
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Electronic ballast for lamps LB-20. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
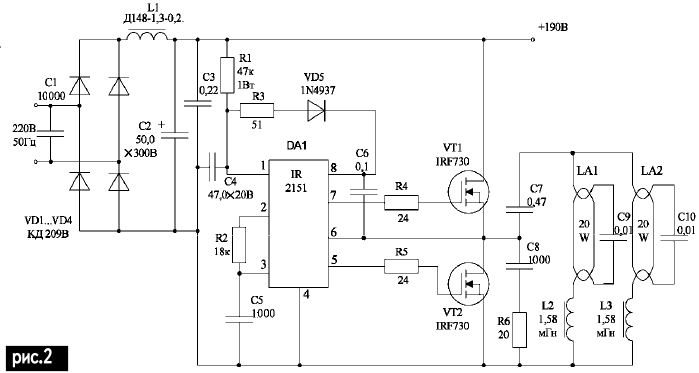
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Lighting The main disadvantage of incandescent lamps is low efficiency and, accordingly, high consumption of electrical energy. It is possible to reduce the consumption of electrical energy when lighting rooms if you use fluorescent lamps with a higher efficiency. Abroad, electronic ballasts are currently widely used, providing "smooth", non-pulsing light. The widespread introduction of electronic ballasts into the industry has previously been hampered by the high cost of components, the insufficiently fast switching speed of transistors, and expensive production. All these shortcomings have been eliminated with the release of the new economical IR2151 MOS gate drivers from International Rectifier and similar companies. These drivers are monolithic power integrated circuits capable of driving two transistors, MOSFET or IGBT half-bridge converters. They can operate at supply voltages up to 600 V, have clear output pulse shapes with duty cycles from 0 to 99%. The functional diagram of the IR 2151 driver is shown in Figure 1. The driver contains an input part on operational amplifiers, which can operate in a self-oscillating mode. The frequency is determined by additional attachments connected to the outputs Cst, Rt. Zero pause generators provide delays in turning on the output transistor by 1 µs after the previous transistor is closed. Galvanic isolation is carried out in the upper-side channel, then the voltage is amplified by a field-effect transistor power amplifier, and the output voltage from the HO output is fed to the gate of the power transistor. The lower arm is powered by a master oscillator through a pause generator at zero and a delay device. To ensure the stability of the driver, there is a zener diode inside that limits the voltage to 15 V. The scheme of the electronic ballast is shown in Fig.2. The frequency of the converter is determined by the circuit R2C5 fg = 1/(1,4R2C5) = 40 kHz. The driver is powered through resistor R1, stabilized by an internal zener diode up to 15 V and filtered by capacitor C4. The upper side gate amplifier is powered according to the charging "pump" circuit, i.e. through resistor R3 and diode VD5. The output voltage of the converter from the capacitor C7, supplied to the fluorescent lamps, has a rectangular shape. The lamps are connected according to a series resonant circuit in such a way that the currents of the lamps flow through the incandescences, after switching on, the incandescences are heated and the lamps are ignited. The resonant frequencies of the circuits C9, L2 and C10, L3 are 40 kHz. To reduce the crest factor for the consumption of electrical energy, the rectifier load is selected as inductive (choke L1 and capacitor C2, capacitor C3 connected in parallel serve to reduce the amplitude of the high-frequency variable component). In this case, there is no need for an input noise suppression filter and a "soft" connection to the network is provided (the crest factor is the ratio of the amplitude of the consumed current to the rms value of the same current). To limit the switching speed of transistors at the level of 40-50 ns, resistors R4 and R5 with a resistance of 24 ohms are included in the gates of the transistors. Limiting switching speeds is necessary to reduce the effect of parasitic circuit board inductances and capacitances. Limiting switching speeds at this level allows for a reliable working design. When building a circuit, it is necessary to correctly select the resistance of the limiting resistor R1, for this, all currents flowing through it should be taken into account: I0 - the quiescent current of the IR2151 microcircuit; I2 - current required to turn on the gate VT2; Iv - current of the time-setting resistor R2; In - charging "pump" current to power the upper arm amplifier; Ic - current of the internal zener diode of the microcircuit for stable operation of the stabilizer. The quiescent current of the IR2151 at normal temperature is 1mA and decreases by 10% when the temperature rises by 100°C. We take it equal to I0=1,1 mA. The current required to turn on the VT2 gate is determined by the formula I2 = 2Qgfpr, where Qg is the gate charge of the IRF730 transistor (Qg = 18 nC); fpr - conversion frequency equal to 40 kHz, i.e. I2 = 1,4 mA. The current of the timing resistor R2 Iв = 0,25 Ucc/R2 = 0,25 15/18•103 = 0,21 mA. The current of the charging "pump" has two components: 1) when a switching signal is applied to the gate of the transistor VT1, the voltage at the first moment is small and the current amplitude is approximately 10 mA with a duration of 200 ns; 2) when a turn-off signal is applied to the gate of transistor VT1, the voltage at the first moment remains approximately equal to the supply voltage of the top-level output amplifier of the microcircuit, the current amplitude is approximately 20 mA for a duration of 200 ns, then the current of the charging "pump" Iн=(10•10-3+20•10-3)200•10-9•40•103=0,24мА. The current of the internal zener diode of the microcircuit can be in the range from 0,1 to 5 mA. Taking into account the change in the voltage of the supply network, we select the current of the internal zener diode Ic = 0,5 mA. Let's determine the total current flowing through the resistor R1, IR1 = I0 + I2 + Iv + In + Ic = 1,1 + 1,4 + 0,21 + +0,24 + 0,5 = 3,45 mA Resistor R1 R1 \u190d (15 - 3,45) / 10 * 3-50 \uXNUMXd XNUMX kOhm. We select the standard value of 47 kOhm. Structurally, the electronic ballast is made on two boards. The input part (capacitor C1, diodes VD1 ... VD4, inductor L1, capacitor C2) is mounted by surface mounting. When connecting to an industrial network, a 0,5 A fuse must be connected in series. The rest of the circuit is located on the printed circuit board. The placement of elements on it is shown in Fig.3.
As rectifier diodes VD1 ... VD4, you can use any low-frequency ones with an average forward current of more than 0,2 A, a maximum reverse voltage of more than 350 V (for example, D226, D237B, V, Zh, KD109V, KD209A, KD209B or KTs405 bridge rectifier) . Instead of the IR2151 driver, you can use IR2152, IR2153, IR2154, IR2155 without any changes in the circuit. Instead of field-effect transistors IRF730, you can use similar IRF720, IRF740. Radiators for transistors are not required. All resistors of the MLT-0,125 type circuit, resistor R1 - MLT-1, R6 MLT-0,5. As a choke L1, you can use a similar one with an inductance of 1,3-2,0 H for a current of 0,20,25 A; a choke from lamp black-and-white TVs DR2,3-0,21 is also suitable. Capacitors C8, C9, C10 type K31U-3E-5, you can use capacitors type KSO, K73-17. Capacitor C2 type K50-7; C5, C6 - KM5; C1, C3, C7 type K73-17 for voltage 400 V. The printed circuit board is designed in such a way that the values of the resistor R1, capacitors C9, C10 can be selected by parallel connection. Inductances L2 and L3 are wound on rings made of alsifer brand VCh-32R with a diameter of 29 mm and contain 320 turns of PEV-2 wire with a diameter of 0,3 mm. Ferrite Sh7x7 µ2000NM with a gap of 0,5 mm can be used as a core. Without any changes in the circuit, instead of LB-20 lamps, currently widely available 18 W lamps can be used. It should also be noted that with an electronic ballast, lamps with failed filaments ignite and burn (in this case, the lamp incandescences must be short-circuited). A normally operating ballast on a 190 V circuit should consume a current of 0,2 - 0,21 A (measurement can be performed between two boards of the structure). The completed illuminator has worked for 5 months at the moment, gives greater illumination than from a 100 W incandescent lamp, switching on without current surges, ignition of the lamps occurs almost instantly and, most importantly, much less eye fatigue is noticed when working with literature. Author: D.P. Afanasiev
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Solar system without Jupiter ▪ Solar panels over water channels ▪ Electric cars help reduce asthma risk ▪ Three-legged driver with four arms
▪ site section Lighting. Article selection ▪ article Organization Theory. Lecture notes ▪ Article At what temperature does water have its maximum density? Detailed answer ▪ article Japanese paper tree. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: