
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Use of network transformers with high voltage. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
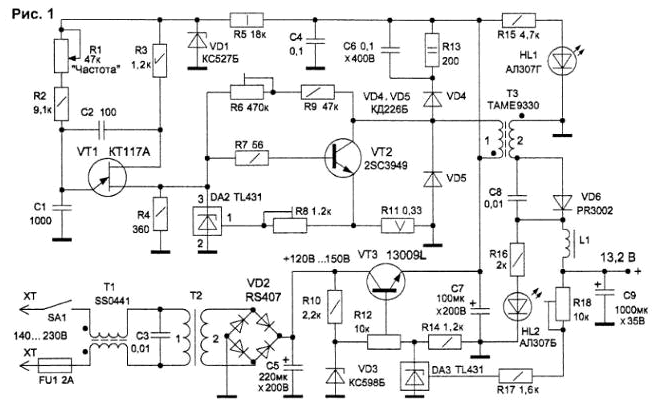
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Miscellaneous electrical devices Radio amateurs often do not find the use of transformers from decommissioned radio equipment for various purposes with a high output voltage. It is often not possible to rewind such transformers to the desired voltage due to the difficulties of disassembly (rusted iron, winding covered with a thick layer of varnish, old frame, etc.). With an increased secondary voltage and a primary voltage of 110-127-220 V, network transformers were made for lamp equipment of the last century. Before using such transformers, you should first check the windings for an open circuit. If they are serviceable, it is worth trying to determine the network and secondary windings by the pin numbers, and then look in the reference books for data on this transformer. In the absence of information, it will be necessary to act experimentally. The mains voltage is applied to that winding, which is preliminarily defined as the primary one (through a 1-2 A fuse) and the voltages on other windings are measured. If they are higher than the mains voltage, the most step-up winding can be used in the mains connection. Then the voltage on the remaining windings will be reduced. The transformer needs to be “driven” for some time in such an inclusion to make sure that it does not overheat with no-load current. Another method is to apply an alternating voltage (from a power supply or a separate transformer) 6 ... 12 V to the winding of the investigated transformer with low resistance, and "classify" them according to the measured voltages on the remaining windings. Sometimes there are 3-phase transformers (380/220 V). If a 380 V winding is connected to a 220 V network, then the voltage on the secondary winding will be reduced by 1,7 times, i.e. approximately 170 V. To determine the permissible power of the secondary winding of the transformer, it is loaded, for example, with one or more incandescent bulbs (220 V, 25 ... 100 W). If the voltage on the secondary winding under load has decreased by no more than 10%, such a transformer can be used in equipment with an appropriate power consumption. In particular, to obtain standard constant voltages (12 ... 15 V), the proposed inverter can be connected to the transformer (Fig. 1). The inverter circuit, due to the reduced input voltage, does not require the use of high-voltage transistors and power filter capacitors, which are quite expensive.
Capacitors (200V) can be removed from the power supplies of older computers and monitors. From them, a high-frequency transformer T3 is also used. In such transformers, there are usually fewer windings on one side of the winding leads than on the opposite side. The number of windings - one, maximum, two. On the secondary side, the winding leads are usually made with a bundle of two or more single-core wires, since the currents of the secondary windings are greater than the primary ones, and a thick single-core wire is not used in such windings due to the skin effect (distribution of high-frequency current over the surface of the wire , not inside). It is unlikely that it will be possible to determine the windings by internal resistance in high-frequency transformers: they are all low-resistance and present high inductive resistance only at frequencies used in power supplies (20..200 kHz). The need for such conversion frequencies is understandable: the higher the frequency, the smaller the dimensions and weight of the high-frequency transformer. In the inverter circuit, a triple conversion occurs:
The input filter T1-C3 eliminates network noise and prevents the penetration of impulse noise from the inverter into the network. On the transistor VT3, an inverter supply voltage stabilizer is assembled, which reduces the input voltage, protecting the inverter and power circuits from increased voltage. The stabilized voltage depends on the parameters of the zener diode VD3, it can be set by the resistor R12 within 100 ... 150 V, based on the output parameters of the power transformer T2 A parallel stabilizer (controlled zener diode) DA3 is connected to the base circuit of the transistor VT3, through which the inverter output voltage is stabilized when the load changes. The master pulse generator is made on a unijunction transistor VT1 and an RC chain (R1 + R2) -C1. Capacitor C1 is charged through resistors R1, R2 until the voltage across it reaches the trigger threshold VT1. At this moment, the transistor opens and capacitor C1 is discharged through resistor R4. When the voltage across capacitor C1 drops to a minimum value (approximately 2 V), the transistor closes and the cycle repeats. Capacitor C2 speeds up the switching of the transistor. The oscillation period of the generator is practically independent of the supply voltage and temperature. The generator supply voltage should not exceed 35 V, therefore, a parametric stabilizer VD1-R5 is included in the power circuit. The inverter transistor key is made on a powerful bipolar transistor VT2. a pulse of positive polarity from the load R4 of the unijunction transistor VT1 is fed to the base VT2. The transistor opens, and a current pulse is created in the primary circuit of the high-frequency transformer T3, saturating the transformer with energy. At the end of the pulse, the key transistor closes, and the energy stored in the transformer is transferred to its secondary circuit. Arising at the terminals of the secondary winding. T3 voltage is rectified by the diode VD6 and smoothed by the filter L1-C9. The operating mode of the key transistor depends on the bias voltage created by the R6-R9 chain from the VT2 collector to the base of the transistor. The amplitude of the current pulses in the primary winding of the transformer. T3 is limited by the feedback circuit from the emitter load VT2 (R11) to the control electrode of the controlled zener diode DA2. Transistor VT2 closes a little earlier than the positive pulse ends. This eliminates the possible saturation of the high frequency transformer T3. The VD4-R13-C6 chain allows you to utilize the reverse current of the primary winding of the T3 transformer. From damage by reverse voltage pulses of the transformer T3, the key transistor is protected by a VD5 diode connected in parallel. An increase in the output voltage on the capacitor C9 with a decrease in load is transmitted through resistors R17-R18 to the control electrode DA3. This lowers the voltage at the base of the transistor VT3, the transistor closes and reduces the inverter supply voltage. As a result, the load voltage also decreases, i.e. the output voltage stabilizes. The circuit uses radio components, mainly from outdated computer power supplies. Replace the KT117A transistor with KT117B or 2N1489...2N1494 (2N2417A...2N2422). The high-voltage transistor VT2 must have a permissible emitter-collector voltage of at least 400 V at a current of more than 4 A at a frequency of at least 15 MHz. The transistor is mounted on a 65x40 mm aluminum heatsink through a mica spacer. The stabilizer transistor VT3 is installed on the same radiator. High-frequency transformer T3 - from computer power supplies such as R320, A-450X-1T1 or monitors - KG9242K, 9025,9701.9121T. CS-9250, 4127. The T3 transformer can also be made on a ferrite ring with a diameter of 36.42 mm. The primary winding consists of 36 turns of PEL wire 0,62 mm, the secondary - of 18 turns of a bundle of 3 wires 0,62 mm. The ring is preliminarily split into two halves, wrapped with fiberglass and, after winding, glued with BF-6 glue. The device is made on a printed circuit board made of one-sided fiberglass with dimensions of 115x63 mm (Fig. 2). Transformer T2 with a secondary voltage of 110...127 V with a power of 80...150 W is installed separately in the housing.
When setting up, the inverter circuits are first disconnected from the capacitor C7 and a 40 ... 60 W (220 V) light bulb is connected instead. On it, the regulator R12 sets the voltage to 110 ... 150 V. By connecting the inverter, observe the glow of the HL2 LED. If this happens, a load is connected to the output (a light bulb from a car 12 V, 50 W). Resistors R1 and R6 set its maximum brightness at a load voltage of 13,2 V. By adjusting R8, the minimum temperature of the key transistor VT2 is achieved. Disconnecting the load may affect the inverter output voltage. You can stabilize it by changing the resistance R18. Authors: V.Konovalov, A.Vanteev, Creative laboratory "Automation and telemechanics", Irkutsk
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Cloud connected microcontroller ▪ Photovoltaic module with 23,8% conversion efficiency
▪ section of the site for the radio amateur-designer. Article selection ▪ article The bony hand of hunger. Popular expression ▪ article How are flies born? Detailed answer ▪ article The functional composition of Normende TVs. Directory
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: