
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Laboratory power supply with adjustable current limit, 0-30 volts 3 amps. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies To set up or repair radio devices, you must have several power sources. Many houses already have such devices, but, as a rule, they have limited operational capabilities (permissible load current up to 1 A, and if current protection is provided, then it is inertial or without the ability to regulate - trigger). In general, such sources cannot compete with industrial power supplies in terms of their technical characteristics. To acquire a universal laboratory industrial source is quite expensive. The use of modern circuitry and element base makes it possible to make a power supply at home, which, in terms of its main technical characteristics, is not inferior to the best industrial designs. At the same time, it can be simple to manufacture and configure. The main requirements that such a power supply must meet are: voltage regulation in the range of 0 ... 30 V; the ability to provide current in the load up to 3 A with minimal ripple; adjustment of operation of current protection. In addition, the current protection operation must be fast enough to prevent damage to the source itself in the event of a short circuit at the output. The ability to smoothly adjust the current limit in the power supply allows you to exclude damage when setting up external devices. All these requirements are met by the universal power supply circuit proposed below. In addition, this power supply allows you to use it as a source of stable current (up to 3 A). The main technical characteristics of the power supply:
Electric circuit of the power supply, fig. 4.10, consists of a control circuit (node A1), a transformer (T1), a rectifier (VD5 ... VD8), a power control transistor VT3 and a switching unit for the transformer windings (A2).
The control circuit (A1) is assembled on two universal operational amplifiers (op-amps) located in one housing and is powered from a separate transformer winding. This ensures that the output voltage is adjusted from zero, as well as more stable operation of the entire device. And to facilitate the thermal mode of operation of the power control transistor, a transformer with a sectioned secondary winding was used. The taps are automatically switched depending on the level of the output voltage using relays K1, K2, which allows, despite the high current in the load, to use a heat sink for VT3 of small size, as well as to increase the efficiency of the stabilizer. The switching unit (A2), in order to switch the four taps of the transformer with only two relays, switches them on in the following sequence: when the output voltage exceeds 7,5 V, K1 turns on; when the level of 15 V is exceeded, K2 turns on; when 22 V is exceeded, K1 is turned off (in this case, the maximum voltage is supplied from the transformer windings). The indicated thresholds are set by the used zener diodes (VD11 .VD13). Switching off the relay when the voltage drops is performed in the reverse order, but with a hysteresis of approximately 0,3 V, i.e. when the voltage drops by this value lower than when turned on, which eliminates chatter when switching windings. The control circuit (A1) consists of a voltage regulator and a current regulator. If necessary, the device can operate in any of these modes. The mode depends on the position of the regulator "G (R18). The voltage regulator is assembled on the elements DA1.1-VT2-VT3. The stabilizer circuit works as follows. The desired output voltage is set by resistors "coarse" (R16) and "fine" (R17). In the voltage stabilization mode, the voltage feedback signal (-Uoc) from the output (X2) through a divider of resistors R16-R17-R7 is fed to the non-inverting input of the operational amplifier DA1 / 2. A reference voltage of +3 V is supplied to the same input through resistors R5-R7-R9. At the moment the circuit is turned on, a positive voltage will increase at the output DA1 / 12 (it comes to control VT2 through transistor VT3) until the voltage at the output terminals X1-X2 will not reach the level set by resistors R16-R17. Due to the negative voltage feedback coming from the X2 output to the input of the DA1 / 2 amplifier, the output voltage of the power supply is stabilized. In this case, the output voltage will be determined by the ratio:
where Accordingly, by changing the resistance of resistors R16 ("rough") and R17 ("fine"), you can change the output voltage Iout from 0 to 30 V. When a load is connected to the output of the power supply, a current begins to flow in its output circuit, creating a positive voltage drop across the resistor R19 (relative to the common wire of the circuit). This voltage is supplied through the resistor R18 to the connection point R6-R8. From the zener diode VD2, a reference negative voltage (-4 V) is supplied through R6-R9. Operational amplifier DA1.2 amplifies the difference between them. While the difference is negative (that is, the output current is less than the value set by resistor R18), +1 V acts at the output DA10 / 15. Transistor VT1 will be closed and this part of the circuit does not affect the operation of the voltage regulator. When the load current increases to a value at which a positive voltage appears at the DA1 / 7 input, a negative voltage will be at the DA1 / 10 output and the transistor VT1 will open slightly. A current flows in the R13-R12-HL1 circuit, which will reduce the opening voltage based on the regulating power transistor VT3. The glow of the red LED (NI) signals the transition of the circuit into the current limiting mode. In this case, the output voltage of the power supply will decrease to such a value at which the output current will have a value sufficient to ensure that the current feedback voltage (Uop) taken from the resistor R16 and the reference at the connection point R6-R8-R18 mutually compensated, i.e. there is zero potential. As a result, the output current of the source will be limited at the level set by the position of the slider of the resistor R18. In this case, the current in the output circuit will be determined by the ratio:
where Diodes (VD3) at the inputs of operational amplifiers protect the microcircuit from damage if it is turned on without feedback or if the power transistor is damaged. In operating mode, the voltage at the inputs of the op-amp is close to zero and the diodes do not affect the operation of the device. Capacitor C3 limits the amplified frequency band of the op-amp, which prevents self-excitation and increases the stability of the circuit. Design features The parts of the circuit marked with a dotted line (nodes A1 and A2) are located on two printed circuit boards 80x65 mm in size made of one-sided fiberglass 1 ... 3 mm thick. For node A1, the topology and arrangement of elements are shown in fig. 4.11.
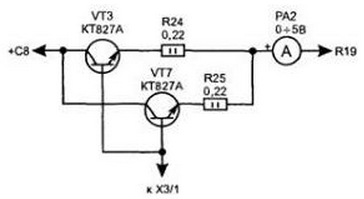
Node A2 can be made by volumetric installation and its dimensions depend on the type of relays used. When assembling, the following parts were used: tuned resistors R5 and R6 of the SPZ-19a type; variable resistors R16.R18 type SPZ-4a or. PPB-1A; fixed resistors R19 type C5-16MV for 5 W, the rest are from the MLT and C2-23 series of the corresponding power. Capacitors C1, C2, C3, C10 type K10-17, electrolytic C4 ... C9 type K50-35 (K50-32). LEDs HL1, HL2 fit any with a different glow color. Transistors VT1, VT2 can be replaced by KT3107A (B). The power transistor VT3 is installed on a radiator with an area of about 1000 cm3. Connector X1 on the board. A2 type. RSh2N-15-XNUMX. Relays K1, K2 are made in Poland, size R-15 with a winding for an operating voltage of 24 V (winding resistance 430 Ohm) - due to their unpackaged design, they have small dimensions and sufficiently powerful switching contacts. Microammeter RA1 small-sized type M42303 or similar with an internal shunt for a current of up to 3 or 5 A. For ease of operation of the power supply, the circuit can be supplemented with a voltmeter showing the output voltage. The network transformer T1 is manufactured independently on the basis of an armored unified industrial transformer with a power of 160 W (for example, from the OSM1 series TU16-717.137-83). The iron at the location of the coil frame has a section of 40x32 mm. It will be necessary to remove all secondary windings, leaving only the mains winding (if the primary winding is rated for 380 V, then we wind 300 turns from it). We start winding with a winding 8-9-10 - it contains 38 + 38 turns of wire. PZP with a diameter of 0,23 mm. Winding 7-6-5-4-3 contains 16 + 15 + 15 + 15 turns of PEL wire with a diameter of 1,5 mm Secondary windings of the transformer must provide 18 + 18 V and 7,5 + 7,5 + 7,5 voltages at idle 7,5 + XNUMX V, respectively. With error-free installation in the circuit of node A1, it will only be necessary to configure the maximum output voltage adjustment range of 0 ... 30 V with resistor R5 and the maximum protection current of 3 A with resistor R6. The switching unit (A2) does not need to be configured. It is only necessary to check the switching thresholds of the relays K1, K2 and the corresponding increase in voltage across the capacitor C8. When the circuit is operating in the voltage stabilization mode, the green LED (HL2) is lit, and when the current stabilization mode is switched on, it is red (HL1). To increase the maximum allowable current in the load to 5 A, it will be necessary to make changes to the circuit, shown in Fig. 4.12 (two power transistors are installed in parallel). This is due to the need to ensure reliable operation of the device in the event of a short circuit at the output terminals.
In the worst case, power transistors must withstand a power overload for a short time P=U in*I=35*5=175 W. And one KT827A transistor can dissipate power no more than 125 watts. Switching voltage from the transformer T1 turns K1 and K2 are inertial and do not provide an instantaneous reduction in the voltage coming from the secondary winding T1, but they will reduce the thermal power dissipation on the power transistors during long-term operation of the source. In the case of a power supply for a current of 5 A, it is also necessary to reduce the value of the resistor R19 to 0,2 Ohm and, taking this into account, recalculate the values of the resistor R18 using the formula:
Author: Shelestov I.P.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Molecule crossed with light at room temperature ▪ Male and female perception of colors
▪ section of the site Factory technology at home. Article selection ▪ Article It's a shame, annoying. Popular expression ▪ What wind is considered a hurricane? Detailed answer ▪ article Root bell. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Comments on the article: Vasilii [up] This power supply really works, excellent stabilization, current protection. Can be made for any current and voltage. Easy to manufacture, does not require adjustment. And if you add adjustable overvoltage protection, you get a lab. a power supply that is not inferior in performance to expensive industrial designs. Krasimir Adjusting the current from how many milliamps will begin to be regulated ??? Anatoly It works well, but there are three, in my opinion, significant drawbacks. When turned off, there is a strong surge of voltage, in the event of a break, or poor contact in the current and voltage regulators, the values increase to the maximum. For example: you work at a voltage of 5 volts, and the voltage suddenly jumped to 30 volts. And lastly, automation (switching the secondary winding of the trance) at a voltage of 210 volts no longer works.
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


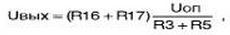
 .
.
 .
.

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: