Attachment to a digital voltmeter for measuring resistance. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Measuring technology
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The simplest prefix on a field-effect transistor will allow you to measure resistance with a digital voltmeter. The circuit is a simple current stabilizer.
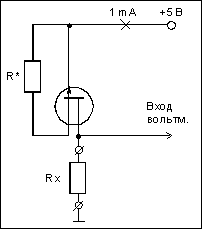
Resistor R* sets the current in the power supply circuit to 1 mA. Field effect transistor - any suitable one.
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Measuring technology.
See other articles Section Measuring technology.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Memristors - electronics of the future
22.09.2012
Recently, new information has appeared indicating that there is very little left before the practical implementation of memristors. Scientists have found a new material for their manufacture - not yet used in this area, inexpensive and at the same time consistent with alternatives.
Every day we use a variety of electronic devices - from radio alarm clocks and programmable food processors to smart computers. Many of them use flash memory. However, few people know that flash technology has almost reached a dead end and is already approaching the limits of available power and small size.
Further we are waiting for even smaller and faster memory drives, but on completely different physical principles - this, perhaps, is precisely the same transparent electronics, the foundations of which were laid at the University of Oregon. This is a resistive random access memory (RRAM), also called a memristor. This is one of the basic passive elements of microcircuits. The principle of its operation is based on hysteresis - that is, the behavior of the system is determined by its prehistory. When a current passes through the memristor, its atomic structure changes and, accordingly, the resistance of the element. Such elements can be smaller, faster and cheaper than modern transistors - the basis of today's electronics.
"Flash memory is attractive because of its low price and the same size, but its potential is gradually drying up," says John Conley, professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the University of Oregon. , or surfing the web on the glass of a coffee table."
Researchers from Ohio State University have confirmed that an inexpensive and environmentally friendly compound - tin-zinc oxide - has a great future in this area and can become the basis of new technologies where computer memory will be based not on the charge of an electron, but on the resistance of a conductor.
Memristors have a simple structure, are able to write and erase information faster, and consume less energy. There has been interest in the private industry for some time to use these new semiconductors in the production of thin film transistors that drive liquid crystal displays. In particular, the so-called. IGZO technology (indium-gallium-zinc-oxide). However, indium and gallium are becoming more and more expensive, and tin-zinc oxide, also a transparent compound, promises to be commercially more promising.
So the day is not far off when any window pane can become a monitor screen.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Super glue for broken bones
▪ 65 thousand plastic flowers
▪ Stem cells - generators of hair follicles
▪ The new Rubik's Cube will teach itself how to solve
▪ HP EliteBook Folio Notebook PC
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Riddles for adults and children. Article selection
▪ article by Samuel Butler. Famous aphorisms
▪ article When is Pi Day celebrated? Detailed answer
▪ article Turn prickly. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Pulse charger. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ Article How much vitamin C is in an apple? Chemical Experience
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: