
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Charger for car battery. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
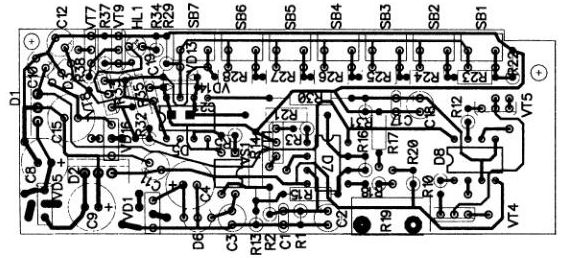
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells The service life of a car battery depends not only on the quality of the product, but also on proper operation. Some motorists assume that if you drive a car all the time, then everything will be in order with the battery. However, everyone knows that driving around the city consists of periods with a fairly frequent launch of the starter and a low mileage from point A to point B, as a result of which the battery does not have time to renew the spent energy, it is undercharged, and this, in turn, leads to sulfation of the plates and loss of the nominal capacity of the battery , the author, after two years of operation of a new battery, measured its capacity, it turned out to be less than 50%. In some articles, the authors recommend charging batteries before winter operation, but it seems to me that this should be done 2-4 times a year. Moreover, it is necessary to train the battery before charging by the method of 2x-3x multiple discharge-charge. In this case, the charge can also be carried out by the desulfating method, i.e. 30 sec. charged with a current of 0,1C, 10 sec. discharged with a current of 0,01C. The author has developed a device (Fig. 1), which allows you to work both in automatic and manual mode. Consider the operation of the device in manual mode. After applying 220 volts to X1 and turning on the switch SA1, a voltage appears at the output of the secondary winding of the transformer T1, which in turn is rectified by the diode bridge VD16 and filtered by the capacitor C14. Relay K1 and stabilizer D3 are powered from this bridge, the voltage from which is supplied to power the microcontroller D5. From the third and fourth windings of the transformer T1, voltage is supplied to the diode bridge VD5 and voltage regulators D1 (+12 volts), D2 (-17.6 volts) from which operational amplifiers D4, D7 are powered. From the fifth winding of the transformer T1, the voltage is rectified by the diode bridge VD9-VD12, filtered by the capacitor C7 and serves to power two parallel-connected current sources (ITUN) D7.1, D7.2, VT3-VT6, R9-R12, R30, R31, C17, C18 which are controlled by PWM pulses from pin 5 of the D5 microcontroller. From the sixth winding of the transformer T1, the voltage is rectified by the diode bridge VD1, filtered by the capacitor C4 and stabilized by the D6 microcircuit. From this microcircuit, the battery discharge control circuit (ITUN) consisting of D4.1, VT1, VT2, R1-R4, C1, C2 and TUN is powered by PWM pulses from the 3rd leg of the microcontroller through a decoupling optocoupler VS1. On the operational amplifier D4.2, a battery voltage control circuit is assembled. A voltage divider is assembled on resistors R13, R14. The R17-R20 chain serves to shift the level of the measured voltage by subtracting the reference voltage from the voltage on the battery. Diodes VD13. VD14 are used to protect the input of the analog-to-digital converter of the microcontroller D5. From the 2nd output of the microcontroller on one bus, the control of the indicator assembled on HL2, VT8, R32-R34 and the transistor key assembled on VT7 is organized. VT9 R35, R37, R38 which turns on the K1 relay, the HL2 indicator indicates the following modes Hi.2 is constantly on - the battery is being discharged by an external load, HL2 is off, the device is in stop mode or manual mode, HL2 - long ignition, long extinction - mode charge, H1.2 - short ignition; short extinction - desulfation mode. The SB1 button switches the device to STOP mode, SB2 - START, the device is switched to charge or charge / discharge mode. The SB3-SB6 buttons set the current in the charge-discharge mode. After turning on the device, the SB7 button switches to the desulfation mode, while the HL2 LED lights up for a short time. In the desulfation mode, after turning on the start button, the battery is discharged to 10,2 volts by the external load HL1. Then charge with a current of 5,5 A for 30 seconds and discharge with a current of 0,55 A for 10 seconds, the procedure is repeated until the voltage on the battery stops increasing for 2 hours. then the current decreases to 2,75 A and recharging takes place for another 2 hours. If the voltage starts to decrease, the charging is turned off. In manual mode, charging is carried out with a current of 5,5 V, up to a stable voltage on the battery for 2 hours. Buttons SB3-SB6 can change the charge/discharge current. current indication is carried out by a RA1 milliammeter and the SA2 switch set to position "A", when switching to position "V", the voltage can be controlled. The battery should be connected to the charger only after the power is turned on, otherwise the VT2 transistor may fail. To prevent this event, it is recommended to make an isolated 12-21/16/9/9 V voltage converter that will be powered directly from the battery, and the secondary windings with rectifiers will be connected to D1, D2, D3, D6. The device uses a type transformer. TS180. We leave the primary winding in place, and unwind the rest. First, we wind the fifth winding with a PEV2 wire with a diameter of 1,5 mm - 50 turns, then the second with a wire with a diameter of 0,5 mm - 26 turns, the sixth with a diameter of 0,3 mm -20 turns, the third and fourth with a diameter of 0,4, 50 turns each. indicator PA1 type M2001 / 1-M4, which needs to be slightly modified, shift zero to the right of the real zero, and by connecting the ammeter and shunt R8 recalibrate the scale values. It is also necessary to calibrate the voltage values \u6b\u7band select resistors R12 or R4. In the device, you can use any relay for a coil voltage of 5 volts and a contact current of XNUMX ... XNUMX A. The circuit is assembled on a printed circuit board made of one-sided fiberglass (Fig. 2), 40x95 mm in size.
The microcontroller contains a microprogram whose HEX codes are in Table 1.
After assembly, the device must be set to the cut-off voltage during discharge. To do this, disconnect the left side (according to the diagram) of the resistor R13. we connect a laboratory power supply to it and supply 10,2 volts from it. We start the device in automatic mode, this will turn on the relay and the HL1 light, rotate the tuning resistor R19 until the relay turns off. This completes the setup and checks the performance of the entire device. Author: Abramov S.M.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Electronics powered by the ear ▪ Maxim RS-485/RS-422 transceivers MAX33072E/MAX33073E ▪ LED lasers are a threat to aircraft ▪ A phone with a regular battery charges four times faster
▪ site section Clocks, timers, relays, load switches. Article selection ▪ article General sociology. Lecture notes ▪ article How to relieve stress and discharge? Detailed answer ▪ shark knot article. Tourist tips ▪ article Mixing colors. physical experiment
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: