
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Redundant power supply, 12/220 volts 180 watts. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
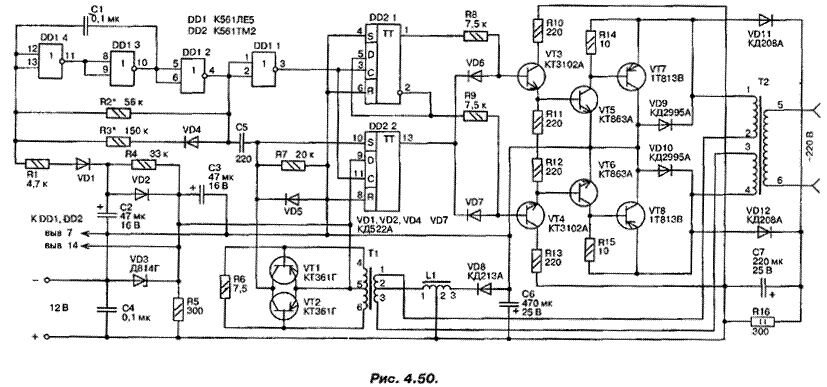
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies In everyday life, especially in rural areas, there are frequent cases when the power supply is suddenly turned off. In such a situation, an emergency power supply can help out. As a primary source for it, a 12 V car starter battery is the most accessible. The energy that it is able to give is quite enough to power a TV, lighting lamp and other household appliances for several hours. When developing an emergency converter, the problem usually arises of obtaining a sinusoidal voltage at its output. But not all energy consumers need it. So, the form of voltage is completely indifferent to incandescent lamps and heating devices, it is important that its effective value is equal to the nominal network value. In the switching power supplies of modern TVs and computers, the alternating voltage is pre-rectified, so it is necessary that its amplitude value be the same as in the network - 1,4 times more effective. The transformer power supplies of many UMZCH, radio receivers and tape recorders made according to traditional schemes are also capable of operating with a non-sinusoidal voltage waveform. The proposed device generates bipolar rectangular pulses with an amplitude of about 300 V with such a duty cycle that their effective voltage is 220 V. The conversion frequency is chosen to be 80 Hz, which somewhat facilitates the operation of power transformers for most consumers. True, at such a frequency those devices in which there are alternating current electric motors - record players, reel-to-reel tape recorders, fans and some others will not work normally. Due to the relatively low voltage of the primary source (12 V), the efficiency of the converter is significantly affected by the voltage drop across the electronic keys used in it. For most silicon transistors, a saturation voltage of more than 1 V is characteristic, for germanium it is much less. Tests have shown that the best results have a key made on a silicon transistor with a reduced saturation voltage - KT863A and germanium - 1T813V. At a current of 10 A, the voltage drop across it does not exceed 0,6 V. The circuit of an emergency converter for powering household equipment from a car battery is shown in fig. 4.50. Main technical characteristics:
A master oscillator is assembled on the DD1 chip. After switching on the supply voltage, the duration of the pulses generated by it is very small. As the capacitor C2 is charged through the resistor R4, it increases to the working one, which ensures a smooth start of the converter. With each pulse of the master oscillator trigger DD2.1 changes state. The signals from its direct and inverse outputs alternately open transistors VT3 and VT4, which control power switches on transistors VT5 ... VT8. Trigger DD2.2 limits the duration of the open state of transistors. The front of the pulse at the output of element DD1.1 sets this trigger to a state corresponding to a high voltage level at output 13. The differentiating circuit C5, R7 generates a pulse that resets the trigger at the end of the master oscillator pulse. The voltage level at output 13 becomes low and, thanks to the diodes VD6 and VD7, one of the transistors - VT3 or VT4, which was open, closes. In operating mode, the signals at pin 13 DD2 and pin 3 DD1 are identical. The voltage on the winding 4-6 of the current transformer T1, loaded with resistor R6, is proportional to the current flowing through the power switches. If it exceeds 1,2 V, one of the transistors - VT1 or VT2 (depending on polarity) - will open and reset the trigger DD2.2. As a result, both power keys will be closed. Thus, overcurrent protection is provided. Inductor L1 limits the rate of current rise through the power switches. When they are closed, the energy accumulated in the magnetic field of the inductor is returned through the VD8 diode to the power source. Diodes VD11, VD12 and the circuit R16, C7 dampen voltage surges on power switches. Low-power converter units are mounted on a single-sided printed circuit board made of foil-coated fiberglass. The location of printed conductors and elements on the board is shown in fig. 4.51.
The power part is made by surface mounting, and the transistors VT7 and VT8 are equipped with heat sinks with an area of 160 cm2. Diodes VD9 and VD10 are installed on the same heat sinks. Most of the details are not subject to strict requirements. As C1, a ceramic capacitor should not be used, the capacitance of which strongly depends on temperature. Transistors VT3 and VT4 must have a current transfer coefficient of at least 60. In the absence of 1T813V transistors, they are replaced with similar ones with a different letter index. In extreme cases, GT806A or P210 can be used, however, the output power of the converter will decrease as a result of such a replacement. It will be necessary to change the current protection threshold by increasing the value of the resistor R6 to 16 ohms. It is not recommended to replace KT863A transistors with others; in extreme cases, it is permissible to use KT863B. The use of transistors with a higher saturation voltage will adversely affect the efficiency of the converter. Diodes KD2995A can be replaced by KD2997, KD2999, KD213A. The current transformer T1 is wound on a W-shaped magnetic core made of electrical steel with a cross section of 0,56 cm2. Winding 1-3 is two turns of copper tape with a width of the frame size and a thickness of 0,1 mm with a tap from the middle, winding 4-6 - 260 turns of PEV-1-0,3 mm wire, also with a tap from the middle. The T2 transformer is made on the basis of the TS-180 from the UNT-47/59 TV. Its network winding serves as an output converter. All secondary windings were removed, in their place two primary windings of 35 turns of PEV-1 wire 01,6 mm each were wound. Any other transformer of suitable power is suitable, having a network winding and two for a voltage of 8 V each. Choke L1 is wound on a ferrite magnetic core Ш16х20 with a non-magnetic gap of 1,1 mm. Its winding 1-2 contains nine turns of wire PEV-1 01,6 mm, and 2-3 - 17 turns of wire PEV-1 01 mm. Setting up the converter comes down to setting the pulse frequency of the master oscillator. It should be equal to 160 Hz with a duty cycle of 2. The generator is tuned without supplying voltage to the power switches. To do this, it is enough to break the conductor connecting terminal 2 of the L1 inductor to the positive pole of the battery. The frequency and duty cycle of the pulses are controlled at pin 3 of the DD1 microcircuit, achieving the desired values by selecting resistors R2 and R3. After that, having restored the power supply circuit of the keys, you should make sure that the effective value of the output voltage is 220 V (it should be measured with a voltmeter of the electromagnetic system, since a conventional avometer will give incorrect readings). By changing the resistance of the resistor R3, it is possible to regulate the output voltage within a small range. Author: Semyan A.P.
Solidification of bulk substances
30.04.2024 Implanted brain stimulator
30.04.2024 The perception of time depends on what one is looking at
29.04.2024
▪ Wind turbine efficiency increased
▪ section of the site Data transfer. Article selection ▪ article by Pierre Teilhard de Chardin. Famous aphorisms ▪ Article What is the difference between income and profit? Detailed answer ▪ article Sikhote-Alin. Nature miracle ▪ article Installation and power wires. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: