Sources of bipolar reference voltage
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Reference voltage sources, as a rule, are built according to the parametric principle based on voltage and current stabilizers, such as precision zener diodes, field-effect transistors, etc. To ensure the temperature and time stability of the output parameter, it is necessary that a certain operating current flows through these elements. The required mode is set using ballast resistors and stabilization of the supply current.
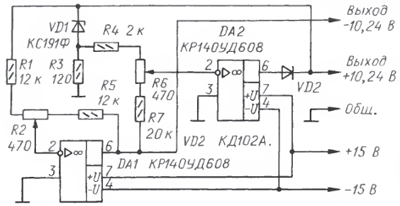
Fig. 1
On fig. 1 shows a diagram of a bipolar reference voltage source based on the stabilization of the static resistance of a precision silicon zener diode VD1 (see L. B. Mashkinov. Reference voltage source. - RF Patent No. 2251139, bull. No. 12, 2005). The device is covered by negative feedback through the operational amplifier DA2. The variable resistor R6 sets the required value of the output positive relative to the common voltage wire. In order for the negative output voltage to be equal to the positive (in absolute value), the inverting follower on the op-amp DA1 must have a transfer coefficient strictly equal to one. This is achieved by a variable resistor R2.
Since the operational amplifiers DA1, DA2 are powered by a bipolar voltage, at the moment the device is turned on, the zener diode VD1 may turn on in the forward - diode - direction, and then the polarity of the output voltage of the source arms will change to reverse. The diode VD2, passing only positive voltage from the output of the op-amp DA2, eliminates the possibility of a polarity reversal.
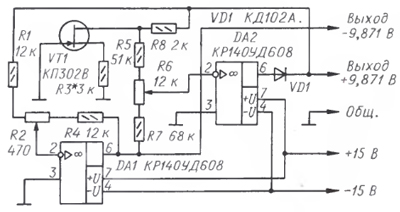
Fig. 2
As the measurements showed, the exemplary source has a temperature and time stability that practically corresponds to the characteristics of the Zener diode VD1. With the output bipolar voltage indicated on the diagram, it was used to power ten-bit DACs and ADCs.
On fig. 2 shows a diagram of a similarly operating exemplary voltage source using a field effect transistor VT1 as an exemplary element. It is known that the characteristic of the transistor indicated in the diagram at a drain current of about 200 μA has a thermally stable point. The required current value is set by selecting the resistor R3. The stability of the output voltage of the source turned out to be almost the same as that of the source on the zener diode.
The load capacity of both sources does not exceed 20 mA.
Such devices can be used in laboratory practice. The use of a more advanced element base (precision zener diodes, op amps with less zero voltage drift and a high gain) will improve the parameters of the described sources.
Author: L. Mashkinov, Chernogolovka, Moscow Region; Publication: radioradar.net
 See other articles Section Power Supplies.
See other articles Section Power Supplies.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive A new way to get airbrushed
03.05.2015
When we talk about something light and weightless, we often use the adjective "air". However, air still has mass, albeit small - one cubic meter of air weighs a little over a kilogram. Is it possible to create a solid material that would occupy, for example, a cubic meter, but at the same time would weigh less than a kilogram? This problem was solved at the beginning of the last century by the American chemist and engineer Stephen Kistler, who is known as the inventor of the airgel.
The 3D-printed macrostructure of the airbrush gives it unique mechanical properties without losing its "graphene" nature. Credit: Ryan Chen/LLNLThe 3D printed macrostructure of airbrushed airbrush gives it unique mechanical properties without losing its "graphene" nature.
Probably, for many, the first association with the word "gel" is associated with some kind of cosmetic product or household chemicals. Although, in fact, a gel is a completely chemical term that refers to a system consisting of a three-dimensional network of macromolecules, a kind of framework, in the voids of which there is a liquid. Due to this molecular framework, the same shower gel does not spread over the palm of your hand, but takes on a tangible form. But it is impossible to call such an ordinary gel airy - the liquid, which makes up most of it, is almost a thousand times heavier than air. This is where the experimenters came up with the idea of how to make an ultra-light material.
If you take a liquid gel, and in some way remove water from it, replacing it with air, then as a result, only a skeleton will remain of the gel, which will provide hardness, but at the same time have practically no weight. This material is called airgel. Since its invention in 1930, a kind of competition has begun among chemists to create the lightest airgel. For a long time, a material based on silicon dioxide was mainly used to obtain it. The density of such silicon aerogels ranged from tenths to hundredths of a gram per cubic centimeter. When carbon nanotubes began to be used as a material, the density of airgels was reduced by almost two orders of magnitude. For example, airgraphite had a density of 0,18 mg/cm3. To date, the palm of the lightest solid material belongs to airbrush, its density is only 0,16 mg / cm3. For clarity, a meter cube made of airbrushed paper would weigh 160 g, which is eight times lighter than air.
However, chemists are driven by far not only sports interest, and graphene as a material for airgels began to be used not by chance. Graphene itself has a lot of unique properties, which are largely due to its flat structure. On the other hand, aerogels also have special characteristics, one of which is a huge specific surface area, which amounts to hundreds and thousands of square meters per gram of substance. Such a huge area arises due to the high porosity of the material. Chemists have already succeeded in combining the specific properties of graphene with the unique structure of airgels, but researchers from the Livermore National Laboratory for some reason also needed a 3D printer to create airbrush.
In order to print airgel, first it was necessary to create a special ink based on graphene oxide. In addition to the fact that they should be airbrushed, it is necessary that such ink be suitable for 3D printing. Having solved this problem, chemists got their hands on a method by which it is possible to produce airbrush with the desired microarchitecture. This is very important, because in addition to the properties inherent in graphene, such a material will also have interesting physical properties. For example, the sample that the authors of the study received turned out to be surprisingly elastic - an airbrushed cube could be compressed ten times without harm to the material, while it did not lose its properties during repeated compression-stretching.
The ability to repeatedly compress distinguishes the printed airbrush from the one obtained by the "usual" way. One of the practical applications of the new airbrush could be flexible electric batteries, where the large inner surface of the material would be used as an electrode, while the printed structure would give it the desired flexibility.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ There is enough wind for energy for everyone
▪ Automation against pirates
▪ Samsung JetBot Robot Vacuum Cleaners
▪ Magnetic resonance imaging of a single atom
▪ Vision cells in the brain determine color and shape
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the website Audiotechnics. Article selection
▪ article Alexandre Dumas (son). Famous aphorisms
▪ article What films and albums were sold on pirated DVDs? Detailed answer
▪ article Tourist product sales manager. Job description
▪ article Replacing the carbon microphone in the phone. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Converter of single-phase mains voltage to three-phase with a frequency of 50 - 400 Hz. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: