
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Switching power supply on a unijunction transistor. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
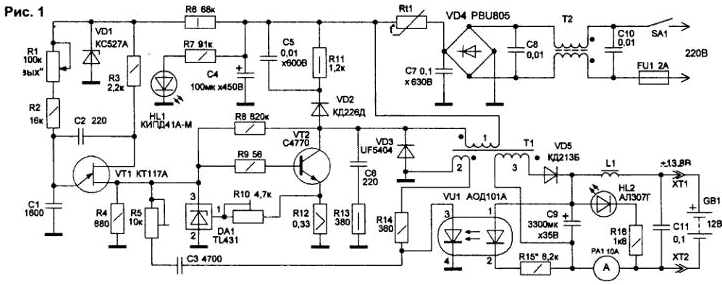
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies Low-frequency power supplies on power transformers, due to their large dimensions and weight, as well as low efficiency, are everywhere replaced by pulsed ones. The development of high-power high-frequency transistors and pulse transformers on ferrite cores makes it possible to transfer energy to the load at frequencies commensurate with the length of radio waves, and to bring the weight and size indicators of such sources to minimum values. The proposed source is designed to power powerful equipment and charge car batteries. The source is built on the basis of a single-cycle converter, which includes a master oscillator based on a unijunction transistor and a blocking oscillator based on a powerful bipolar transistor. The principle of operation of the source is based on a 3-fold voltage conversion. The alternating voltage of the mains is rectified (converted to a high-voltage DC) and fed to the key converter. A high-frequency key with a transformer converts direct voltage into a pulsed low-voltage one. The latter is straightened and fed to the load. In flyback converters (inverters), during the period of the closed state of the transistor key, energy is accumulated in the transformer, and its transfer to the load occurs when the key is open. In such inverters, the unipolar magnetization of the transformer leads to residual magnetization of the ferrite core, and a non-magnetic gap in the magnetic circuit is required to reduce it. The energy stored in the transformer during the switching pulse does not always have time to dissipate during the pause, which can lead to saturation of the transformer and loss of magnetic properties by the core. To eliminate this effect, the primary circuit of the transformer is shunted with a high-speed diode with a resistive load. The source diagram is shown in Fig.1.
Switching interference in switching power supplies occurs due to the switching mode of operation of powerful control elements. To protect the network and the converter from impulse noise, a line filter is installed on a two-winding inductor T2 with capacitors C7, C8, C10 to suppress unbalanced interference. The limitation of the charging current of the filter capacitor C4 is made on the posistor Rt1, the resistance of which decreases with an increase in its temperature. The impulse noise of the converter that occurs at the moments of switching of the key transistor VT2 and transformer T1 is eliminated by parallel circuits VD2-C5-R11 and C6-R13, interference in the load circuit is suppressed by the inductor L1. The duration of pauses between pulses of the output current slightly increases, but does not worsen the conversion. The inverter startup pulse shaper is made on a unijunction transistor VT1. The supply voltage VT1 is stabilized by the diode VD1. The charging voltage on the capacitor C1 periodically opens VT1 and creates a sequence of pulses on the resistor R4 with a frequency determined by the values of R1, R2 and C1. Capacitor C2 accelerates the switching process of transistor VT1. When power is applied, a constant voltage (rectified by the diode bridge VD4) from the filter capacitor C4 through the winding 1 of the transformer T1 is supplied to the collector of the transistor VT2, on which the blocking generator is assembled. The flow of the collector current through the winding 1 T1 is accompanied by the accumulation of energy in the magnetic field of the core. The pulse voltage from the resistor R4 opens the transistor VT2 for a few microseconds, the collector current VT2 at this time increases to 3 ... 4 A. After the end of the positive pulse, the collector current stops. The termination of the current causes the appearance in the coils of the transformer EMF of self-induction, which creates a pulsed voltage in the winding 3. Diode VD5 with capacitor C9 rectify and filter this voltage, which is fed through the inductor L1 to the load. The impulse voltage from the winding 2 T1 through the resistors R5, R9, R14 is supplied to the base of the transistor VT2, and the circuit enters the self-oscillation mode. Capacitor C3 maintains the stability of the blocking oscillator. The output voltage is stabilized by the VU1 optocoupler, which provides galvanic isolation of high-voltage and low-voltage output circuits. Increasing the load voltage, for example, by increasing its resistance, turns on the LED of the optocoupler VU1, the photodiode of which opens and shunts the signal from winding 2 T2. The pulse voltage at the base of VT2 decreases, respectively, the time of its open state decreases. The duration of positive pulses on winding 3 T1 also decreases, which causes a decrease in the output voltage (and the charging current of the battery GB1). When the load voltage decreases, the described process occurs in reverse. In the event of a current overload of the transistor VT2, the pulse voltage across the resistor R12 in the circuit of its emitter increases. Then the parallel voltage regulator DA1 opens and shunts the base voltage VT2. This also reduces the duration of its open state (up to the breakdown of self-oscillations). The cutoff current of the transistor VT2 is adjusted by the resistor R10. After the overload is eliminated, the blocking generator is restarted from the pulse shaper on VT1. The choice of high frequency transformer depends on the load power. The power of the transformer directly depends on the frequency of the oscillator and the brand of ferrite. With an increase in frequency by 10 times, the power of the transformer increases by almost 4 times. Due to the complexity of self-manufacturing of a pulse transformer, the device uses a transformer from an outdated monitor. Suitable transformers and from TVs. For orientation, we give approximate data of the transformer T1. Core - B26M1000 with a gap in the central rod. Winding 1 contains 56 turns of PEV-2 wire 0,51 mm, winding 2-4 turns 0,18 mm, winding 3-14 turns with a bundle of 3 wires 0,31 mm. The device is assembled on a printed circuit board with dimensions of 115x65 mm (Fig. 2).
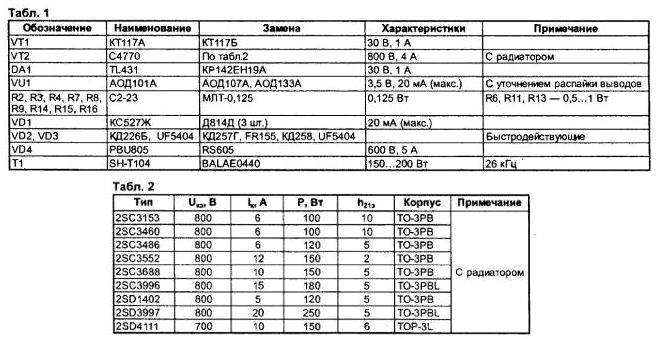
The jumpers are located on the side of the radio components. The radiator of the key transistor VT2 is used from the computer processor. For better cooling, you can use a fan from a computer power supply by connecting it to the source output through a 33 ... 56 Ohm resistor. The types of elements used are given in Table 1, a possible replacement of the converter transistors - in Table 2. Adjustment of the assembled circuit begins with a thorough check of the board. A 220 V light bulb of any power is included in the break in the network wire, instead of a load, a car light bulb (12 V, 20 candles). In case of faulty parts and installation errors, the network light is on with a bright light, and the car light is off. If the circuit is working, the network light does not light up or burns with a weak glow, and the car light is bright. The brightness of the light bulb in the load (output voltage) can be adjusted by resistor R1. The threshold for overcurrent protection is set by resistor R10, voltage stabilization (at maximum load) is regulated by resistor R5. By selecting R15 (if necessary), the current of the VU1 optocoupler LED is adjusted within 5 ... 6 mA. If you have an oscilloscope, it is convenient to first check the operation of the generator on the transistor VT1 by applying a supply voltage of 30 ... 50 V to the inverter from a laboratory source. The oscillator frequency can be changed by resistor R1 or capacitor C1. With weak feedback (high resistance R5) or incorrect connection of winding 2 T1, the blocking generator on VT2 may be disconnected from a short-term overload and not restart. Authors: V.Konovalov, A.Vanteev, Creative laboratory "Automation and telemechanics", Irkutsk
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Adults evaluate children according to words ▪ Photoelectronic memory based on a colony of bacteria ▪ ASUS TUF Sabertooth Z97 and Gryphon Z97 Motherboards ▪ The lawn mower runs on grass and is guided by Google maps ▪ The magnetic charge of the proton and antiproton is measured
▪ site section Parameters of radio components. Article selection ▪ article Bottle machine. History of invention and production ▪ article When did civilization appear? Detailed answer ▪ article Trolleybus driver. Job description ▪ article Ball in the hole. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: