
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Resettable fuse Phoenix. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
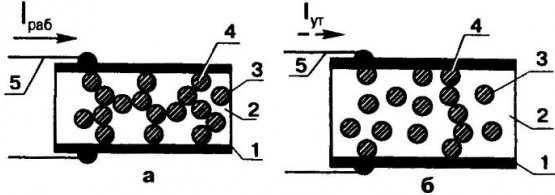
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Protection of equipment from emergency operation of the network, uninterruptible power supplies Current overloads, short circuits in power supply circuits... To protect against this scourge, the equipment uses a tool as old as the world - fuses. Some are mounted in special holder holders, others are soldered into a printed circuit board, which, although it simplifies the design itself, makes it difficult to replace burnt-out “inserts” with serviceable ones. Current overloads, short circuits in power supply circuits... To protect against this scourge, the equipment uses a tool as old as the world - fuses. Some are mounted in special holder holders, others are soldered into a printed circuit board, which, although it simplifies the design itself, makes it difficult to replace burnt-out “inserts” with serviceable ones. Recently, a third type of fuses has become widely available - self-resetting. Like the fabulous Phoenix bird, these protection products for electrical and radio equipment are capable of “self-regeneration”. But not by magic, but thanks to the special properties of an anti-overload plate made of plastic, made on the basis of a crystalline polymer, in the thickness of which a mass of particles of electrically conductive carbon black is dispersed. Both planes of such a plate are coated with metal (spraying) and equipped with wire or tape leads. Under normal operating conditions, carbon particles dispersed in the plastic come into contact with each other and with the sprayed electrodes, creating multiple parallel-series electrical conductive paths for lpa6 (Fig. 1a). However, when a current overload occurs, the phoenix fuse plate heats up. There is a transition of the polymer into an amorphous state and a sharp increase in the volume of the plastic, pushing the carbon grains apart so that only a very small number of conductive chains are preserved (Fig. 1b).
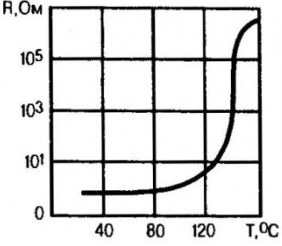
Accordingly, the ohmic resistance of the anti-overload plate increases abruptly, which also depends on temperature (Fig. 2). As a result, the electrical circuit is practically disconnected. This state, which protects the equipment, can last indefinitely; it is maintained by a tiny leakage current lyr.
Of the variety of self-resetting fuses, the most popular among radio amateurs are “phoenixes”, the designation of which includes the abbreviation MF-R (or MF-S) and a number expressing the maximum operating current in tenths of A (see table). They are produced in three typical versions (Fig. 3). Modifications designed to protect batteries from short circuits and overheating during charging are equipped with tape terminals.
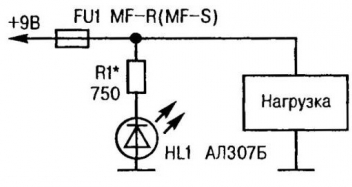
As with fuses with a wire fuse, the speed of the “phoenix” strongly depends on the multiplicity of the overload current relative to Inom. Typical MF-R040, for example, operate in 6 seconds at 0,1 A and ten times faster at 10,5 A. When the reasons that caused the current overload are eliminated, the “phoenix” fuse cools down for some time, returning to its original operating state. Of course, the process of this self-healing is also influenced by the ambient temperature. When protecting the load circuit with such a specific fuse, it is advisable to introduce at least the simplest signaling of its status, for example, using an LED (Fig. 4). The serviceability of the load circuit can be judged by the glow of HL1. When it is turned off protectively, the voltage supplied to the LED indicator drops sharply and HL1 goes out. With the elimination of the damage in the circuit and the cooling of the “phoenix”, the electrical conductivity of the latter becomes high again. An indicator of restoration of functions and readiness of the fuse for operation is the resumption of LED illumination.
The properties of the “phoenix” fuse can be used in the design of a fairly simple circuit breaker for periodically switching on the load (Fig. 5a). When power is applied, switch SA1 unlocks the composite transistor VT1-VT2, in the collector circuit of which there is a winding of the electromagnetic relay K1, which closes contacts 4 and 5. A current begins to flow through the fuse FU1 and the lamp EL1, the magnitude of which is critical for the “phoenix”. After waiting for the time it takes to heat up the anti-overload plate, the fuse trips, causing the composite transistor to turn on and, accordingly, de-energize the relay winding K1. Contacts 4 and 5 open, disconnecting the load - lamp EL1. After the plate cools down (and therefore self-healing of the “phoenix”), the composite transistor VT1-VT2 opens again, and the whole process is repeated.
Main characteristics of self-restoring fuses of the most common MF-R and MF-S series
It is advisable to debug the operation of the circuit diagram of such an automatic machine on a breadboard. It is preferable to use a small-sized 4-volt battery as a power source. The lamp (or group of lamps) must be designed for a voltage of 3,5-4 V and a current of about 1 A. For switching such a load, the RES-9 relay with a winding resistance of 30 Ohms is ideal. Moreover, if instead of the EL1 lamp we solder a resistor made up of two parallel-connected MLT-2 10 Ohm resistors, it will be possible to use the second normally open relay contact (not shown in the circuit diagram) to turn on a more powerful lamp or household electrical appliance powered from the lighting mains . The board for mounting an already debugged machine can be easily made from one-sided foil PCB or getinax. The required outlines of the pseudo-printed conductors of the board can be obtained by cutting through the foil to the insulating base. Author: P.Yuriev
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Fastest laptop graphics processor from Nvidia ▪ Optimists are not afraid of a heart attack ▪ 5000 tons of extraterrestrial particles fall to Earth every year ▪ New technology for cooling things with ions
▪ section of the site Medicine. Selection of articles ▪ article Circle around your finger. Popular expression ▪ article When did the first Negro appear in America? Detailed answer ▪ article Electrician of cable networks. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article Focus with ink. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: