
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Shaver converter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
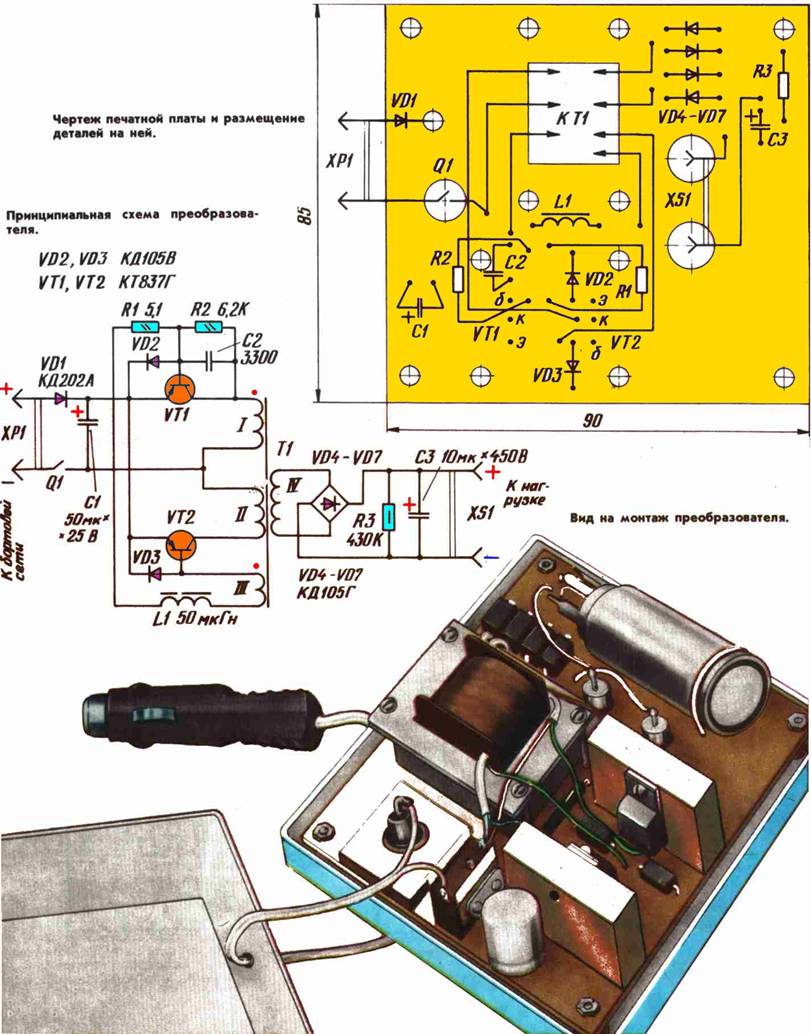
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters The converter is designed to power electric shavers with a commutator motor ("Kharkov-5", "Agidel", etc.) from the vehicle's on-board network, designed for a rated operating voltage of 220 V DC and consuming power up to 16 W. The converter is also suitable for powering a car stroboscope that does not contain a built-in voltage converter. The current consumed by the converter without load does not exceed 0,4 A, under load with a current of 60 mA - 1,4 A. The efficiency factor is not worse than 0,75. The converter is made according to a push-pull transformer circuit on transistors VT1, VT2 and differs from other similar devices in that the emitter junctions of the transistors are connected in series, that is, one winding of the transformer T1 (winding III) is used to power the base circuits of both transistors. Diodes VD2, VD3 provide the passage of the control current, bypassing the emitter junction closed in one or another half-cycle of the transistor. The voltage drop across the open diode is enough to reliably close the transistor. At the same time, diodes serve to protect the emitter junction of transistors from breakdown. Resistor R1 limits the base current. Resistor R2 and capacitor C2 make up the starting circuit of the converter when it is turned on. The generation frequency of the converter at idle is about 850 Hz, and under load - about 650 Hz. The pulses taken from the secondary winding IV of the transformer are rectified by a bridge assembled on diodes VD4 - VD7 and filtered by capacitor C3. At the moments of transistor switching, short-term voltage pulses with a large amplitude occur, leading to an increase in the output voltage of the converter in idle mode. The load resistor R3 serves to reduce the output voltage at idle and discharges the capacitor C3 when the converter is turned off. The KT837G silicon transistors used in the converter dissipate relatively little power and ensure its efficient operation. However, due to the large values of their static coefficient and the limiting frequency, the converter is prone to switching to parasitic generation with an increased frequency (several tens of kilohertz). This phenomenon was especially pronounced when working with a stroboscopic lamp due to the sharply changing load current. The conducted studies have shown that the most effective way to ensure the stability of the converter is to connect the inductor L1 in series to the power circuit of the base circuits of the transistors. Diode VD1 serves to protect the device in case of incorrect polarity of connecting its input terminals to the vehicle's on-board network. If a special adapter is used to turn on the converter, which is included in the cigarette lighter socket, connection in the wrong polarity becomes impossible and this diode can be excluded. Transformer TI is assembled on a magnetic circuit Ш8Х 16 with plates 0,08 ... 0,15 mm thick made of steel E310, E320 or E330. You can use a magnetic core of a slightly larger size. Windings I and II contain 45 turns of wire PEV-1 0,47 ... 0,51, III - 15 turns of wire PEV-1 0,2 ... 0,35 ... IV - 900 turns of wire PEV-1 0,17...0,25. Winding IV is wound first, then I and II, the last - winding III. All windings are laid turn to turn with insulation between layers. Windings I and II are wound in two wires at the same time; the identity of the parameters of these windings is necessary to reduce secondary voltage surges. If the converter is also intended to work with a stroboscopic lamp, the insulation between the primary and secondary windings should be chosen more reliable - it is calculated for a voltage of at least 2 kV. Any transistors of the KT837 series with a saturation voltage between the collector and emitter of not more than 0,9 V can be used in the device, for example, with indices G-K, P-F. It is also possible to use germanium transistors of the P214, P215, P216 series, etc. In this case, the L1 inductor can be excluded. However, it should be noted that with germanium transistors, the converter will have worse parameters. Diode VD2, VD3 - any of the KDYU5, KD208, KD209 series. Diodes VD4 - VD7 (or a ready-made rectifier unit) must be designed for a reverse voltage of at least 800 V. Capacitor C1 - K50-6; C2 - any, for example, KLS, KM; C3 - K50-12. Throttle L1 - serial, DM-0,2 or homemade. Transistors are installed on rectangular heat sinks 35x25X8 mm in size, made of copper or duralumin. Diode VD1 should also be provided with the same heat sink with dimensions of 20x30x6 mm. The converter is mounted on a printed circuit board made of foil fiberglass 2 mm thick. The drawing of the board and the location of the parts on it are shown on the tab. A rectangular hole is cut into the board to mount the transformer. The board is installed in a rectangular plastic box with a lid. The female connector XS1 is mounted on the box and the power switch Q1 is on the board. For adjustment, the converter is connected to a 13 V DC voltage source, and a characteristic whistle should be heard, indicating the operation of the generator. In the absence of generation, it is necessary to swap the conclusions of the winding III. The criterion for the normal operation of the converter can be the current consumed at idle; if it is more than 0,3 ... 0,4 A, it is necessary to slightly reduce the number of turns of winding III. The voltage at the output of the converter without load should be no more than 380 V, and when the electric shaver is connected, it should be at least 200 V. It must be reliably started at a supply voltage of 10 V or more. When operating the device, you must first turn it on to the vehicle's on-board network, and then turn on the load. Otherwise, the converter may enter the parasitic generation mode. This does not pose a danger to them: the consumed current does not exceed 0,4 A. When the load is disconnected, the device switches to normal generation mode.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Artificial heart from self-organized stem cells ▪ Vinyl record sales surpass CD sales for the first time ▪ Germanan is a rival of graphene ▪ Asimo's humanoid robots continue to improve
▪ site section Spectacular tricks and their clues. Article selection ▪ article Bi-Ampling or Bi-Warering? The art of audio ▪ article Ziziphora capitate. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Outgoing call time counter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Colored rings in jellies. Chemical Experience
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: