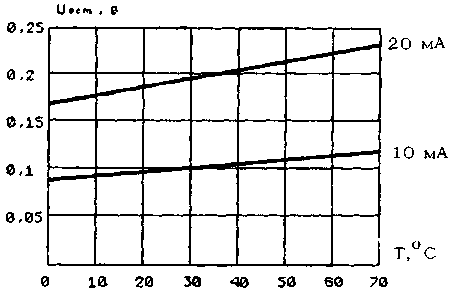
Dependence of the residual voltage on the ambient temperature at different values of the switching current
The material was prepared by Dmitry Marchenko; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Application of microcircuits.
See other articles Section Application of microcircuits.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Bread with invisible fibers will improve well-being
30.11.2022
Researchers at Australia's RMIT University have teamed up with technology company Microtec Engineering Group, which supplies starch processing equipment, to develop a fiber-digesting product.
This is how FiberX was born, a flavorless functional fiber that can be added to low fiber foods such as white bread, cakes, pasta, pizza and sauces.
To get the innovative invisible fiber, project leader from the RMIT Center for Food Research and Innovation Asghar Farahnaki and his team used advanced starch modification technology with approved food materials.
FiberX is considered bland and tasteless, but it is also suitable for fortifying low calorie, low glycemic foods.
"Now we can add extra fiber to foods like white bread without changing the taste or texture, which is one of the biggest problems with many commercially available fiber supplements today," Farahnaky says.
Bread with up to 20% added fiber tastes indistinguishable from any other. But the product becomes more useful and nutritious.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Alternative to traditional touch screens
▪ Updated NFC specification
▪ WiFi Mesh System Xiaomi Mesh Router Suits
▪ Synthesis of bones and enamel
▪ LeMaker Cello Developer Board
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Batteries, chargers. Article selection
▪ article Biological theory of fermentation. History and essence of scientific discovery
▪ article Which fictional race owes its appearance to the Beryozka ensemble? Detailed answer
▪ article Eucalyptus round. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Increasing the supply voltage of the output stages of transmitters. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Belarusian proverbs and sayings. Large selection
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese






 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: