
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Civil radio communications
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
You can improve the quality of speech reception by installing a low-pass filter (LPF) in the audio amplifier of your radio or transceiver. The modern elemental base makes it possible to manufacture compact active low-pass filters that can be built into almost any equipment.
Figure 1 shows a fourth-order active low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 3,3 kHz. It is assembled on a two-channel operational amplifier LM358AM. The filter gain is equal to one (0 dB). The filter provides 20 dB of out-of-band rejection at 5 kHz and 40 dB at 8 kHz.
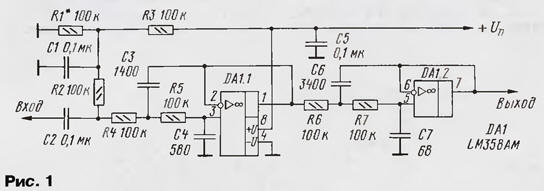
If it is required to manufacture a low-pass filter with a transmission coefficient of more than one, then the filter circuit must be changed, as shown in Fig. 2.

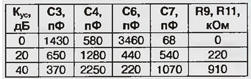
The filter gain is determined by the values of the resistors R9 and R11. The table shows the calculated ratings of the filter elements for various filter gains (for resistors R8 and R10 with a resistance of 100 kOhm). When repeating the device, resistors R4 - R7 and capacitors C3, C4, C6, C7 should be selected with deviations from the required rating of no more than 3 ... 5%. In addition, it is desirable to use capacitors with the lowest possible TKE.
The filter is made by surface mounting on a printed circuit board of double-sided foil fiberglass (Fig. 3).
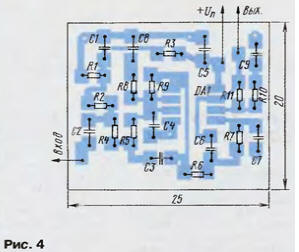
The second side of the board is left metallized and is used as a common wire. A sketch of the board with the elements located on it is shown in fig. 4. The board is designed for mounting a filter with any transfer coefficient. For a filter with a transfer coefficient of 0 dB, resistors R8 and R10, as well as capacitors C8 and C9, are not installed. Jumpers are installed instead of resistors R9 and R11. All capacitors are leadless K10-17 for surface mounting, resistors are P1-12.
The filter requires almost no adjustment. Almost any stabilized source with a voltage of 3 ... 12 V is suitable for its power supply. However, it should be noted that with a supply voltage of less than 9 V, it is necessary to select a resistor R1 to obtain the maximum undistorted output signal. For the LM358AM chip, with a supply voltage of 3 V, the resistance of the resistor R1 should be 62 kOhm. In this case, the maximum amplitude of the undistorted output signal (at a load of 1 kΩ) will be 0,7 V. At a supply voltage of 6 V, it will be 2,5 V, and at 9 V - 5 V. The current consumed by the filter from a 3 V power supply is - approximately 0,5 mA, and at a voltage of 12 V - 0,7 mA.
Other types of parts can be used in the device, for example, the K157UD2 microcircuit (with the corresponding correction circuits), resistors - MLT, S2-33, R1-4, capacitors - KLS, K10-17, KM, but this will entail an adjustment of the topology and board dimensions.
Author: I.Nechaev (UA3WIA)
 See other articles Section Civil radio communications.
See other articles Section Civil radio communications.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
A New Way to Control and Manipulate Optical Signals
05.05.2024
The modern world of science and technology is developing rapidly, and every day new methods and technologies appear that open up new prospects for us in various fields. One such innovation is the development by German scientists of a new way to control optical signals, which could lead to significant progress in the field of photonics. Recent research has allowed German scientists to create a tunable waveplate inside a fused silica waveguide. This method, based on the use of a liquid crystal layer, allows one to effectively change the polarization of light passing through a waveguide. This technological breakthrough opens up new prospects for the development of compact and efficient photonic devices capable of processing large volumes of data. The electro-optical control of polarization provided by the new method could provide the basis for a new class of integrated photonic devices. This opens up great opportunities for ... >>
Primium Seneca keyboard
05.05.2024
Keyboards are an integral part of our daily computer work. However, one of the main problems that users face is noise, especially in the case of premium models. But with the new Seneca keyboard from Norbauer & Co, that may change. Seneca is not just a keyboard, it is the result of five years of development work to create the ideal device. Every aspect of this keyboard, from acoustic properties to mechanical characteristics, has been carefully considered and balanced. One of the key features of Seneca is its silent stabilizers, which solve the noise problem common to many keyboards. In addition, the keyboard supports various key widths, making it convenient for any user. Although Seneca is not yet available for purchase, it is scheduled for release in late summer. Norbauer & Co's Seneca represents new standards in keyboard design. Her ... >>
The world's tallest astronomical observatory opened
04.05.2024
Exploring space and its mysteries is a task that attracts the attention of astronomers from all over the world. In the fresh air of the high mountains, far from city light pollution, the stars and planets reveal their secrets with greater clarity. A new page is opening in the history of astronomy with the opening of the world's highest astronomical observatory - the Atacama Observatory of the University of Tokyo. The Atacama Observatory, located at an altitude of 5640 meters above sea level, opens up new opportunities for astronomers in the study of space. This site has become the highest location for a ground-based telescope, providing researchers with a unique tool for studying infrared waves in the Universe. Although the high altitude location provides clearer skies and less interference from the atmosphere, building an observatory on a high mountain poses enormous difficulties and challenges. However, despite the difficulties, the new observatory opens up broad research prospects for astronomers. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive hydrogen bubble
09.02.2016
Materials scientists do not like hydrogen: even steel walls are not a barrier to this gas. Moreover, once it enters a metal, it manifests its harmful nature: it travels in the form of individual protons, which, having fallen into any discontinuity, can merge into a molecule. The molecule will not leave the discontinuity anywhere, and this is the way to the so-called hydrogen embrittlement. In general, storing hydrogen is difficult. And for hydrogen energy, it is just necessary to receive, store and transport large volumes of hydrogen. It is possible that a polymer that does not let hydrogen through at all will help solve this important problem.
In 2007, David Johnson, then a graduate student at the University of New Mexico, was studying hydrogen-producing microorganisms. In the course of work, he discovered some strange white bubbles in the samples. Interested, Johnson gave them for analysis, and it turned out that hydrogen is inside the bubbles, and it does not fly anywhere from them. At that time, the researcher failed to find out who makes hydrogen bubbles and why.
In 2009, as part of a special university research development program, he met microbiologist Michael Townsend. He read Johnson's dissertation, reproduced his results and found that this biopolymer is made by yeast at a certain combination of sugar concentration, acidity and temperature. After that, Terry Lombard, the director of the intellectual property protection and implementation program, became interested in their work. He helped patent a new polymer called a hydromer and is now looking for partners to develop coatings for hydrogen vessels. Who knows, maybe it is yeast that will help humanity get easily accessible energy.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ microscopic diamond ring
▪ Revealed the secret of non-freezing water on Mars
▪ Surprise encourages exploration
▪ Invulnerable displays from LG
▪ Hybrid iron with vacuum cleaner
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the Antenna website. Article selection
▪ article Philosophy is the servant of theology. Popular expression
▪ article What kind of war began after the defeat in a football match? Detailed answer
▪ article Deputy Director for Economic Affairs. Job description
▪ article Ventilation of the workplace. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Loudspeakers with dipole radiators. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese





 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: