A device for recharging a Ni-Cd battery. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
In the magazine "Radio", 2003, No. 1 on p. 33 Yu. Vinogradov's article "Automatic device for additional discharge of Ni-Cd battery" was published. The disadvantages of this machine are the complexity of the circuit, the large current consumption (about 20 mA at the end of the discharge), the ambiguous status indication - the absence of the LED glow can be for two different reasons: the discharge mode or power failure.
The scheme of the proposed device is shown in fig. 1. These shortcomings are eliminated in it. It is much simpler according to the scheme, the current consumed by it does not exceed 10 mA, it has an unambiguous indication of operating modes. The basis of the device is the integrated comparator K554SAZ (OA1). An exemplary voltage of 4 V is applied to its inverting input from the engine of the tuning resistor R1 - the battery is discharged to this level. The voltage across the tuned resistor is stabilized by a parametric stabilizer on resistor R3 and LED HL1. Depending on the spread of the LED parameters, it can be in the range of 1,8 ... 2,1 V.
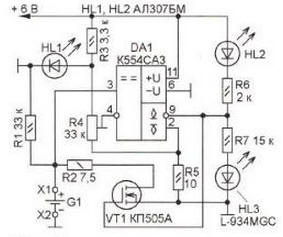
Fig. 1
A dischargeable battery G1 is connected to the non-inverting input of the comparator DA1. Its discharge is carried out by a current of about 150 mA through the resistor R2, switched by the transistor VT1. The output stage of the integrated comparator DA1 is made on an open collector transistor (pin 9) and an emitter (pin 2). While the voltage of the battery being discharged is greater than the exemplary one, the output transistor of the comparator DA1 is closed. On its collector (pin 9) there is a high-level voltage that keeps the transistor VT1 open, which connects the load resistor R2 to the battery. the discharge process is in progress, as indicated by the HL3 green LED of increased brightness. LED HL2 off.
As the battery G1 discharges, its voltage decreases, and when it becomes equal to the exemplary one, the comparator OA1 switches, its output transistor opens and shunts the HL3 LED, as a result of which it goes out. The emitter current of this transistor creates a voltage drop across the resistor R5, to which the lower output of the tuning resistor R4 is connected. The voltage on its engine rises - this is how the hysteresis mode of operation of the DA1 comparator is organized, preventing its frequent switching. Transistor VT1 closes and disconnects resistor R2 from the battery, stopping it from discharging. The red HL2 LED is turned on - an indicator of the end of the discharge.
The device is assembled on a universal breadboard with dimensions of 23x35 mm and placed in a case - a pen case, as shown in the photo (Fig. 2). A rectangular cutout is made in the case, in which the movable negative contact X2 moves - this made it possible to discharge both disk and cylindrical batteries with a capacity of 0,06 to 2,3 Ah.

Fig. 2
LED HL1 can be anything. LEDs HL2 and HL3 are installed on the front panel, it is desirable that they be of different colors of glow, and the latter must be super-bright so that its light is noticeable when the current flowing is less than 1 mA. Transistor KP505A (VT1) can be replaced with KP504A, KP501A or a powerful switching, controlled by a logic level, such as IRLU2905.
Establishing the device consists in setting a reference voltage of 1 V at the inverting input of the comparator DA1 by moving the trimmer resistor R4.
Author: Moroz K.
 See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Electric car that absorbs carbon dioxide
05.08.2022
Scientists at the Technical University of Eindhoven in the Netherlands have built an electric car that absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as it moves. According to the developers, such a car is able to absorb more CO2 than its life cycle will produce.
The monocoque and body panels of the Zem electric vehicle are made using additive manufacturing from recycled plastics. Also, "secondary" plastic is used in interior trim. The interior uses artificial leather made from cellulose fibers of pineapple leaves.
The windows are glazed with polycarbonate. Multimedia system, electronics and lighting equipment - reusable. As stated, they can be removed and used in other products. It is also planned to reuse the body panels of the car.
Zem is equipped with a 30-horsepower electric motor and nine traction batteries with a capacity of 2,3 kWh each. Also, the electric car was equipped with a differential from Audi with a relatively high gear ratio, a regenerative braking system and built-in solar panels.
The main feature of Zem is the air purification system, disguised as a radiator grille. As it moves, it absorbs CO2 from the air. The filter is designed for 320 km. run. If necessary, it can be cleaned, and CO2 taken from the air can be poured into cylinders at charging stations. In the future, it can be used in the production of sustainable fuels and plastics.
According to the developers, every 20 km run at a speed of about 60 km/h, the Zem electric prototype removes about 2 kg of CO2 from the atmosphere.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ clockwork water strider
▪ UCC28780 Zero Voltage Switching Flyback Controller
▪ A woman's heart is quarrelsome
▪ Gigabyte GSmart series of smartphones
▪ Waste sorting machines
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the website Basics of First Medical Aid (BFA). Selection of articles
▪ article Shooting: Tips for novice TV people. video art
▪ article Where did Odysseus spend most of his time returning from Troy to his homeland? Detailed answer
▪ article Working with portable power tools and hand-held electric machines (power tools). Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Consumer electronics. Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers. Directory
▪ article Unsoldering the interface cable for Siemens phones. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: