
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Power switch with remote control. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
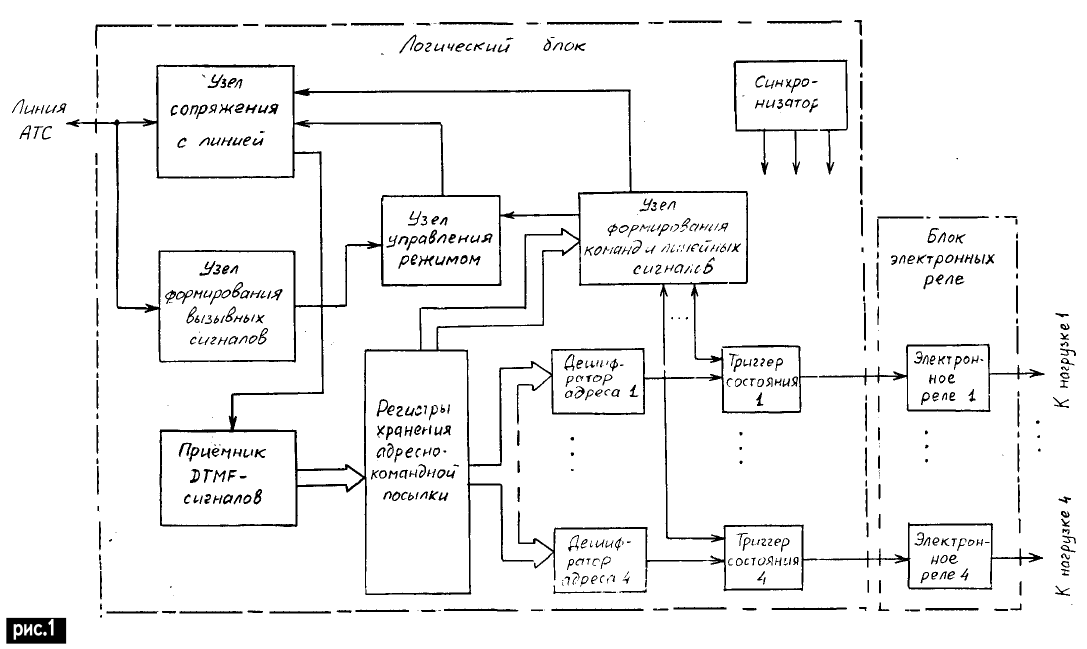
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Telephony The proposed device is designed to work in the public telephone network. It allows you to remotely, using a telephone line, turn on and off network electrical appliances of low and medium (up to 1 kW) power. The device has four channels, (controls four loads). The number of channels can be arbitrarily increased by extension. The switch is powered from the 220 V AC mains. It is possible to connect the device at its installation site to the telephone line without observing the polarity in parallel with the local telephone set (MTA). In standby mode, the device does not load the line, does not respond to voice signals and pulse or DTMF dialing signals coming from the MTA or from the line. Remote control of switch loads (changing their states) is carried out only in the line occupation mode. The switch occupies the line after a certain number of incoming ringing signals (messages) arrive at the MTA from the PBX. To manage the loads, standard DTMF signals are used, coming from a remote telephone set (UTA), with which the switch has established a connection. If the UTA does not have a DTMF dialing function, it can be controlled from a beeper, which is brought by the user to the microphone of the UTA handset. The switch operates in interactive mode, i.e. not only receives control commands from the line, but also issues signals to the line, by which the user can judge the execution of his commands and the current state of the loads. Each of the loads has its own address - a three-digit combination consisting of the numbers 0 - 9, the symbols #, * and the letters A, B, C, D. The device accepts four commands: turn on the load with a certain address, turn off the load with a certain address, request the current load state with some address and release the line. The device outputs three types of signals to the line: "notification of the user about the occupation of the line" - an intermittent signal with a fundamental tone of 1024 Hz with a duration of 3,5 - 4 s; "Notification of the user about the switched on state of the load with a certain address" continuous signal with a fundamental tone of 1024 Hz with a duration of 2 s; notification of the user about the off state of the load with a certain address "- an intermittent signal with a basic tone of 1024 Hz with a duration of 2 s. If, after the switch has occupied the line, no DTMF signals are received from it for 1-2 minutes, the line is automatically released and the device returns to standby mode. The electrical parameters of the switch, regarding its interaction with the telephone line, do not go beyond the limits established for telephone sets of any complexity class [1]. Own and control signals of the device in frequency lie within the bandwidth of the telephone channel (0,3 - 3 kHz). On the basis of the proposed device, it is possible to create a system for remote discrete control of any parameter or an individual notification system for a large number (theoretically up to 163) of subscribers via one telephone line, for example, within one institution. The block diagram of the switch is shown in Fig. 1, and the schematic diagram of the logical (digital) unit of the device is shown in Fig. 2. The line interface node, made on VD1, DA1, VT1, VT2, ensures the occupation of the line, the reception of DTMF signals from it, which form address-command packages (ACP), and the input of the device's own signals into the line. The ringing signal generation unit, made on VD2, U1, DD14.1, generates digital level pulses from the PBX ringing messages. The mode control node (DD9DD11, DD15.1, DD13.3, DD13.4, DD17.1) counts the ringing pulses and generates a line seizing signal after a predetermined number of them arrive. The receiver of DTMF signals (DD1), together with the storage registers of the automatic transmission (DD4-DD7), forms in parallel the codes of the addresses and commands received from the line. Channel address decoders (VD3VD50, DD15.2-DD15.5, DD16) generate signals at their outputs that open access to channel status triggers (DD21). The change in the states of these triggers is carried out by the signals of the command generation unit and linear signals (DD8, DD18-DD20, DD14.2-DD14.4, DD17.3, DD17.4). The same node polls triggers and sends corresponding signals to the line. The synchronizer, made on the DD12 chip, is the source of pulse sequences of 1, 2, 1024 and 1/60 Hz, which are necessary for the operation of the device. All these frequencies are stabilized by a ZQ2 quartz resonator. In standby mode, pin 6 of the counter DD10.1 has a high level, which blocks the count of DD10.1 coming from pin 4 DD12 of 1 Hz pulses. The counter DD9 is reset, its account is also prohibited by a high level with pin 6 DD10.1. The trigger DD11.1 is in a low state, the transistor VT1 is open high on pin 2 of DD11.1, and the transistor switch DA1 is open. The line is not loaded. Pin 5 of the counter DD21 has a high level, which blocks the count of DD2.1 coming from pin 6 DD12 of 2 Hz pulses. The same level prohibits counting counter DD2.2 and receiving data registers DD4-DD7. Upon receipt of the PBX ringing lines from the line, positive pulses appear on pin 2 of DD15.1, which are in phase with the envelope of the parcels. Each of these pulses resets DD10.1. The low level on pin 6 of DD10.1 after zeroing is held for about 7 s, therefore, with a pause between pulses of about 4 s [1], the counter DD9 is allowed to count them. One of the outputs DD9 (vyv.9 DD9) is connected to the input "S" (vyv.6) trigger DD11.1. At the end of the eighth pulse, a high level appears on pin 9 of DD9, turning DD11.1 into a high state. A low level with pin 2 DD11.1 locks the transistor VT1, the DA1 key closes, and the line is loaded with the resistance of the resistors R15 and R17 connected in parallel (transistor VT2 is open). Jumper between one of the outputs DD9 and input "S" DD11.1, you can set the number of calls, after which the switch will occupy the line (from one to nine). After the line is occupied, after about 7 s, the zeroing occurs and the counting of DD9 is prohibited by a high level with pin 6 DD10.1, but this does not affect the state of the trigger DD11.1. If the handset is picked up before the specified number of calls arrive at the MTA, the DD9 account is reset and disabled 7 seconds after the last incoming call, and the device remains in standby mode. At the moment the line is occupied by a positive drop from pin 1 DD11.1, the single vibrator DD11.2 is started, and the counter DD10.2 is reset. The high level from pin 13 of DD11.2 allows for 3,5 - 4 s the passage through DD14.2 of an intermittent signal with a fundamental tone of 1024 Hz. Through VT2, this signal enters the line and notifies the user that it is occupied by the switch. After that, the device waits for the arrival from the automatic transmission line. The automatic transmissions are fed to the input of the pre-amplifier on the element DD13.1, from its output through the diode limiter R18, HL1, HL2 they are fed to the input of the receiver-decoder of DTMF signals DD1. The automatic transmissions have the format - XXXY, where XXX - three DTMF-signals of the address (on the left the most significant bit, on the right - the junior one); Y - command DTMF signal. ACP from the keyboard of the beeper or UTA is typed by the user without pauses between sending the address and the command. Before the arrival of the first DTMF signal of the automatic transmission, the counter DD2.2 and registers DD4-DD7 are reset, the multiplexer DD3 has a high level on pin 1, and low on pins 5, 2, 4. When the first DTMF signal is recognized, a high level appears at the output "early detection" ESO (vyv.16) DD1, resetting the counter DD2.1. The code of the decrypted DTMF signal appears at pins 11-14 of DD1, after which a high level appears at the "late detection" output of DSO (vyv.15) DD1, along the edge of which the counter DD2.2 switches. A high level appears on pin 5 of DD3, along its edge the DTMF signal code is written to register DD5. The second DTMF signal is recorded in the same way in DD6, the third - in DD7, the fourth (command) DTMF signal is recorded in DD4. The low level on pin 5 of DD2.1 is maintained after resetting DD2.1 for about 2 s. If the pause between DTMF signals during dialing exceeds this interval, then the counter DD2.2 and registers DD4DD7 will be reset to zero before the end of the dial. From the outputs of the register DD4 (vyv.1, 15, 14, 13) the code of the command DTMF signal is fed to the command decoder DD8. Code one corresponds to the command "turn on", code two - "off", triples - "request status", fours - "release the line". The remaining command codes (and DD8 outputs) are not used in the device, however, you can use them instead of those shown in the diagram, reassigning them accordingly. Switch channel addresses are set by soldering diode lines in address decoders H1-H4. The idea of address decoding is taken from [2]. For example, the diagram in Fig. 2 shows the decoder H1 of the address "265". When the code of this address appears on the output bus of the registers DD5-DD7, a high level will be set at the output H1 (pin 3 DD16.1). All register outputs, which, in accordance with the address code, should be high, are connected to the inputs of the diode resistor element AND (VD4, VD8, VD9, VD11, VD13, R20), and the outputs, which should be low, are connected to the inputs of the diode - resistor element OR (VD3, VD5-VD7, VD10, VD12, VD14, R21). After decoding the command, i.e., the appearance of a high level at one of the DD8 outputs, the status triggers of all four channels are accessed. In case of receipt of the "enable" command, the logic levels from the outputs of the H1-H4 address decoders are fed through the DD20 multiplexer gates to the "S" inputs of the DD21 triggers (pin 4, 6, 12, 14). The trigger corresponding to the channel, the address of which is fixed in the registers, will go to the high state at the moment the command is decoded. When a "turn off" command is received, the outputs H1-H4 are connected through the valves DD19 to the inputs "R" DD21 (pin 3, 7, 11, 15), and the trigger corresponding to the selected channel, at the moment the command is decoded, goes into a low state. Interrogation of DD21 triggers is performed by the DD18 microcircuit with a diode-resistor element AND (VD55-VD58, R34) connected to its outputs by the "on", "off" and "request status" commands. One input of each of the four logic elements DD18 is connected to the output of the decoder H1-H4, respectively, the other input is connected to the output of the corresponding trigger DD21 (vyv.2, 9, 10, 1 DD21). After decoding the command, a high level is present at one of the DD8 outputs for about 2 s, and during this time, a continuous signal with a fundamental tone of 14.2 Hz enters the line through the open element DD1024, if the trigger in the selected channel is in a high state, or an intermittent signal with the same root tone if the trigger is low. An intermittent signal also enters the line if a non-existent (not assigned to any of the channels) address is fixed in the registers. 2 s after decoding the command, a high level appears on pin 5 of DD2.1 and registers DD4-DD7 are reset. When the switch's own signals enter the line, the DD1 chip is set to a high level at the PDH input (pin 6 of DD1) into a low power mode with the inability to decode the input signals. You can also change the state of each of the DD21 triggers manually using the buttons SB1 "Channel 1" - SB4 "Channel 4", SB5 "On", SB6 "Off". To do this, simultaneously press the button of the desired channel and the button of the desired action. Each DTMF signal decoded by the DD1 chip causes the DD10.2 counter to be reset to high with a high level from the DSO "late identification" output (vyv.15 DD1), thus prolonging the line device occupation time. If DTMF signals are not received at the DD1 input during a time interval of 1 to 2 minutes, a log "11.1" is written to the DD0 trigger along the edge of the high level received at its clock input from pin 12 of DD10.2, and the device releases line. The release of the line by the switch at the user's command occurs after dialing the AKP, consisting of an arbitrary address and the command "free line" (number "4"). The high level that appeared as a result of the decoding of this command on pin 1 of DD8 puts DD11.1 into a low state. After the line is released, the device returns to standby mode. The current consumption of the logic block of the switch from the source of +5 V depends on the number of included loads. When all loads are turned off, it does not exceed 7 mA, when all of them are turned on - 30 mA. Schematic diagram of the block of electronic relays is shown in Fig.3. The levels coming along the lines "Chain 1" - "Chain 4" from the outputs of the channel triggers of the logic block are recorded in the register DD1 along the fronts of rectangular pulses generated from the mains alternating voltage 220 V by the circuit VD2, R18, R17, VD1. Outputs DD1 (vyv.1, 15, 14, 13) determine the state of the triac switches VS1-VS4. Thus, the switching on and off of the channel loads occurs at the moments when the mains voltage passes through zero (on an increasing half-wave (sinusoids). The elements VD3-VD6, R19, R20, C1-C4 form a transformerless power supply for optocouplers U1-U8, LEDs HL1-HL4 and DD1 microcircuits.The filter on the elements C5, C6, L1, L2 suppresses switching surges of the mains voltage.LEDs HL1-HL4 indicate the on state of the corresponding load.Due to the use of optocouplers U1-U4, complete galvanic isolation of the telephone line and the 220 V network is provided, which eliminates the ingress into the line voltage. One of the possible options for the schematic diagram of a beeper for remote control is shown in Fig.4. The basis of the device is the electronic dialer chip DD1 HM9102D. From the TONE output (vyv.12) DD1, the DTNF signals of the number entered from the keyboard are fed through the divider R8, R9 to the input of the DA1 A283D microcircuit, which is used in the device as an audio frequency amplifier. The supply voltage to DD1 and DA1 is supplied through a transistor switch VT1, which opens low at pin 4 of DD2.2 when the SB16 "ON" button is pressed and closes at a high level at pin 4 of DD2.2 when SB17 "OFF" is pressed. When the power is turned on with the "ON" button, the negative pulse generated by the chain C1, R6 resets the counter DD3. In the absence of pressing the keyboard buttons SB1-SB15 after about 100 s, a high level is set at pin 2 of DD3, along the edge of which the chain C8, R13 generates a positive pulse. Transistor VT2 for the duration of this pulse opens and connects pin 6 DD2.2 to the common wire, which is equivalent to pressing the "OFF" button. When DTMF signals are received from DD1 before the expiration of the specified time interval, the counter DD3 is reset each time by pulses from the NSA output (vyv.13) DD1, thus prolonging the on state of the circuit. The current consumption of the beeper with a closed VTI key does not exceed 25 μA, with an open key in silent mode 7,5 mA, in the mode of generating DTMF signals 20 mA. The auto-off time can be varied by selecting the desired DD3 output with a jumper or by selecting the elements R10, C3 of the pulse generator on the DD2.4 element. Device details. The switch and beeper used resistors of the MLT type, non-polar capacitors KM, with the exception of C2 (see Fig. 2) of the K73-16 type, C3-C6 (see Fig. 3) of the K73-17 type, polar capacitors K50-35, varistor RU1 (Fig. 2) CH1-2-1. Instead of the DD2 KT1 chip indicated in the diagram (Fig. 3170), you can use its analogues: MV8870 [3], MT8870, NM9270, as well as the domestic analogue KR1008VZh18 [1]. Instead of the DD4 HM1D microcircuit indicated in the diagram (Fig. 9102), you can use its analogues KS58C20N, KS58006, UM91260C, the domestic analogue of KR1008VZh16 [1]. Instead of UZCH DA1 A283D, you can use its Russian counterpart K174XA10. Dynamic head VA1 type 0,5 GDSH-2. Coils L1, L2 of the power filter (Fig. 3) are wound simultaneously with two wires on a ring 20x10x4 mm made of M2000NM-1 ferrite with MGTF 0,5 wire until filled. Quartz resonators ZQ1 (Fig. 2) and ZQ1 (Fig. 4) at a frequency of 3,579545 MHz can be replaced with quartz or ceramic resonators at a frequency of 3,58 MHz. Buttons SB1-SB6 (Fig. 2) - KM1-1, buttons SB1-SB17 (Fig. 4) - keyboard matrix from the TV remote control. The switch is mounted in a housing with dimensions of 150x220x100 mm. Network sockets XS1-XS4, LEDs HL1-HL4 (Fig. 3) and buttons SB1-SB4 (Fig. 2) are placed on the top panel. Triacs VS1-VS4 (Fig. 3) are installed on radiators with an area of 150 cm2 each. Setting up the switch comes down to setting the required amplification DD13.1 (Fig. 2) by selecting R16 until a confident recognition of DTMF signals by the DD1 chip is achieved. The level of the switch's own signals can be changed, if necessary, by selecting R17. In case of unstable operation of the mode control unit, a resistor with a resistance of 4-12 kOhm should be installed between pin 100 of DD150 and the common wire. It is highly desirable to use a backup battery to prevent the contents of the state triggers from being reset when the mains power fails. It can be installed, for example, at the input of a +5 V voltage regulator (not shown in Fig. 3). If it is present, the resistor R4 (Fig. 2) can be excluded from the circuit. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that by increasing the number of registers DD4-DD7 to eight and using the K3KP561 chip as DD2, it is possible to make the channel addresses seven-digit. When setting up the beeper, it is required to set the maximum amplitude of the output signal of the ultrasonic frequency converter in the absence of its limitation by adjusting R9 (Fig. 4). The presence of the buttons "H", "P" and "R" on the keyboard is optional. Three AA batteries are used as batteries. References:
Author: P. P. Redkin
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ REM sleep warms up the brain and saves from hypothermia ▪ Home appliances will determine when the owners are sleeping
▪ site section And then an inventor (TRIZ) appeared. Article selection ▪ article Aphorisms of famous people. Big selection ▪ article Hammer drill. home workshop
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: