
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Semi-automatic surge protector. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
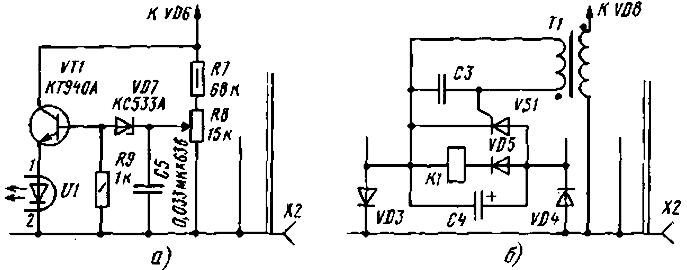
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Protection of equipment from emergency operation of the network, uninterruptible power supplies The protection of household radio equipment from “jumps” and sharp deviations of the mains voltage from the norm for many regions of our country remains a problem with unpredictable consequences. The author of the article analyzes the situation and shares his personal experience of practical solution of this problem. The proposed device protects the radio equipment by quickly disconnecting from the mains when its voltage changes beyond the permissible limits. It is relevant, first of all, near overhead power lines, where the probability of wire short circuits, for example, during strong gusts of wind, is high. Especially dangerous is the short circuit of one of the phase wires to "zero". In this case, the voltage in the network rises to 380 V. Usually, in such cases, the oxide capacitors of the power supply break and the electrolyte leaks out, which adversely affects the operation of one or another radio device. Reducing the mains voltage to 160 V is also dangerous, in particular for switching power supplies. In such cases, they operate at long current loads through the power transistor, which can cause it to fail due to overheating. A semiautomatic device, the scheme of which is shown in Fig. 1, helps me to solve the problems described. 1996. From a similar device described in the article by I. Nechaev "Automatic device for protecting network equipment from voltage surges" ("Radio", 10, No. 48,49, p. 1), it differs mainly only in that when " jumps" voltage disconnects the load from the network, and it can be turned on again only after pressing the start button SBXNUMX. In the previously described machine, when the mains voltage is "walking", the load is fed intermittently - and this is a very unfavorable mode of operation for any radio equipment, especially PCs and TVs. The basis of the proposed semiautomatic device is a powerful electromagnetic relay K1. To power its winding with direct current, a rectifier MOCTVD1-VD4 is used, connected to the network through quenching capacitors C1 and C2. Turn on the device by briefly pressing the button SB1. In this case, relay K1 is activated and its closing contacts K 1.1 block the contacts of the start button. Capacitor C1 provides the necessary starting current for the relay when turned on. In operating mode, the relay is held by the current flowing through capacitor C2, up to a mains voltage of at least 160 V. When setting up the device, the capacitance of capacitor C2 (and sometimes capacitor C1) has to be selected individually for each type of relay. When the mains voltage rises to 240 V, the zener diodes VD7 and VD8 open. At the same time, the optocoupler U1 is activated and the trinistor VS1 opens. It blocks the power supply circuit of the relay winding K1. As a result, the relay releases and its opening contacts K1.1 disconnect the load of the device from the AC mains. Capacitor C3, a shunt resistor R3 in the control circuit of the trinistor VS1, prevents the surge protection from tripping. Resistors R1, R2 limit the current surges through the contacts of the start button SB1, at the same time being "fuses" in the event of a breakdown of the capacitor C1 or C2. Diode VD5 improves the performance of the device, which is determined mainly by the type of relay used and is a fraction of a second. The release time of the RENZZ relay used in the described device does not exceed 4 ms, which is quite enough for reliable operation of the protection. Resistor R5 limits the current flowing through the optocoupler LED U1. By selecting it (within 8 ... 25 kOhm), it is possible to adjust in small values (5 ... 10 V) the protection threshold for exceeding the input voltage. Structurally, the semiautomatic device is made in the form of a portable extension cord. On its front wall-cover there is a power outlet X2, a push-button switch SB1 (KM2-1 or P2K without fixing) and an indicator VL1. The electromagnetic relay (RENZZ), the VS1 trinistor and all other parts are mounted on a printed circuit board made of one-sided foil material, which is placed in a plastic case. Relay K1 can be of any type, for an operating voltage of 12 ... 60 V, and its contacts are designed for a current of at least 2 ... 3 A at a mains voltage of 220 V. In this case, the rated voltage of capacitor C4 should be correspondingly. Capacitors C1 and C2 - K73, MBM, MBGO for a rated voltage of at least 350 V (C2 is better by 400 V). Zener diodes VD7 and VD8 are interchangeable with similar ones, the total stabilization voltage of which can be from 310 to 340 V at a current of 10 ... 12 mA. With a lower total stabilization voltage of these devices (250 ... 300 V), the resistor R5 should be 30 ... 47 kOhm and more power dissipated. In this case, it will be possible to increase the instability of the protection response threshold. It is permissible to replace the AOD101A (U1) diode optocoupler with a transistor AOT110 or AOT127 series by connecting the resistor R4 to the emitter of the phototransistor, the anode of the trinistor VS1 to the output of its collector, and install a resistor with a resistance of 1 MΩ between the base and the emitter. At the same time, the trinistor can also be with a large control current, for example, the KU201 or KU202 series. Establishing the device is reduced mainly to the selection of capacitors C2 and C1. Selecting the first of them, they achieve turning off the device when the mains voltage drops to 160 ... 170 V, and the second - reliable switching on with the start button SB1. The selection of the resistor R5 is also possible - to ensure reliable operation of the protection system at a mains voltage exceeding 240 ... 250 V. At the same time, one should not forget about electrical safety measures - after all, all elements of the device are galvanically connected to a high-risk power grid. In conclusion, some practical advice related to possible changes in the protection device itself. If there are difficulties with the selection of high-voltage zener diodes VD7 and VD8, then it is possible to use one KS533A zener diode with an additional KT940A transistor, as shown in Fig. 2a. Variable resistor R8 sets the threshold voltage of the protection system. However, its reliability will decrease somewhat, since the transistor VT1 can "go to the open" and the device will not turn off the load if the input AC voltage is exceeded. Zener diodes, as a rule, fail to "short", and this only leads to a load disconnection. The device can be simplified by replacing the trinistor VS1 and the optocoupler U1 with an optothyristor of the appropriate power - with an output pulse current of at least 1 A, for example, the AOU160 series. A semiautomatic device with such an optocoupler should reliably block the power supply of the winding of relay K1 by quickly discharging capacitor C4. The most common optocoupler of the AOU103 series can withstand a pulsed current of up to 0,5 A, which may not be enough for reliable operation of the device. In general, the optocoupler can be replaced by a low-power pulse transformer. Suitable, for example, the matching transformer of the amplifier 34 of a portable transistor radio or similar, the windings of which contain 150 ... 300 turns of wire PEV-2 0,15 ... 0,3. A winding with a smaller number of turns is connected to the control circuit of the trinistor VS1 (Fig. 3,6), and a winding with a large number of turns is connected instead of the emitting diode of the optocoupler U1. Resistors R3 and R4 in this case are removed from the device. Long-term operation of several semi-automatic machines, including those with the changes made, showed their reliable operation. For reliable operation of the device, a button should be installed as SB1, designed for the full starting current of the protected device. It is desirable to install a limiting resistor with a resistance of about 1 ohms in the anode circuit of the thyristor VS10, it will protect the thyristor from possible breakdown by the discharge current of capacitor C4.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ 32-bit microcontroller V850E/RS1 ▪ Single-chip system Qualcomm Snapdragon 855 Plus ▪ A metallic substance that does not conduct heat when an electric current is passed ▪ Mean Well Fanless Digital Power Supply PHP-3500
▪ site section Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters. Article selection ▪ article We have nothing to fear but fear itself. Popular expression ▪ article Why is it cooler at the top of the mountain? Detailed answer ▪ article Volcano Krakatoa. Nature miracle
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: