
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Saving data in the memory of radio stations. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
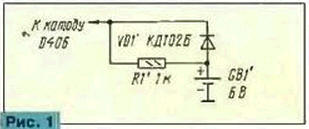
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Civil radio communications Some CB car radios, such as ALAN-48 PLUS, HYGEN 717, have a memory mode that allows you to remember the frequencies of several channels and other parameters when you turn off the radio station with the power switch. However, the information in the memory is retained only until the supply voltage is also turned off. This article describes how to save information in this mode as well. In car radios, even in the off state, the processor memory unit still receives voltage from the on-board network. In this case, all data in the RAM block is saved. This was done in the expectation that the car owners, as a rule, never disconnect the battery. However, most motorists at night, during parking, etc., still turn off the negative battery terminal from the car body ("mass") with a special switch, which leads to a complete de-energization of the processor, i.e. data loss. If car radios are used at home and are powered by a mains power supply, then the power supply must be left on all the time to save data in the processor memory, which is uneconomical. True, you can put up with this, but it should be borne in mind that when you transfer the radio station from the car home or back, when the supply voltage disappears completely, the data from the memory block is lost. When the radio station is operated only in a car, solving this problem is quite simple: you need to install a resistor between the negative terminal of the battery and the body in parallel with the ground switch. The resistance of the resistor can be from several hundred ohms to units of kilo ohms. Such a resistor will not affect the performance of the vehicle's electrical equipment in any way and at the same time will not allow the engine to be started when the battery is disconnected from the ground. This resistor will not burn out because the current through it is limited. When the "mass" switch is off, the entire on-board network is powered through a resistor. For the normal operation of the devices, the current flowing through it is not enough, however, it is enough to feed the processor memory block. Such a simple method can also be successfully used to save data in car radios with processor control. If it is necessary to move the equipment from place to place, the solution to the problem will be to install a small-sized autonomous power source in the radio station case. In the radio station ALAN-48 PLUS, for the purpose of "recharging" there is a voltage divider R422R423C434 (according to the scheme of the radio station), through which a voltage of 4.. this output through the diode D5 is powered by a voltage regulator on the transistor G406. As an additional source, you can use, for example, several small-sized batteries or galvanic cells connected in series. Then, in standby mode, they would feed the processor memory block, and recharge during operation. Since the current consumed by the processor memory block is about 10 μA in standby mode, small-capacity cells or batteries are suitable. Small-sized D-0,03 batteries are suitable, but it is better to use galvanic cells from wrist watches - they are more reliable and have smaller dimensions. Cells or accumulators (4 in total) must be assembled into one battery and insulated, for example, placed in a case made of insulating material. As such a case, you can use a piece of an old felt-tip pen, fountain pen, etc. The battery is connected to the processor through a resistor R1 'and a diode VD1' in accordance with the circuit in fig. 1. To do this, remove the resistors R422, R423 from the radio station board, and place the battery in any convenient place, securely fastening it.
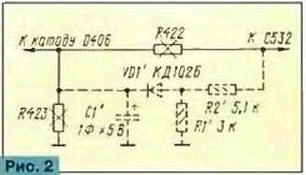
In standby mode, the battery through the diode VD1' will power the processor memory block, and during operation it will be recharged through the resistor R1. In addition, a resistor is needed to protect the voltage regulator on the Q415 transistor from failure in case of possible malfunctions in the battery. The disadvantage of this solution is that the battery of cells or batteries requires periodic monitoring and replacement. And although this will not have to be done often, nevertheless - unnecessary trouble. To avoid this, large capacitors can be used. Suitable, for example, K58-9B, the so-called ionistors. They have a large capacity with relatively small dimensions, have a small leakage current and work well mainly for a high-resistance load, which is the processor memory block. Installing a K58-9B capacitor with a capacity of 1 F for a voltage of 5 V instead of the GB1 battery does not cause any particular difficulties. It is convenient to place it next to the processor by drilling additional holes, or instead of the C434 capacitor. Resistors R422 and R423 are removed from the board. Practice has shown that 2 ... 3 V is enough to power the processor memory block. The capacity of the specified capacitor is enough to save data for several days (up to a week). Therefore, if the radio station is used frequently, even for a short time (for example, within a minute), then during this time the capacitor will be charged and will be ready for a new storage cycle. Despite the large capacity, the charging current of this capacitor will be small - a few tens of milliamps, so there will be no noticeable overload of the stabilizer and it will not have any harmful effect on the operation of the radio station. To increase the data storage time, it is desirable to reduce the capacitor discharge current. To this end, the D406 diode can be replaced with domestic types KD102A, KD102B or KD104A, the reverse current of which does not exceed 0,1 μA. Installing smaller capacitors will result in a proportional reduction in the duration of data storage in the processor's memory. It is possible to combine the power supply of the memory unit from a capacitor and from an external source. In this case, the data will be saved indefinitely due to the power from an external source and for several days after it is turned off. This modification is shown in Fig. 2.
Resistors R422 and R423 are removed and resistors R1', R2, diode VD1' and capacitor C1' are installed in their place. When using an external power source (battery, network unit), the voltage to the memory unit will begin to flow through the voltage divider R1'R2' and the diode VD1' will simultaneously recharge the capacitor C1'. In the absence of external voltage, the memory unit will receive power from the capacitor C1'. Some portable radios also have a memory function. To store data, the memory unit is powered directly from the battery. When the power supply elements are replaced, information is lost. In this case, it is enough to save it for a short time, necessary for the replacement of elements. Therefore, it is possible to install a capacitor type K58 with a much smaller capacity, which takes up less space and fits in a portable radio station. Connecting a resistor in parallel with the ground switch may not help in all cases. For example, if you open the door with the "mass" turned off, the interior lighting lamp will bypass the power of the radio station and the information will be lost. Authors: I. Nechaev, I. Berezutsky, Kursk
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024 Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024 The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
▪ Computer with GTX Titan and liquid cooling ▪ Noctua Cooling Systems with Active Noise Canceling Technology
▪ section of the site Children's scientific laboratory. Article selection ▪ article Northern Minerva. Popular expression ▪ article At what holiday did the British burn cats alive in the 17th century? Detailed answer ▪ article Tricycle Triad-350. Personal transport
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: