
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Auto-charging of the backup battery. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells To ensure reliable operation of many stationary devices, it is necessary to use backup power. Most often, a battery is installed for these purposes, but it must be monitored, avoiding a strong discharge and put on a recharge in time. It is more convenient to entrust this duty to automation. Recharging the battery requires a suitable device (internal or external). The charger can be made as part of an uninterruptible power supply system and fully automate the process, i.e. it can turn on when the battery voltage drops below the threshold level, or use a "floating" recharge. A floating charge means connecting the battery in parallel with the load (Fig. 2.18), when the power source serves only to compensate for self-discharge currents in the batteries. In this case, the scheme is the most simple. In these circuits, the incoming voltage from the transformer is chosen so that the charging current passing through the battery compensates for the natural self-discharge current.
The required voltage after the rectifier can be selected experimentally by installing additional diodes or using taps from the secondary winding of the transformer (some unified transformers, for example, from the TN, TPP, etc. series, have the ability to slightly change the voltage in the secondary circuit by switching taps in the primary winding) . At the same time, we control the current in the battery circuit using an ammeter. Usually the floating charge current value should not exceed 0,005...0,01 nominal for the battery. Reducing the charge current only leads to an increase in the duration of the process (in this application, the charge time does not matter - it will always be sufficient). Such schemes can be used if your network is stable enough and the supply voltage does not go beyond the tolerance (in large cities they monitor this). Otherwise, a voltage stabilizer and a diode are installed between the transformer and the battery, which prevents the battery current from flowing into the stabilizer when the transformer is not turned on (Fig. 2.19). The KR142EN12 chip can be replaced by a similar imported LM317.
Since the battery load in the security device consumes microcurrent, it makes no sense to control the voltage on it during operation - it will always be nominal at idle. Such control is performed while simulating the maximum load on the battery, which will require the complexity of the charger circuit to fully automate the process. A more advanced charger circuit is shown in fig. 2.20. It not only maintains a stable voltage on the battery, but also has an adjustable current protection that prevents damage to the cells in the event of an output short circuit (or battery failure). Current limitation is also useful in cases where a new battery is connected (not yet charged or previously very discharged). In this case, limiting the current at the required level prevents overloading the supply network transformer (it can be low-power - 14 ... 30 W, since in the "Alarm" mode the required current may well be provided by the battery itself). In addition, there is a temperature protection inside the chip that turns off its output when it overheats, which prevents damage to components.
To assemble the device, you can use a single-sided printed circuit board made of fiberglass, shown in Fig. 2.21, its appearance is shown in fig. 2.22.
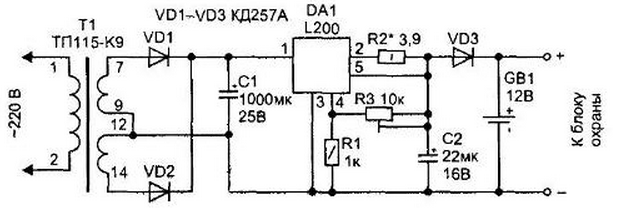
The transformer (T1) can be replaced by TP115-K9 - it has 2 windings of 12 V each with a permissible current of up to 0,8 A. At idle, the winding will have a voltage of 16 V, and after rectification and smoothing by a capacitor - 19 V, which is quite enough for the operation of the stabilizer (most of the time the circuit will operate just in idle mode). Another circuit that works similarly is shown in Fig. 2.23. Its basis is the L200 chip (there are no domestic analogues), which has pins (2 and 5) to control the current in the load. The given inclusion of the microcircuit is typical: the maximum current in the load circuit Imax \u2d 0,45 / R2 depends on the value of the resistor R3, and the desired voltage is set by the resistor RXNUMX.
The stabilizer can provide an output current from 0,1 to 2 A and has internal overheat protection. To mount the elements of the second charger circuit, you can use the printed circuit board shown in fig. 2.24.
About setting up all schemes with stabilization. You will need a milliammeter, a voltmeter (preferably digital) and a powerful resistor simulating the load. All this is connected according to the scheme shown in Fig. 2.25.
First, when the battery is disconnected, we set a voltage of 13 watts at the output of the stabilizer with the corresponding trimmer resistor. After that, switch S1 to turn on the resistor Rn and check the current limit. It can be installed by anyone by selecting the current feedback resistor - R3 in the circuit of fig. 2.20 (for example, for a current of 220 mA - R3 = 3,9 Ohm; for 300 mA - R3 - 3,3 Ohm) or R2 in the circuit in fig. 2.23. Now, instead of the resistor Rh, we connect the battery GB1. The required current in the charge circuit (for the energy intensity of a particular battery) is set by adjusting the output voltage. The final setting should be done after the battery is fully charged - this current should compensate for the self-discharge of GB1. Author: Shelestov I.P.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ External 2TB HDD Buffalo HD-PCFU3-C ▪ Advanced driver voice assistant ▪ Mining farm with solar panels ▪ Computer mouse controlled by mouth
▪ site section Computer devices. Article selection ▪ article Fundamentals of medical knowledge. Crib ▪ article What is pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism? Detailed answer ▪ article Stony raspberry. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Comments on the article: Michael An intelligible explanation of the operation of the circuits and a selection of parts do honor and trust to the author of this article. Thank you for your disinterested help to beginners in mastering the basics of electronics!
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese







 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: